The Nose Is Located Blank And Blank To The Ears
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
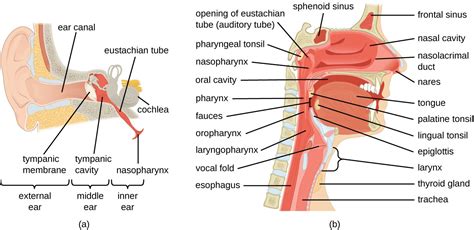
Table of Contents
The Nose: Anatomical Location, Function, and Clinical Significance
The nose, a prominent feature of the human face, is located medially and inferiorly to the ears. This seemingly simple statement belies a complex anatomical structure with crucial functions impacting respiration, olfaction, and even facial aesthetics. Understanding the nose's precise location within the head and its intricate relationships with surrounding structures is vital for medical professionals and anyone interested in human anatomy. This article delves deep into the nose's location, exploring its anatomical relationships, functional roles, and clinical significance.
Anatomical Location: Medial and Inferior to the Ears
The phrase "medially and inferiorly to the ears" precisely defines the nose's position in the human head. Let's break this down:
-
Medially: This refers to the nose's position toward the midline of the body. The nose sits centrally on the face, directly between the eyes and above the mouth. It's the most prominent midline structure of the facial skeleton.
-
Inferiorly: This indicates the nose's position below the ears. The ears are located laterally (to the sides) and superiorly (above) the nose. This vertical relationship is easily observable.
Further specifying the nose's location involves its relationships with other facial structures:
-
Superior to the mouth: The nose sits above the oral cavity, separating the nasal and oral passages. The nasal septum forms a partition between the two.
-
Inferior to the forehead: The root of the nose connects seamlessly with the forehead, contributing to the overall facial contour.
-
Lateral to the eyes: The nose is situated between the medial canthi (inner corners) of the eyes, forming a significant part of the mid-facial region.
-
Anterior to the brain: This is a deeper anatomical relationship. The nasal cavity is the entry point to the respiratory system, leading to the pharynx, larynx, and ultimately the lungs, all posterior (behind) the nose and face.
The External Nose: A Detailed Look
The external nose is the visible portion, composed primarily of cartilage and skin. Its key anatomical features include:
-
Root: The superiormost point where the nose connects with the forehead.
-
Bridge: The bony and cartilaginous structure forming the central, vertical part of the nose.
-
Dorsum: The entire length of the nasal bridge, from root to tip.
-
Tip: The inferiormost part of the nose, composed primarily of cartilage.
-
Alae: The flared cartilaginous portions forming the sides of the nostrils.
-
Nostrils (Nares): The external openings of the nasal cavity.
-
Columna nasi: The fleshy tissue separating the nostrils.
The skin covering the nose varies in thickness and texture, being thinnest over the tip and thicker over the dorsum. This variation influences the appearance and susceptibility to various conditions.
Internal Anatomy of the Nose: Nasal Cavity and Beyond
The external nose leads to the internal nasal cavity, a complex air passage with several important features:
-
Nasal Septum: A vertical partition of cartilage and bone dividing the nasal cavity into two halves. Deviations in the septum can affect airflow and necessitate surgical correction (septoplasty).
-
Nasal Conchae (Turbinates): Three bony projections on the lateral walls of the nasal cavity that increase the surface area of the nasal mucosa, allowing for better warming, humidification, and filtering of inhaled air.
-
Nasal Mucosa: A highly vascularized mucous membrane lining the nasal cavity. The mucosa contains goblet cells that secrete mucus, trapping dust, pollen, and other particles, and ciliated cells that move the mucus posteriorly toward the pharynx.
-
Olfactory Epithelium: Specialized tissue located in the superior part of the nasal cavity responsible for the sense of smell. Odorant molecules bind to olfactory receptors, triggering nerve impulses that travel to the brain.
-
Paranasal Sinuses: Air-filled cavities within the bones surrounding the nasal cavity (frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary sinuses). These sinuses contribute to voice resonance and humidification of inhaled air. Sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinuses, is a common condition.
Functional Significance of the Nose's Location
The nose's medial and inferior location relative to the ears is not arbitrary. This positioning contributes significantly to its functions:
-
Airway Protection: The nose acts as the primary filter for inhaled air. Its strategic location allows for efficient filtration before air reaches the lungs, protecting the lower respiratory tract from pathogens and irritants.
-
Airway Warming and Humidification: The nasal mucosa and the extensive surface area of the nasal conchae effectively warm and humidify incoming air, preventing damage to the delicate tissues of the lower respiratory system.
-
Olfactory Function: The superior location of the olfactory epithelium within the nasal cavity allows for the detection of airborne odorant molecules, providing a crucial sense for survival, communication, and enjoyment.
-
Facial Aesthetics: The nose's central location on the face makes it a key determinant of facial appearance and identity. Its shape and size contribute significantly to overall facial harmony.
Clinical Significance: Disorders Affecting the Nose
The nose's prominent location and crucial functions make it susceptible to various disorders:
-
Nasal Fractures: Trauma to the nose can result in fractures of the nasal bones or cartilage, often requiring medical intervention.
-
Rhinitis (Hay Fever): Inflammation of the nasal mucosa, often triggered by allergens, causing congestion, sneezing, and runny nose.
-
Sinusitis: Infection or inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, causing pain, pressure, and nasal congestion.
-
Nasal Polyps: Benign growths in the nasal mucosa that can obstruct airflow and cause nasal congestion.
-
Septal Deviation: A crooked nasal septum that can obstruct airflow and lead to breathing difficulties.
-
Nasal Tumors: Rare but potentially life-threatening, nasal tumors can be benign or malignant.
-
Rhinoplasty: This surgical procedure alters the shape or size of the nose for cosmetic or functional reasons.
-
Septoplasty: A surgical procedure to correct a deviated nasal septum.
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS): A minimally invasive surgical procedure to treat chronic sinusitis.
The nose's intricate anatomy and important functions highlight the need for careful medical attention when problems arise. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing most nasal disorders effectively.
The Nose in Different Cultures and Societies
The nose holds significant cultural and social importance across the globe. Its shape and size have been linked to beauty standards and social status throughout history. Different cultures have developed unique perspectives and traditions surrounding the nose, reflecting diversity in aesthetics and beliefs. Some cultures value a particular nasal shape or size, associating it with beauty, nobility, or specific traits.
Conclusion
The nose's location, medially and inferiorly to the ears, perfectly positions it for its critical roles in respiration, olfaction, and facial aesthetics. Its complex anatomical structure, encompassing both external and internal components, allows it to efficiently filter, warm, and humidify inhaled air, while also facilitating the sense of smell. Understanding the nose's anatomy and its intricate relationships with surrounding structures is essential for comprehending its vital functions and appreciating the clinical significance of disorders that can affect this important organ. The nose is more than just a facial feature; it is a vital component of the human body, inextricably linked to our health and well-being. Further research and advancements in medical technology continue to improve our understanding of the nose and its role in maintaining overall health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Represents A Consistant Standard Of Living
Mar 22, 2025
-
American Academy Of Cpr And First Aid Exam Answers
Mar 22, 2025
-
Glad Hands Are Used To Connect The
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Statement Best Describes President Lyndon Johnson
Mar 22, 2025
-
Match The Description With The Concept Being Demonstrated
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Nose Is Located Blank And Blank To The Ears . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
