The Idea Of Facility Layout Is To
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 7 min read
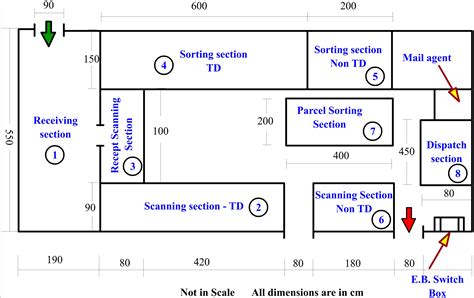
Table of Contents
The Idea of Facility Layout: Optimizing Space, Flow, and Efficiency
The idea of facility layout is to optimize the arrangement of resources within a facility to maximize efficiency, productivity, and profitability. It's more than just placing equipment and workstations; it's a strategic process that considers workflow, material handling, safety, and employee well-being. A well-designed layout can significantly reduce operational costs, improve product quality, and boost employee morale. Conversely, a poorly designed layout can lead to bottlenecks, wasted time, increased accidents, and ultimately, a less profitable business. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of facility layout, examining its core principles, different types, and the crucial steps involved in creating an optimal design.
Understanding the Core Principles of Facility Layout
Effective facility layout rests on several key principles, each playing a vital role in achieving the overall objectives. These principles guide the decision-making process and ensure a cohesive and efficient design.
1. Material Handling: Minimizing Movement and Waste
A primary goal of facility layout is to minimize the distance materials travel within the facility. Efficient material handling reduces transportation costs, improves workflow, and minimizes the risk of damage or loss. The layout should facilitate a smooth flow of materials from receiving to production to shipping, reducing unnecessary movement and handling. This often involves strategically positioning departments and workstations to reduce backtracking and wasted steps.
2. Workflow Optimization: Streamlining Processes
The layout should directly support the smooth flow of work through the facility. Processes should be sequenced logically, minimizing delays and interruptions. This involves analyzing the entire workflow, from raw materials to finished products, identifying bottlenecks, and designing the layout to eliminate or alleviate them. Consider techniques like value stream mapping to visually identify and improve workflow processes.
3. Space Utilization: Maximizing Efficiency
Efficient use of space is crucial. The layout should make optimal use of available space while minimizing wasted areas. This requires careful planning and consideration of the size and placement of equipment, workstations, storage areas, and aisles. Analyzing space utilization data helps identify areas for improvement and optimize the arrangement of resources.
4. Safety and Ergonomics: Prioritizing Employee Well-being
Employee safety and well-being are paramount. The layout should minimize hazards and promote a safe and comfortable work environment. This includes providing adequate space for movement, installing safety equipment, and designing workstations ergonomically to reduce strain and fatigue. A safe and comfortable workplace boosts employee morale and productivity.
5. Flexibility and Scalability: Adapting to Change
Future growth and potential changes should be considered. The layout should be adaptable to changing needs and allow for expansion or modification without significant disruption. This may involve incorporating modular designs or leaving space for future expansion. A flexible layout ensures the facility remains efficient and relevant in a dynamic business environment.
Types of Facility Layouts: Finding the Right Fit
Different types of facility layouts are suitable for different types of operations and industries. The choice depends on factors such as product variety, production volume, and the nature of the production process.
1. Product Layout (Line Layout): High Volume, Low Variety
This layout arranges workstations in a sequence according to the steps in the production process. It's ideal for high-volume, low-variety production, such as assembly lines for automobiles or electronics. The advantage is high efficiency and specialization, but it's inflexible and susceptible to disruptions if one part of the line breaks down.
2. Process Layout (Functional Layout): Low Volume, High Variety
This layout groups similar machines or equipment together, regardless of the production sequence. It's suited for low-volume, high-variety production like job shops or custom manufacturing. It offers flexibility and adaptability but can lead to longer processing times and higher material handling costs.
3. Fixed-Position Layout: Large, Immobile Products
This layout keeps the product in a fixed location, and workers and equipment move around it. It's used for large, immobile products like ships or buildings. Coordination and planning are crucial to avoid delays and conflicts.
4. Cellular Layout (Group Technology): Moderate Volume, Moderate Variety
This layout groups machines and equipment into cells based on product families or similar production processes. It combines the efficiency of product layout with the flexibility of process layout, suitable for moderate volume and variety. It reduces material handling, improves workflow, and increases efficiency.
