To Develop Psychographic Segments The Marketer Must Understand Consumers
Breaking News Today
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
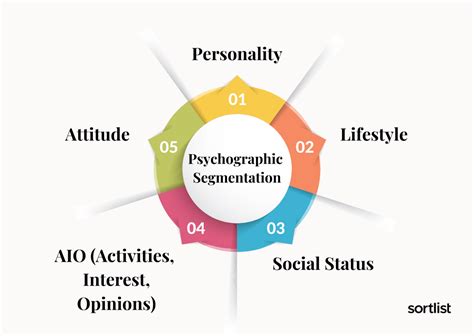
Table of Contents
To Develop Psychographic Segments, the Marketer Must Understand Consumers
Understanding your consumer is paramount to successful marketing. While demographics tell you who your consumers are (age, gender, location, income), psychographics delve into why they buy, what motivates them, and what values they hold. Developing robust psychographic segments allows for targeted, resonant messaging that significantly boosts marketing ROI. This article explores the crucial role of consumer understanding in building effective psychographic segments, detailing the methods, challenges, and ultimate rewards.
The Importance of Understanding Consumers for Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation goes beyond surface-level demographics. It's about understanding the inner workings of your target audience – their attitudes, values, lifestyles, interests, and personality traits. This deep dive allows marketers to create campaigns that emotionally connect with consumers, fostering brand loyalty and driving sales. Without this understanding, marketing efforts risk being generic and ineffective, failing to resonate with the intended audience.
Why is consumer understanding so crucial?
- Targeted Messaging: Psychographic segmentation enables highly targeted messaging. Instead of broadcasting a single message to everyone, you can tailor your communication to specific psychographic groups, maximizing impact and minimizing wasted resources.
- Enhanced Brand Loyalty: When consumers feel understood and valued, they are more likely to develop a strong brand preference and remain loyal customers.
- Improved Product Development: Understanding consumer values and lifestyles can inform product development, ensuring your offerings align with their needs and desires.
- Increased ROI: By focusing marketing efforts on segments most likely to convert, you can significantly improve your return on investment.
- Competitive Advantage: A deep understanding of your target audience gives you a competitive edge, allowing you to anticipate trends and develop strategies that resonate powerfully.
Methods for Understanding Consumers and Building Psychographic Segments
Several methods can help marketers gain a comprehensive understanding of their consumers and build effective psychographic segments:
1. Qualitative Research: Unveiling the "Why" Behind Consumer Behavior
Qualitative research methods are essential for uncovering the underlying motivations and beliefs driving consumer behavior. These methods focus on in-depth understanding rather than broad generalizations. They include:
- In-depth Interviews: One-on-one interviews allow for detailed exploration of consumer attitudes, values, and experiences. Open-ended questions encourage rich, nuanced responses.
- Focus Groups: Moderated discussions with small groups of consumers provide valuable insights into shared opinions and beliefs. Observing group dynamics can reveal hidden influences on consumer behavior.
- Ethnographic Studies: This immersive research method involves observing consumers in their natural environment, gaining firsthand understanding of their habits and lifestyles. This can involve home visits, shadowing, or participating in relevant activities.
- Social Media Listening: Monitoring social media conversations, reviews, and online communities can reveal valuable insights into consumer sentiments, preferences, and pain points.
Example: A brand selling organic skincare products might conduct in-depth interviews with potential customers to understand their concerns about chemical ingredients, their commitment to sustainability, and their views on ethical sourcing.
2. Quantitative Research: Measuring and Quantifying Consumer Attitudes
Quantitative research methods provide measurable data, allowing marketers to quantify consumer attitudes and behaviors. These methods include:
- Surveys: Online or offline surveys can collect data from a large sample size, enabling statistical analysis of consumer preferences and demographics.
- Experiments: Controlled experiments can test the effectiveness of different marketing messages or product features on consumer behavior.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing existing customer data, such as purchase history and website interactions, can reveal patterns and trends in consumer behavior.
