The Higher The Temperature Of An Object The
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
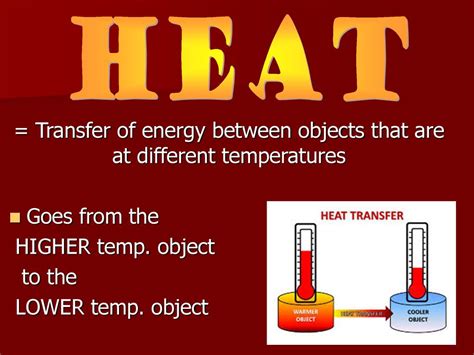
Table of Contents
The Higher the Temperature of an Object, the… What? Understanding Thermal Radiation and its Impacts
The statement "the higher the temperature of an object, the..." is incomplete, but incredibly insightful. It opens the door to a fascinating exploration of thermodynamics, particularly the relationship between temperature and thermal radiation. Let's delve into the complete picture, exploring the consequences of increased object temperature and how this impacts various aspects of our world.
The Relationship Between Temperature and Thermal Radiation
The higher the temperature of an object, the more thermal radiation it emits. This is a fundamental principle governed by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law. This law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body across all wavelengths is directly proportional to the fourth power of the black body's thermodynamic temperature. In simpler terms, a small increase in temperature leads to a significant increase in radiated energy.
Understanding Blackbodies
A blackbody is a theoretical object that absorbs all electromagnetic radiation incident upon it. While perfect blackbodies don't exist in nature, many objects approximate their behavior. The Stefan-Boltzmann Law applies perfectly to blackbodies, providing a baseline for understanding the radiation emitted by real-world objects.
The Importance of Wavelength
The higher the temperature of an object, the shorter the wavelength of the peak emitted radiation. This is described by Wien's Displacement Law. As an object heats up, it shifts from emitting primarily infrared radiation (invisible to the human eye) to visible light, eventually moving through the visible spectrum from red to orange, yellow, white, and blue as temperature increases. This is why a heated piece of metal glows red, then orange, then white-hot at progressively higher temperatures.
The Impacts of Increased Temperature: A Multifaceted Perspective
The increased thermal radiation emitted by a hotter object has far-reaching consequences, affecting everything from everyday life to complex scientific phenomena.
1. Light and Vision: From Incandescence to Plasma
The most readily apparent effect of increased temperature is the emission of light. This is the principle behind incandescent light bulbs, where a tungsten filament is heated to such a high temperature that it emits visible light. At even higher temperatures, we see the formation of plasma, a superheated state of matter where electrons are stripped from atoms, creating ionized gas that emits light in a characteristic manner. Examples include lightning strikes and the sun's corona.
2. Heat Transfer and Thermodynamics: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
Increased temperature drives heat transfer through three primary mechanisms:
- Conduction: Heat transfer through direct contact. A hotter object will transfer heat more efficiently to a cooler object.
- Convection: Heat transfer through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). Higher temperatures create density differences, leading to fluid flow and heat transfer.
- Radiation: Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves. This is the dominant mechanism for heat transfer in a vacuum and plays a significant role even in other environments. The intensity of radiative heat transfer increases dramatically with temperature.
The interplay of these three mechanisms determines the overall rate of heat transfer and has profound implications in various applications, from designing efficient heating systems to understanding climate change.
3. Material Science and Engineering: Melting, Boiling, and Phase Transitions
The higher the temperature of an object, the more likely it is to undergo phase transitions. Increasing temperature can cause solids to melt into liquids, and liquids to boil into gases. The specific temperatures at which these transitions occur depend on the material's properties. Understanding these phase transitions is critical in materials science, enabling the creation of new materials with desired properties and the optimization of existing processes.
4. Astronomy and Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution and Planetary Atmospheres
The temperature of celestial bodies plays a crucial role in shaping the universe. The temperature of a star dictates its luminosity, color, and lifespan. Different stages of stellar evolution are characterized by distinct temperature ranges, from the relatively cool red giants to the incredibly hot blue supergiants. Similarly, the temperature of a planet's atmosphere determines its climate and habitability, influencing the presence of liquid water and the possibility of life. Understanding the relationship between temperature and radiation is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos.
5. Environmental Science and Climate Change: The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
The temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere is influenced by the balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial radiation. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap outgoing radiation, leading to a warming effect. Increased concentrations of greenhouse gases due to human activities enhance this effect, causing global warming and climate change. Understanding the relationship between temperature, radiation, and greenhouse gases is critical for addressing the challenges of climate change.
6. Chemical Reactions and Kinetics: Reaction Rates and Equilibrium
Temperature significantly affects the rate of chemical reactions. Higher temperatures generally lead to faster reaction rates, as molecules possess more kinetic energy and are more likely to collide with sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. This is described by the Arrhenius equation. Understanding temperature's influence on reaction rates is crucial in chemical engineering, enabling the optimization of industrial processes and the development of new technologies.
7. Biology and Physiology: Enzyme Activity and Metabolic Processes
Temperature also plays a vital role in biological processes. Enzymes, the catalysts of life, have optimal temperature ranges for activity. Extreme temperatures can denature enzymes, disrupting metabolic processes and potentially causing cell death. Maintaining a stable internal temperature is crucial for the survival of many organisms, highlighting the importance of temperature regulation in biology.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
The relationship between temperature and thermal radiation extends beyond the basic principles discussed above. Advanced concepts, such as:
- Planck's Law: A more precise description of blackbody radiation, accounting for the distribution of energy across different wavelengths.
- Kirchhoff's Law of Thermal Radiation: Relates the emissivity and absorptivity of a material at a given temperature and wavelength.
- Greybody Radiation: Describes the radiation emitted by real-world objects, which deviate from the ideal behavior of a blackbody.
These advanced concepts provide a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between temperature and radiation, leading to more accurate predictions and a more nuanced comprehension of the phenomena involved.
Conclusion: The Far-Reaching Influence of Temperature
The simple statement, "the higher the temperature of an object, the..." unveils a universe of complexity. It underscores the fundamental connection between temperature and thermal radiation, impacting diverse fields from astronomy to biology. Understanding this relationship is not merely an academic exercise; it is crucial for addressing some of the most pressing challenges facing humanity, including climate change, energy production, and the development of new technologies. As we continue to explore this rich area, further advancements in our understanding will undoubtedly lead to innovative solutions and a deeper appreciation for the fundamental laws governing our universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
One Way To Positively Influence Values Is By
Apr 02, 2025
-
Go Math Grade 7 Answer Key Pdf
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Correct Regarding The Ph Scale
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Origin Of Most Federal Bureaus
Apr 02, 2025
-
Many Urban Blues Singers Began Their Careers As
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Higher The Temperature Of An Object The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
