The Transaction History At An Electronic Goods Store
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
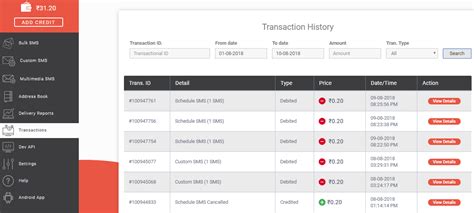
Table of Contents
Diving Deep into Electronic Goods Store Transaction History: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the transaction history at an electronic goods store is crucial for various stakeholders, from store owners and managers aiming to optimize business strategies to data analysts seeking to uncover valuable insights. This detailed guide explores the multifaceted nature of this data, examining its components, potential applications, and the importance of effective data management.
Understanding the Components of Transaction History Data
Electronic goods store transaction history encompasses a vast array of data points, each contributing to a comprehensive picture of sales, customer behavior, and inventory management. Let's break down the key components:
1. Customer Information:
- Unique Customer ID: A unique identifier assigned to each customer, ensuring data privacy and accurate tracking.
- Contact Details: Name, address, phone number, and email address, enabling targeted marketing and customer service.
- Purchase History: A detailed record of all past transactions, including dates, products purchased, and payment methods used.
- Customer Segmentation Data: Demographic information (age, gender, location), purchase behavior patterns (frequency, average spend, preferred product categories), and potentially psychographic data (lifestyle, interests) derived from purchase history and other interactions.
2. Product Information:
- Product ID: A unique identifier for each product sold, allowing for efficient inventory tracking and sales analysis.
- Product Name & Description: Detailed information about the product, including features and specifications.
- Product Category & Subcategory: Categorization of products for easier analysis and reporting. This allows for understanding trends in specific product lines.
- Price & Discounts: The original price, any applied discounts, and the final sale price. This is crucial for calculating profit margins and understanding pricing strategies.
- Inventory Levels: Real-time tracking of available stock, informing restocking decisions and preventing stockouts.
3. Transaction Details:
- Transaction ID: A unique identifier for each transaction, crucial for data integrity and traceability.
- Transaction Date & Time: Precise timestamp of the transaction, enabling analysis of sales trends over time.
- Payment Method: The method used for payment (credit card, debit card, cash, online payment gateways), providing insights into customer preferences and payment processing efficiency.
- Sales Channel: The channel through which the transaction occurred (online store, physical store, mobile app), enabling analysis of channel performance.
- Shipping Information (for online transactions): Shipping address, delivery date, and shipping costs. This is critical for evaluating logistics performance and identifying potential areas for improvement.
- Returns & Refunds: Detailed information about any returned or refunded items, providing insights into product quality, customer satisfaction, and potential issues with specific products.
4. Employee Information (Optional):
- Employee ID: For transactions processed by employees, identifying the associate involved. This helps track individual performance and identify areas of strength or weakness in customer service.
Applications of Transaction History Data Analysis
Analyzing the transaction history data offers a wealth of opportunities for enhancing various aspects of the electronic goods store's operations. Here are some key applications:
1. Sales Forecasting & Inventory Management:
Analyzing past sales trends, seasonality, and product popularity allows for accurate sales forecasting. This enables efficient inventory management, minimizing stockouts and reducing storage costs. Predictive analytics can play a significant role here, forecasting future demand based on historical patterns and external factors like upcoming product launches or promotional campaigns.
2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Transaction history provides invaluable insights into customer behavior. This data allows the creation of personalized marketing campaigns, targeted promotions, and loyalty programs. Identifying high-value customers allows for tailored customer service and retention strategies. Analyzing purchase history helps segment customers based on their preferences, enabling personalized recommendations and offers.
3. Pricing Optimization:
By analyzing sales data at different price points, the store can optimize pricing strategies. This involves understanding price elasticity – how demand changes with price fluctuations – to maximize revenue and profitability. A/B testing different pricing models on various customer segments can further refine pricing strategies.
4. Marketing Campaign Effectiveness:
Tracking sales following specific marketing campaigns allows for assessing their effectiveness. This enables data-driven decisions about future marketing investments, ensuring resources are allocated to the most productive channels. Analyzing which customer segments respond best to which campaigns is also crucial for optimizing marketing ROI.
5. Identifying Slow-Moving & Obsolete Inventory:
Analyzing product sales data helps identify slow-moving or obsolete inventory. This allows the store to adjust its inventory levels, implement clearance sales, or discontinue underperforming products, preventing unnecessary storage costs and freeing up resources.
6. Supply Chain Optimization:
Analyzing transaction data alongside supplier performance data allows for optimizing the supply chain. This can involve identifying reliable suppliers, negotiating better terms, and streamlining the procurement process to minimize delays and costs.
7. Fraud Detection:
Analyzing transaction patterns can help identify fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized credit card transactions or suspicious return patterns. Machine learning algorithms can be used to identify anomalies and flag potentially fraudulent transactions for review.
8. Business Intelligence & Strategic Decision Making:
Comprehensive analysis of transaction history data provides valuable business intelligence, informing strategic decisions about store expansion, product diversification, and overall business growth. Identifying emerging trends and market opportunities is vital for long-term success.
Effective Data Management and Security Considerations
Properly managing and securing transaction history data is paramount. Here are some key considerations:
- Data Storage: Implementing a robust and scalable data storage solution is crucial to handle the large volumes of data generated by a busy electronic goods store. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and flexibility, while on-premise solutions provide greater control over data security.
- Data Security: Protecting customer data from unauthorized access and breaches is crucial. Implementing strong security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, is essential to comply with data privacy regulations (like GDPR and CCPA) and maintain customer trust.
- Data Privacy: Adhering to data privacy regulations is non-negotiable. This involves obtaining explicit consent for data collection, providing transparency about data usage, and ensuring secure data storage and disposal.
- Data Analytics Tools: Utilizing powerful data analytics tools enables efficient analysis of transaction history data. These tools can provide insights that would be impossible to uncover manually. The choice of tool will depend on the store's specific needs and technical capabilities.
- Data Integration: Integrating transaction history data with other relevant data sources, such as customer service interactions and website analytics, provides a more holistic view of the business and enables deeper insights.
- Regular Data Backups: Implementing a robust backup system prevents data loss in case of system failures or cyberattacks. Regular backups ensure business continuity and protect valuable data.
Conclusion: Leveraging Transaction History for Success
The transaction history at an electronic goods store is a treasure trove of information, offering invaluable insights into sales performance, customer behavior, and operational efficiency. By effectively managing and analyzing this data, stores can optimize their business strategies, enhance customer relationships, and achieve sustainable growth. Investing in robust data management systems, employing powerful data analytics tools, and prioritizing data security are crucial steps towards unlocking the full potential of transaction history data and transforming it into a powerful driver of success. By consistently monitoring, analyzing, and adapting based on the insights gleaned from this data, electronic goods stores can ensure their continued competitiveness and profitability in the dynamic landscape of the electronics market.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is Considered A Good Conductor Milady
Mar 26, 2025
-
When Workers May Be Exposed To Blank
Mar 26, 2025
-
Cloud Computing Is Not Typically Suited For Situations
Mar 26, 2025
-
In The 21st Century We Define Justice As
Mar 26, 2025
-
Internet Acquaintances Can Pose A Security Threat
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Transaction History At An Electronic Goods Store . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
