The Ozone Layer Helps To Sustain Terrestrial Life By __________.
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
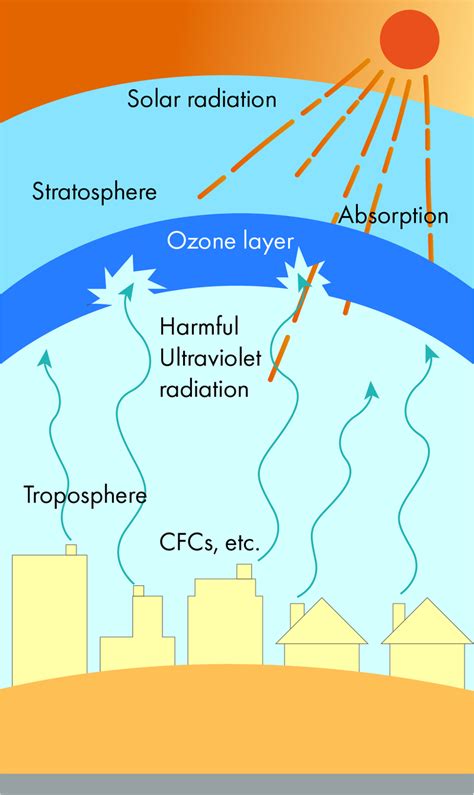
Table of Contents
The Ozone Layer Helps to Sustain Terrestrial Life by Protecting Us From Harmful UV Radiation
The ozone layer, a fragile shield residing in the stratosphere, plays a pivotal role in sustaining terrestrial life. Its primary function, and the reason it's so crucial for our survival, is its ability to absorb most of the sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Without this vital protection, life as we know it would be drastically different, if not impossible. This article will delve deep into the mechanisms by which the ozone layer achieves this protection, the consequences of its depletion, and the ongoing efforts to preserve this essential component of our planet's atmosphere.
Understanding the Ozone Layer: A Molecular Shield
The ozone layer isn't a distinct layer in the atmosphere like a sharply defined boundary; rather, it's a region of relatively high ozone concentration, primarily located in the stratosphere, approximately 15 to 30 kilometers above the Earth's surface. Ozone (O3) itself is a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms, unlike the oxygen we breathe (O2), which has only two. This seemingly minor difference in molecular structure gives ozone its remarkable properties.
Ozone's ability to absorb UV radiation stems from its molecular structure's interaction with UV photons. When a UV photon strikes an ozone molecule, it breaks the molecule apart. This process absorbs the UV radiation's energy, preventing it from reaching the Earth's surface. The process isn't a one-way street; the separated oxygen atoms can recombine to form ozone molecules again, creating a continuous cycle of absorption and reformation. This dynamic equilibrium is crucial for maintaining the ozone layer's protective function.
Types of UV Radiation and Their Effects
The sun emits three main types of UV radiation: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVC is the most energetic and harmful, but thankfully, it's almost entirely absorbed by the ozone layer and the upper atmosphere before reaching the ground. UVB radiation, while also harmful, is partially absorbed by the ozone layer. UVA radiation, the least energetic of the three, penetrates the ozone layer most effectively and reaches the Earth's surface in significant quantities.
Even though UVA radiation is less damaging than UVB, both have detrimental effects on living organisms. Let's examine these effects in detail:
-
UVB Radiation's Impact: UVB radiation is primarily responsible for sunburns. Prolonged exposure can lead to premature aging of the skin, including wrinkles and age spots. More seriously, excessive UVB exposure significantly increases the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma, a particularly dangerous and potentially fatal form of skin cancer. It also damages the eyes, leading to cataracts and other eye problems. Plants are also susceptible to UVB damage, affecting their growth, photosynthesis, and overall productivity.
-
UVA Radiation's Impact: Although less potent than UVB, UVA radiation penetrates deeper into the skin, contributing to premature aging, wrinkles, and indirectly to skin cancer development. It also plays a role in immune suppression, making the body more vulnerable to infections and diseases.