5. Combined Layout: Integrating Different Approaches
In many cases, a facility may use a combination of layouts to optimize different aspects of the operation. For instance, a manufacturing facility might use a product layout for high-volume production and a process layout for specialized tasks or repairs.
Steps Involved in Facility Layout Planning
The process of designing a facility layout is complex and iterative, requiring careful planning and analysis.
1. Planning and Analysis Phase: Gathering Data and Defining Requirements
This initial phase involves gathering data about the facility, its operations, and its future needs. Key data points include:
- Product or service offerings: Understanding the range of products or services produced or offered.
- Production volume and capacity: Determining the current and projected production volume and capacity requirements.
- Material flow and processing steps: Analyzing the movement of materials through the facility and identifying processing steps.
- Equipment and space requirements: Determining the size and space requirements for equipment and workstations.
- Safety and environmental regulations: Considering all relevant safety and environmental regulations.
- Budget and timeline: Establishing realistic budget and timeline constraints.
2. Layout Design Phase: Creating and Evaluating Alternatives
This phase involves developing different layout alternatives and evaluating their feasibility and efficiency. Various techniques can be used, such as:
- Block diagrams: Simple diagrams showing the relative placement of major departments or work areas.
- Relationship charts: Illustrating the importance of proximity between different departments or work areas.
- Computer-aided design (CAD) software: Sophisticated software tools that allow for detailed 3D modeling and simulation of the layout.
- Simulation software: Software to model and simulate the flow of materials and workers in the facility to optimize efficiency and identify potential bottlenecks.
3. Implementation Phase: Putting the Design into Action
Once the optimal layout has been selected, it needs to be implemented. This includes:
- Acquiring and installing new equipment: Procuring and installing new equipment as needed.
- Modifying existing facilities: Making necessary modifications to existing facilities to accommodate the new layout.
- Relocating existing equipment and materials: Moving existing equipment and materials to their new locations.
- Training employees: Training employees on the new layout and procedures.
4. Evaluation and Improvement Phase: Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
The layout should be continually monitored and evaluated for effectiveness. Performance data should be collected and analyzed to identify areas for improvement. This is an ongoing process, and adjustments may be necessary to maintain efficiency and adapt to changing conditions.
Advanced Techniques in Facility Layout
Several advanced techniques further enhance the effectiveness of facility layout planning.
1. Computer-Aided Facility Design (CAFD)
CAFD software employs sophisticated algorithms and simulation capabilities to optimize layouts. It helps to test different configurations and predict performance under various scenarios. This minimizes errors and maximizes resource utilization.
2. Simulation Modeling
Using simulation software allows for the visualization of material flow, workforce movements, and potential bottlenecks before physical implementation. It enables testing various scenarios and identifying areas for improvement, ensuring a more efficient and effective final design.
3. Value Stream Mapping
This lean manufacturing technique identifies and eliminates waste within the production process, directly informing the layout design. By focusing on optimizing the flow of value, it streamlines processes and reduces unnecessary movements.
The Impact of a Well-Designed Facility Layout
A well-designed facility layout has a profound impact on various aspects of a business:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Streamlined workflows and minimized material handling lead to significantly improved efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced Costs: Less wasted time and resources translate to lower operational costs.
- Improved Product Quality: A well-organized layout minimizes errors and enhances the quality of products or services.
- Enhanced Safety: A safe and ergonomically designed layout protects employees and reduces accidents.
- Increased Employee Morale: A comfortable and efficient workplace boosts employee satisfaction and morale.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Faster processing and efficient service delivery improve customer satisfaction.
- Greater Flexibility and Scalability: Adaptable layouts allow for easy expansion and adaptation to changing demands.
In conclusion, the idea of facility layout is far more than just arranging equipment. It is a strategic process that directly impacts the efficiency, productivity, and profitability of any organization. By understanding the core principles, choosing the appropriate layout type, and implementing a well-defined planning process, businesses can create an optimized work environment that drives success. Continuous evaluation and improvement ensure the layout remains effective and adaptable to the ever-changing needs of the business.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Idea Of Facility Layout Is To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
