The Total Capacitance Of Two 15uf Capacitors In Series Is
Breaking News Today
Jun 06, 2025 · 6 min read
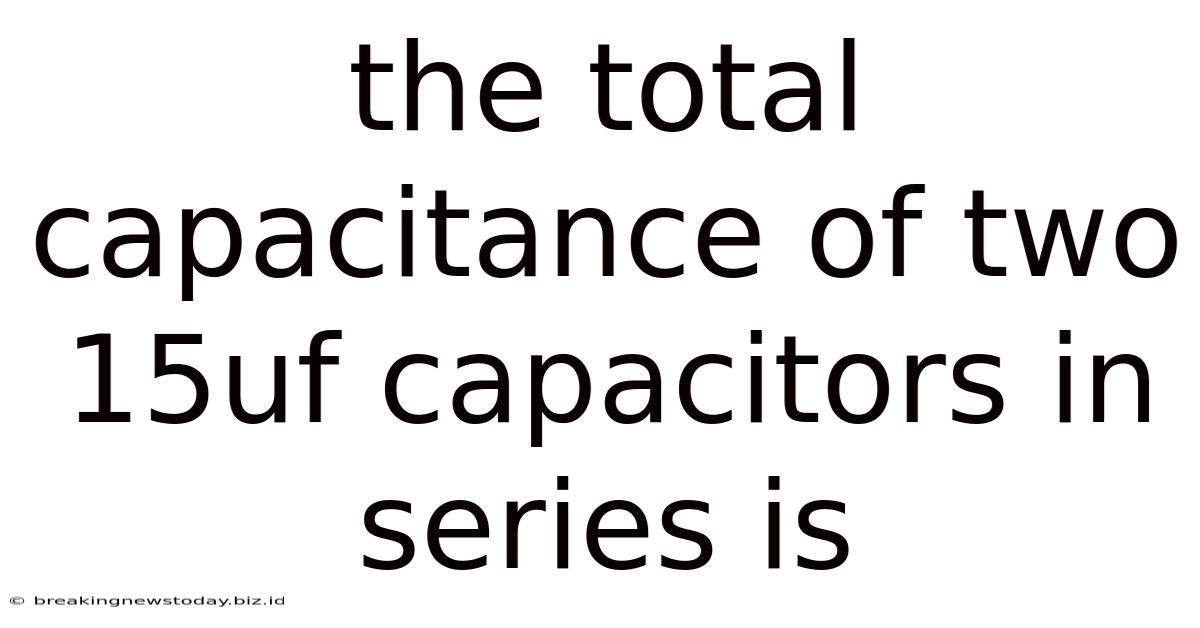
Table of Contents
The Total Capacitance of Two 15µF Capacitors in Series: A Deep Dive into Capacitance Calculations and Applications
Understanding how capacitors behave, especially when connected in series or parallel, is crucial in electronics. This article delves into the specifics of calculating the total capacitance of two 15µF capacitors connected in series, exploring the underlying principles, practical applications, and potential pitfalls. We'll also touch upon the broader context of capacitance, its role in circuits, and how different capacitor arrangements impact circuit behavior.
Understanding Capacitance
Capacitance, measured in Farads (F), is the ability of a capacitor to store electrical energy in an electric field. A capacitor, in its simplest form, consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When a voltage is applied across the plates, an electric charge accumulates on each plate, with an equal and opposite charge on the other. The capacitance (C) is directly proportional to the area (A) of the plates and the dielectric constant (κ) of the insulating material, and inversely proportional to the distance (d) between the plates:
C = κε₀A/d
where ε₀ is the permittivity of free space (a constant).
Different dielectric materials offer varying levels of capacitance for the same physical dimensions. Common dielectric materials include ceramic, film (polyester, polypropylene, etc.), and electrolytic materials. The choice of dielectric influences factors such as voltage rating, temperature stability, and the overall size and cost of the capacitor.
Capacitors in Series
When capacitors are connected in series, the total capacitance is always less than the smallest individual capacitance. This is because the effective distance between the plates increases, reducing the overall ability to store charge. The total capacitance (C<sub>T</sub>) for capacitors in series is calculated using the reciprocal formula:
1/C<sub>T</sub> = 1/C₁ + 1/C₂ + 1/C₃ + ...
For two capacitors, C₁ and C₂, this simplifies to:
C<sub>T</sub> = (C₁ * C₂) / (C₁ + C₂)
Calculating the Total Capacitance of Two 15µF Capacitors in Series
Now, let's apply this formula to our specific scenario: two 15µF capacitors connected in series.
C₁ = 15µF
C₂ = 15µF
Using the formula:
C<sub>T</sub> = (15µF * 15µF) / (15µF + 15µF) = 225µF²/30µF = 7.5µF
Therefore, the total capacitance of two 15µF capacitors connected in series is 7.5µF. This result is significantly lower than the individual capacitances, highlighting the key characteristic of series capacitor connections.
