The Interface Between The Firm And Its Suppliers Is
Breaking News Today
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
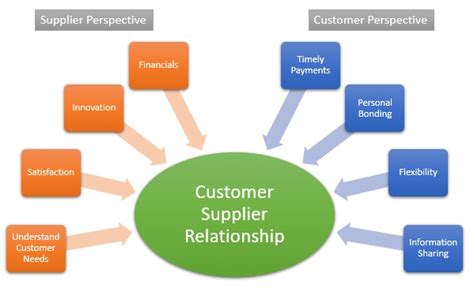
Table of Contents
The Interface Between the Firm and Its Suppliers: A Deep Dive into Supply Chain Management
The relationship between a firm and its suppliers is the bedrock of a successful supply chain. This interface, far from being a simple transactional exchange, is a complex interplay of collaboration, negotiation, and strategic alignment. Understanding this interface is crucial for optimizing efficiency, mitigating risks, and driving innovation across the entire value chain. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of this crucial relationship, exploring key aspects ranging from supplier selection and relationship management to the impact of technology and the evolving landscape of global sourcing.
The Importance of Strategic Supplier Selection
Choosing the right suppliers isn't simply about finding the lowest price. A strategic approach requires a holistic evaluation considering multiple factors that contribute to long-term value creation. This evaluation should go beyond immediate cost savings and consider:
Key Selection Criteria:
-
Financial Stability: Suppliers with strong financial health are less likely to experience disruptions that could impact the firm's operations. Assessing credit ratings, financial statements, and overall market position is crucial.
-
Quality Management Systems: Robust quality control processes are essential to ensure consistent product quality and minimize defects. Certifications like ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality management.
-
Production Capacity and Flexibility: The supplier should possess the capacity to meet current and future demand. Flexibility is vital to respond to fluctuating market needs and unforeseen circumstances.
-
Technological Capabilities: Suppliers with advanced technologies can contribute to innovation and efficiency gains. This includes automation, lean manufacturing techniques, and the use of advanced materials.
-
Ethical and Social Responsibility: Increasingly, firms are incorporating ethical sourcing into their supply chain strategies. This encompasses fair labor practices, environmental sustainability, and responsible resource management.
-
Geographic Location: Proximity can reduce lead times and transportation costs, while geographically diverse sourcing can mitigate risks associated with regional disruptions.
-
Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication is critical for seamless information flow and efficient problem-solving. A supplier's willingness and ability to collaborate are essential for a strong working relationship.
Building and Managing Supplier Relationships
The relationship between a firm and its suppliers is not a one-time transaction; it's an ongoing partnership. Developing and nurturing strong relationships is essential for fostering trust, improving collaboration, and driving mutual success.
Relationship Management Strategies:
-
Collaboration and Communication: Open and transparent communication is vital. Regular meetings, shared information systems, and collaborative problem-solving mechanisms strengthen the bond.
-
Shared Goals and Objectives: Aligning the firm's goals with those of its suppliers fosters a sense of shared purpose and promotes mutual commitment.
-
Performance Measurement and Feedback: Regularly assessing supplier performance against pre-defined metrics and providing constructive feedback are critical for continuous improvement. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should be jointly defined and tracked.
-
Trust and Mutual Respect: Trust is the cornerstone of any successful long-term relationship. Fair dealings, ethical conduct, and mutual respect build strong partnerships.
-
Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Establishing clear processes for addressing disagreements and resolving conflicts proactively prevents escalations and maintains a healthy relationship.
The Role of Technology in Optimizing the Supplier Interface
Technology plays an increasingly crucial role in streamlining the interface between firms and their suppliers. Advanced technologies are transforming supply chain management, enabling greater efficiency, transparency, and collaboration.
Technological Advancements:
-
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software: Integrated SCM platforms provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and supplier performance. This improves planning, reduces lead times, and minimizes disruptions.
-
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: ERP systems integrate various business functions, including procurement, inventory management, and production planning, fostering seamless communication and data sharing between the firm and its suppliers.
-
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain offers enhanced transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain, improving accountability and trust among partners.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms can optimize inventory management, predict demand fluctuations, and improve supplier selection based on data-driven insights.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT sensors embedded in products and equipment provide real-time data on inventory levels, location, and condition, enhancing visibility and efficiency.
Risk Management in the Supplier-Firm Interface
Managing risks associated with the supply chain is critical for business continuity and profitability. A robust risk management strategy requires proactive identification, assessment, and mitigation of potential disruptions.
Key Risk Categories:
-
Supplier Default: Financial instability or operational failures on the part of a supplier can disrupt the firm's operations. Diversifying suppliers and establishing contingency plans mitigate this risk.
-
Geopolitical Instability: Political unrest, natural disasters, or pandemics can disrupt supply chains, especially those with global reach. Geographical diversification and robust contingency planning are essential.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Unexpected events, such as labor strikes, transportation delays, or material shortages, can significantly impact the firm's ability to meet its commitments. Proactive risk assessment and mitigation strategies are crucial.
-
Cybersecurity Threats: Cyberattacks can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data. Investing in strong cybersecurity measures and implementing robust data protection protocols are vital.
-
Ethical and Social Risks: Concerns about labor practices, environmental impact, or corruption can negatively impact the firm's reputation and brand image. Careful supplier selection and monitoring are crucial to mitigate these risks.
The Future of the Firm-Supplier Interface: Collaboration and Innovation
The relationship between firms and their suppliers is evolving rapidly. The trend is towards greater collaboration, integration, and innovation. This includes:
Emerging Trends:
-
Increased Collaboration and Partnership: Moving beyond transactional relationships towards strategic partnerships based on mutual trust, shared goals, and long-term commitment.
-
Greater Focus on Sustainability: Integrating environmental and social responsibility into supply chain management, focusing on reducing carbon footprints, promoting ethical sourcing, and ensuring sustainable practices.
-
Adoption of Advanced Technologies: Leveraging emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, and IoT to enhance efficiency, transparency, and resilience in the supply chain.
-
Emphasis on Agility and Resilience: Building more agile and resilient supply chains capable of responding effectively to unforeseen disruptions and market changes.
-
Focus on Innovation and Value Creation: Collaborating with suppliers to drive innovation, develop new products and services, and create shared value across the entire supply chain.
Conclusion: A Strategic Partnership for Success
The interface between the firm and its suppliers is a critical factor in determining the success or failure of any business. It's not simply a matter of procuring goods or services; it's about building strong, collaborative relationships based on mutual trust and shared goals. By adopting a strategic approach to supplier selection, relationship management, risk mitigation, and technological integration, firms can optimize their supply chains, enhance their competitiveness, and achieve sustainable growth. The future of this interface lies in greater collaboration, innovation, and a shared commitment to building resilient, sustainable, and ethical supply chains that deliver value for all stakeholders. Understanding this dynamic interplay is no longer a competitive advantage; it's a necessity for survival and success in today's rapidly evolving global marketplace.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Concept Of Limited Government Holds That
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Drawback Of Planning Is That It
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True About Fake News
Apr 01, 2025
-
When Recording Progress Notes The Specific Chief Complaint Should Be
Apr 01, 2025
-
You Are Providing Bag Mask Ventilations To A Patient
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Interface Between The Firm And Its Suppliers Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
