This Is A Compact Stem With Nodes And Internodes.
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
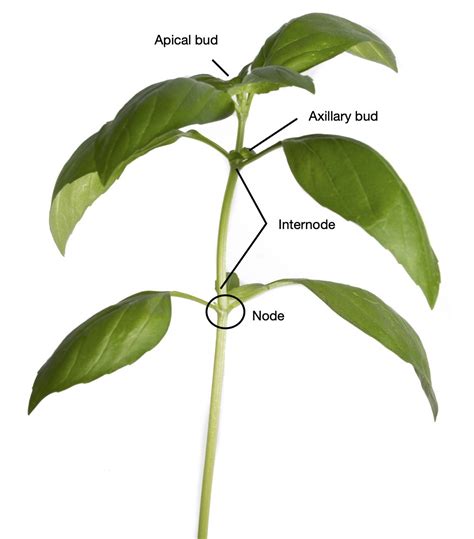
Table of Contents
This Is a Compact Stem with Nodes and Internodes: Exploring the World of Stem Anatomy
This seemingly simple statement, "This is a compact stem with nodes and internodes," opens a door to a fascinating world of plant anatomy and morphology. Understanding the structure and function of stems, particularly those described as compact, is crucial for comprehending plant growth, development, and overall survival. This article delves deep into the intricacies of compact stems, exploring their defining characteristics, variations, evolutionary significance, and ecological implications.
What Defines a Stem?
Before we dive into the specifics of compact stems, let's establish a foundational understanding of what constitutes a stem. A stem is the main structural axis of a vascular plant, supporting the leaves, flowers, and fruits. It serves several vital functions:
- Support: Providing structural integrity, holding the plant upright and supporting its other organs.
- Conduction: Transporting water, minerals, and nutrients between the roots and the leaves via the xylem and phloem vascular tissues.
- Storage: Storing food reserves, providing energy resources for growth and survival during unfavorable conditions.
- Propagation: In some species, stems can participate in vegetative propagation, generating new plants from cuttings or runners.
Understanding Nodes and Internodes
The stem's structure is characterized by distinct features: nodes and internodes.
-
Nodes: These are the points on the stem where leaves, branches, or buds originate. They are regions of intense meristematic activity, responsible for the growth and development of lateral structures. They represent areas of concentrated cellular division and differentiation.
-
Internodes: These are the segments of the stem between successive nodes. The length of the internodes significantly influences the overall appearance and growth habit of the plant. Short internodes result in compact growth, while long internodes contribute to taller, more sprawling growth forms.
The Significance of "Compact"
The term "compact" in the context of a stem refers to the relative shortness of the internodes. In compact stems, the internodes are significantly shorter compared to those found in elongated stems. This results in a dense, closely spaced arrangement of leaves, branches, or flowers. This compact morphology has several implications for the plant:
Advantages of Compact Stems:
-
Reduced Wind Resistance: Compact stems offer reduced surface area exposed to wind, providing greater stability and resistance to wind damage, especially beneficial in exposed or windy environments.
-
Enhanced Light Capture: In dense populations or shaded conditions, a compact structure can maximize light capture by positioning leaves closer together, improving overall photosynthetic efficiency.
-
Protection from Herbivores: The dense arrangement of leaves and branches can act as a physical deterrent to herbivores, making it more difficult for them to access and consume plant tissues.
-
Water Conservation: In arid or semi-arid environments, the compact structure can minimize water loss through transpiration by reducing exposed surface area.
Disadvantages of Compact Stems:
-
Limited Air Circulation: The dense foliage can restrict air circulation, potentially increasing susceptibility to fungal diseases or pest infestations.
-
Reduced Growth Rate: The shorter internodes may limit the overall height and growth rate of the plant compared to those with longer internodes.
-
Competition for Resources: The close proximity of leaves and branches can lead to increased competition for light, water, and nutrients within the plant itself.
Variations in Compact Stems:
Compact stems manifest in various forms across the plant kingdom. These variations often reflect adaptations to specific environmental conditions or ecological niches:
-
Rosettes: In rosette plants, the leaves are tightly clustered at the base of the stem, with extremely short internodes, forming a basal rosette. Examples include many succulents and lettuce.
-
Caudiciform Plants: These plants develop swollen stems, often with extremely short internodes, used for water storage. They are characteristic of arid and semi-arid regions.
-
Dwarf Cultivars: Many horticultural varieties are bred to exhibit compact growth habits, making them suitable for smaller gardens or container cultivation.
Evolutionary Significance:
The evolution of compact stems reflects adaptations to a range of selective pressures, including:
-
Environmental Stress: Compact growth is often favored in environments characterized by water scarcity, strong winds, or intense solar radiation.
-
Competitive Interactions: In dense plant communities, compact stems can provide a competitive advantage by maximizing access to limited resources.
-
Herbivory: The dense structure serves as a defense mechanism, reducing vulnerability to herbivores.
Ecological Implications:
The prevalence of compact stems in different ecosystems has far-reaching ecological implications:
-
Biodiversity: The diverse forms of compact stems contribute to the overall biodiversity of plant communities.
-
Habitat Structure: Compact plants shape habitat structure, influencing the distribution and abundance of other organisms, including insects, birds, and mammals.
-
Nutrient Cycling: The decomposition of compact plant tissues contributes to nutrient cycling within the ecosystem.
-
Soil Stabilization: The dense root systems associated with compact plants can contribute to soil stabilization, reducing erosion.
Practical Applications:
Understanding the characteristics of compact stems has important practical applications in:
-
Horticulture: Breeders utilize knowledge of stem anatomy to develop compact cultivars suitable for various growing conditions.
-
Agriculture: Understanding stem growth and development is crucial for optimizing crop yields and managing plant health.
-
Conservation: Knowledge of compact stem adaptations can inform conservation strategies for endangered plant species.
Conclusion:
The seemingly simple description, "This is a compact stem with nodes and internodes," encompasses a complex interplay of structural features, physiological processes, and evolutionary adaptations. Understanding the significance of compactness, nodes, and internodes is essential for comprehending plant form and function, their ecological roles, and their potential for human application. Further research into the genetic and environmental factors that influence stem compactness will continue to enrich our knowledge of plant biology and its implications for the world around us. The study of compact stems highlights the intricate beauty and remarkable adaptability of the plant kingdom. The exploration of this seemingly simple anatomical structure provides a window into the complexities of plant life and its vital role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystems. From the smallest rosette to the largest caudiciform, the compact stem stands as a testament to the remarkable ingenuity of nature's designs. Continuing research into this fascinating aspect of plant anatomy promises further discoveries and a deeper appreciation of the plant world's incredible diversity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do Bank Loans Help The Nations Economy
Mar 21, 2025
-
Duct Systems Are Designed To Provide Conditioned Air That Matches
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Ability To Engender Trust In Others Refers To
Mar 21, 2025
-
Silvina Tuvo Un Accidente En Su Automovil
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is Another Term For Dti Programs
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about This Is A Compact Stem With Nodes And Internodes. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