Implications and Applications
The reduced capacitance in a series configuration has important implications for circuit design. While it decreases the overall energy storage capacity, it also impacts the voltage distribution across the capacitors. In a series connection, the voltage across each capacitor is inversely proportional to its capacitance. Since both capacitors are identical in our example (15µF), the voltage will be equally divided between them. If the total voltage across the series combination is, say, 30V, each capacitor will have 15V across it.
This voltage division is crucial in applications where a higher voltage needs to be handled than a single capacitor can tolerate. By using multiple capacitors in series, the voltage stress on each individual component is reduced, enhancing reliability and preventing damage. This is common in high-voltage power supplies and filter circuits.
Comparing Series and Parallel Connections
It's essential to contrast series connections with parallel connections. In a parallel configuration, the total capacitance is the simple sum of the individual capacitances:
C<sub>T</sub> = C₁ + C₂ + C₃ + ...
For two 15µF capacitors in parallel, the total capacitance would be:
C<sub>T</sub> = 15µF + 15µF = 30µF
This highlights the fundamental difference: series connections reduce the total capacitance, while parallel connections increase it. The choice between series and parallel configurations depends heavily on the specific requirements of the circuit.
Tolerance and Practical Considerations
The calculations we've performed assume ideal capacitors with perfectly matched values. In reality, capacitors have tolerances. A 15µF capacitor might have a tolerance of ±5%, meaning its actual capacitance could range from 14.25µF to 15.75µF. This tolerance affects the total capacitance in both series and parallel configurations. In a series connection, variations in individual capacitances become amplified, resulting in a larger deviation from the calculated value.
Therefore, it's crucial to consider capacitor tolerance when designing circuits. Using capacitors with tighter tolerances minimizes the uncertainty in the overall capacitance. Furthermore, temperature variations can also subtly influence capacitance, another factor to keep in mind in precision applications.
Capacitor Selection and Circuit Design
Choosing the right capacitors for a circuit is a multifaceted process. Beyond capacitance, several other factors are essential:
-
Voltage Rating: This specifies the maximum voltage that can be applied across the capacitor without causing damage. In a series connection, the voltage rating of each capacitor must be sufficient to handle its share of the total voltage.
-
Dielectric Material: Different dielectric materials offer different characteristics. Ceramic capacitors are inexpensive and suitable for general-purpose applications. Film capacitors are known for their high stability and low losses, ideal for high-frequency circuits. Electrolytic capacitors have high capacitance values for their size but are polarity-sensitive and have lower stability.
-
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance): All capacitors have some inherent resistance, impacting performance at higher frequencies. Low ESR is essential in applications like power supplies where high currents flow.
-
ESL (Equivalent Series Inductance): At higher frequencies, the leads and internal structure of a capacitor exhibit inductive properties, which can limit performance.
Advanced Applications and Considerations
The principles discussed here are fundamental to many electrical engineering applications. Here are some advanced considerations:
-
RC Circuits: Capacitors are frequently used in conjunction with resistors (R) to create RC circuits, which find application in timing circuits, filters, and signal processing. The time constant (τ = RC) of an RC circuit dictates how quickly the capacitor charges or discharges.
-
LC and RLC Circuits: Capacitors, combined with inductors (L) and sometimes resistors (R), form LC and RLC circuits, used in resonant circuits, filters, and oscillators. These circuits exploit the interplay between the energy storage capabilities of capacitors and inductors.
-
Power Factor Correction: In AC power systems, capacitors are used to improve the power factor, reducing reactive power and improving overall efficiency. This is particularly important in industrial settings where large motors draw significant reactive power.
Conclusion
Calculating the total capacitance of two 15µF capacitors in series—yielding a total capacitance of 7.5µF—is a straightforward application of the reciprocal formula for series capacitance. However, this simple calculation underscores the broader importance of understanding capacitance, its behavior in different circuit configurations, and the numerous practical considerations involved in selecting and using capacitors effectively. This knowledge is crucial for designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits, optimizing performance, and ensuring reliability across a wide range of applications. Always remember to carefully consider tolerance, voltage rating, and other parameters to ensure the optimal functionality of your circuits.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Estoy Comprando Los Regalos Para Ellos
Jun 07, 2025
-
A Body Of The Letter Is Composed Of The
Jun 07, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Belongs In Formal Academic Writing
Jun 07, 2025
-
What Is The Most Specific Name For Quadrilateral Wxyz
Jun 07, 2025
-
Aaron Bryce And Craig Are All Distinct Integer Ages
Jun 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Total Capacitance Of Two 15uf Capacitors In Series Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.