The Consequences of Ozone Depletion: A World Exposed
The discovery of the ozone hole over Antarctica in the 1980s brought the dangers of ozone depletion into sharp focus. The hole, a region of significantly reduced ozone concentration, is caused primarily by the release of ozone-depleting substances (ODS), such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, and other man-made chemicals. These ODS rise into the stratosphere, where they break down ozone molecules through a complex series of chemical reactions, disrupting the natural ozone cycle.
The consequences of ozone depletion are far-reaching and severe:
-
Increased UV Radiation: Reduced ozone concentration leads to increased levels of UVB radiation reaching the Earth's surface. This increased exposure directly correlates to higher rates of skin cancer, cataracts, and other health problems.
-
Impact on Ecosystems: Increased UV radiation damages terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Plants exhibit reduced growth and productivity, affecting agricultural yields and food security. Phytoplankton, the base of many aquatic food webs, are also highly vulnerable, with potential consequences for the entire marine ecosystem.
-
Damage to Materials: UV radiation can degrade certain materials, including plastics, paints, and fabrics. This accelerated degradation increases the need for replacement and repair, leading to economic losses.
The Montreal Protocol: A Global Success Story
Recognizing the serious threat posed by ozone depletion, the international community came together in 1987 to sign the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer. This landmark agreement established a framework for the phasing out of ODS. The Protocol's success is a testament to international cooperation and its impact on the recovery of the ozone layer is already visible.
The Montreal Protocol's success is due to several key factors:
-
Global Cooperation: The agreement involved nearly every nation in the world, demonstrating a remarkable commitment to tackling a global environmental problem.
-
Scientific Consensus: The strong scientific evidence linking ODS to ozone depletion provided a solid foundation for policy decisions.
-
Effective Enforcement Mechanisms: The Protocol included mechanisms for monitoring compliance and enforcing regulations.
-
Technological Innovation: The development of ozone-friendly alternatives to ODS provided viable substitutes for industries and consumers.
Ongoing Challenges and Future Outlook
While the Montreal Protocol has been a resounding success, challenges remain. The complete recovery of the ozone layer is expected to take several decades, and the long-term effects of past ozone depletion are still being assessed. Furthermore, the potential for new ozone-depleting substances to emerge necessitates continued monitoring and vigilance.
The Importance of Continued Awareness and Action
Preserving the ozone layer is not a matter that can be taken lightly. It is a critical component of the Earth's climate system, impacting global temperatures, atmospheric circulation, and the biosphere. The continued reduction of ODS emissions and the ongoing monitoring of ozone levels are essential to ensure the complete recovery of the ozone layer and the sustained protection of life on Earth. Individual actions also matter – by supporting environmentally responsible practices and advocating for policies that protect the ozone layer, we can collectively contribute to safeguarding our planet's future.
Furthermore, research into the effects of ozone depletion on specific ecosystems and the development of more efficient and sustainable alternatives to ODS should continue. The success of the Montreal Protocol provides a valuable model for international cooperation in tackling other global environmental challenges. The ozone layer is a testament to the impact that collective human action can have on the environment. However, vigilance and continued commitment are essential to ensure the ongoing protection of this vital shield, and in turn, life on Earth. The ozone layer's role in sustaining life is undeniably paramount, a testament to the intricate balance within our planet's ecosystem. Protecting it remains a crucial task for our collective future.
This ongoing research will help to refine our understanding of the ozone layer's dynamics and enhance our ability to predict and mitigate future threats. The continued success of the Montreal Protocol depends on the sustained commitment of nations worldwide, along with ongoing research, education, and public awareness. The ozone layer, therefore, is not simply a scientific concept; it's a vital element ensuring the habitability of our planet, a responsibility that demands our continuous attention and action. By understanding the intricate processes involved and the profound consequences of ozone depletion, we can collectively work towards a future where this crucial atmospheric component continues to protect life on Earth for generations to come. The ozone layer: a testament to nature's fragility and the power of global cooperation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Siphoning Of Wetlands In Iraq Has Led To
Mar 15, 2025
-
Patients With Perfusing Rhythms Should Receive Ventilations Once Every
Mar 15, 2025
-
In A State Supervised County Administered State
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Quickly Should You Move During Resistance Training
Mar 15, 2025
-
Hazmat Familiarization And Safety In Transportation Module 04 Exam
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Ozone Layer Helps To Sustain Terrestrial Life By __________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
