The Leading Medical Cause Of Death For Student-athletes Is:
Breaking News Today
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
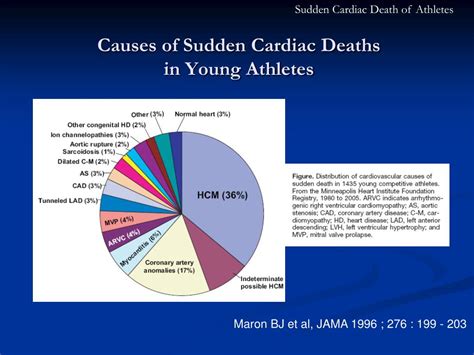
Table of Contents
The Leading Medical Cause of Death for Student-Athletes: A Comprehensive Overview
Student-athletes, often embodying health and vitality, face unique health risks that sometimes tragically lead to death. While various factors contribute to mortality in this population, sudden cardiac death (SCD) stands out as the leading medical cause. This comprehensive article delves into the complexities of SCD in student-athletes, examining its underlying causes, prevention strategies, and the crucial role of comprehensive health screenings.
Understanding Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) in Student-Athletes
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is defined as a non-traumatic, unexpected death from cardiac causes within one hour of symptom onset. In student-athletes, this often occurs during strenuous physical activity, though it can also happen at rest. The devastating impact of SCD on families, teams, and communities highlights the critical need to understand its causes and implement effective prevention measures.
Prevalence and Demographics
While the exact prevalence of SCD in student-athletes is difficult to pinpoint due to variations in reporting and data collection, studies consistently highlight its significance as a leading cause of death. The risk appears to vary slightly depending on the sport, with certain high-intensity activities potentially increasing the risk. However, it's important to remember that SCD can occur in athletes participating in any sport, even those considered low-impact.
Underlying Causes: A Multifaceted Issue
SCD in student-athletes is rarely a single-cause event. It frequently stems from a complex interplay of genetic predispositions, underlying cardiac conditions, and environmental factors. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for developing effective prevention and management strategies.
1. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM): A Leading Culprit
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a leading cause of SCD in young athletes. This genetic condition involves the thickening of the heart muscle, impairing its ability to pump blood efficiently. The thickened heart muscle can obstruct blood flow, leading to arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats) and ultimately, SCD. HCM is often asymptomatic, making early detection challenging.
2. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC): A Stealthy Threat
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is another significant contributor to SCD in young athletes. This genetic disorder affects the right ventricle of the heart, replacing healthy heart muscle with fatty or fibrotic tissue. This tissue disruption can lead to fatal arrhythmias. Like HCM, ARVC often presents subtly, making diagnosis difficult.
3. Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs): A Spectrum of Abnormalities
Congenital heart defects (CHDs) are structural abnormalities present at birth that can increase the risk of SCD. These defects can vary widely in severity and impact. Some CHDs may be identified early in life, while others may remain undetected until a cardiac event occurs.
4. Long QT Syndrome (LQTS): Electrical Instability
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a group of genetic disorders affecting the heart's electrical system. The prolonged QT interval on an electrocardiogram (ECG) indicates an increased risk of potentially fatal arrhythmias, particularly during exercise.
5. Commotio Cordis: A Rare but Devastating Event
Commotio Cordis, a rare but potentially fatal condition, involves a sudden impact to the chest that disrupts the heart's electrical rhythm during a vulnerable phase of the heartbeat. This can lead to ventricular fibrillation and SCD. It typically occurs during athletic activities involving impacts to the chest.
Prevention and Early Detection: A Proactive Approach
Given the potentially fatal consequences of SCD, proactive strategies for prevention and early detection are paramount. This involves a multi-pronged approach encompassing comprehensive pre-participation physical evaluations (PPEs), advanced screening techniques, and public awareness campaigns.
Comprehensive Pre-Participation Physical Evaluations (PPEs)
A thorough PPE is the cornerstone of preventing SCD in student-athletes. While standard PPEs are crucial, incorporating advanced screening tools can significantly improve detection rates. The scope of PPEs should be adjusted based on the athlete's sport and level of competition.
Advanced Screening Techniques: ECG and Echocardiography
Electrocardiograms (ECGs) are valuable tools in detecting underlying cardiac abnormalities. While a normal ECG doesn't guarantee the absence of heart problems, significant abnormalities can readily be identified.
Echocardiograms (echos) provide detailed images of the heart's structure and function. Echos can detect conditions like HCM and ARVC that may be missed by ECG alone.
The Role of Family History and Genetic Testing
A comprehensive family history is essential. Family history of sudden death or cardiac conditions in young relatives is a significant risk factor that necessitates more thorough screening. In cases with a strong family history, genetic testing can be employed to identify specific genetic mutations associated with SCD.
Responding to SCD: Immediate Action and Long-Term Support
In the unfortunate event of SCD, immediate action is crucial. Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) significantly improve the chances of survival. Access to trained personnel and readily available AEDs in athletic settings is vital.
Long-term support for families and teams following an SCD event is critical. Grief counseling, community support programs, and open communication are essential elements of helping those affected cope with the tragedy.
The Future of SCD Prevention in Student-Athletes: Research and Collaboration
Ongoing research is vital to further improve our understanding of SCD in student-athletes. Advances in genetic testing, imaging techniques, and cardiac biomarkers hold promise for earlier and more accurate diagnosis. Collaborative efforts between medical professionals, athletic organizations, and policymakers are crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies and promoting comprehensive health screenings.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Approach to Protecting Young Athletes
Sudden cardiac death remains a significant concern for student-athletes. However, a multifaceted approach combining comprehensive pre-participation physical evaluations, advanced screening technologies, and public awareness initiatives can significantly reduce its incidence and mortality. The emphasis should be on proactive prevention, early detection, and immediate intervention. By working together, we can protect the health and well-being of these young athletes and safeguard their futures. The commitment to ongoing research, education, and collaboration is essential for a brighter future where SCD becomes a rare occurrence in student athletics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
After A Classified Document Is Leaked Online
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Represents Critical Information
Mar 14, 2025
-
Fundamentals Of Physics 12 Edition Instructors Solutions Manual Pdf
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is Photosynthesis Check All That Apply
Mar 14, 2025
-
The Concept Overview Video Assignments Are Organized
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Leading Medical Cause Of Death For Student-athletes Is: . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