Example: A company selling athletic wear might conduct a survey to measure consumer attitudes toward different styles, colors, and functionalities, helping them to segment their audience based on preferences for performance, fashion, or comfort.
3. Combining Qualitative and Quantitative Research: A Holistic Approach
For the most comprehensive understanding, it's crucial to combine both qualitative and quantitative research methods. Qualitative research provides the "why," while quantitative research provides the "how much." This integrated approach allows for a more nuanced and insightful understanding of consumer psychographics.
Example: A company might conduct in-depth interviews to understand the underlying motivations behind consumer preferences for a particular product (qualitative), then conduct a survey to quantify the prevalence of these preferences within their target market (quantitative).
Defining Psychographic Segments: Turning Insights into Actionable Categories
Once you've gathered data on consumer attitudes, values, and lifestyles, the next step is to define meaningful psychographic segments. This involves grouping consumers with similar characteristics into distinct segments. Effective segmentation considers several factors:
- Values: What principles and beliefs are important to these consumers? (e.g., sustainability, family, innovation, status)
- Lifestyle: How do they spend their time and money? (e.g., adventurous, homebody, career-driven, health-conscious)
- Interests: What are their hobbies, passions, and areas of interest? (e.g., travel, technology, art, sports)
- Personality Traits: What personality characteristics define these consumers? (e.g., extroverted, introverted, risk-averse, innovative)
- Attitudes: What are their opinions and feelings about your brand, your category, and related issues?
Examples of Psychographic Segments:
- Eco-conscious Consumers: Value sustainability, ethical sourcing, and environmental protection.
- Tech-savvy Innovators: Early adopters of new technologies, interested in innovation and cutting-edge products.
- Family-oriented Consumers: Prioritize family values, spending time with loved ones, and providing for their children.
- Health and Wellness Enthusiasts: Prioritize physical and mental wellbeing, focused on healthy eating, exercise, and self-care.
- Luxury Seekers: Value high-quality, premium products and experiences, willing to pay a premium for exclusivity and prestige.
Challenges in Developing Psychographic Segments
Developing effective psychographic segments comes with challenges:
- Data Collection: Gathering accurate and comprehensive data can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Data Interpretation: Analyzing qualitative data requires expertise and careful interpretation to avoid biases.
- Segment Overlap: Consumers may belong to multiple psychographic segments, blurring the lines between categories.
- Segment Stability: Consumer attitudes and behaviors can change over time, requiring regular updates to your segmentation strategy.
- Measurement Difficulty: Accurately measuring certain psychographic traits can be challenging.
Utilizing Psychographic Segments for Effective Marketing
Once you've defined your psychographic segments, you can use this information to tailor your marketing efforts:
- Targeted Messaging: Craft messages that resonate with the values, lifestyles, and interests of each segment.
- Channel Selection: Choose the most effective communication channels to reach each segment. (e.g., social media for tech-savvy innovators, print media for family-oriented consumers).
- Product Development: Develop products and services that meet the specific needs and desires of each segment.
- Pricing Strategy: Adjust pricing to align with the perceived value and purchasing power of each segment.
- Brand Positioning: Position your brand to appeal to the values and aspirations of your target segments.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Pursuit of Consumer Understanding
Developing effective psychographic segments requires a deep and ongoing understanding of your consumers. By combining qualitative and quantitative research methods, marketers can gain valuable insights into consumer motivations, values, and lifestyles. This knowledge allows for the creation of targeted, resonant marketing campaigns that foster brand loyalty, drive sales, and build a strong competitive advantage. Remember that consumer understanding is an ongoing process; continuous monitoring and adaptation are essential to maintain relevance and effectiveness in the ever-evolving market landscape. The investment in truly understanding your consumers will ultimately yield significant returns in terms of marketing success and business growth. Don't just sell products; understand your audience's needs and sell solutions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Loop Controller Output Can Be Used As An Alarm
Apr 09, 2025
-
What Do Private Citizens And Companies Decide
Apr 09, 2025
-
In 1996 When Colorado Struck Down The Bowers Decision
Apr 09, 2025
-
Match The Type Of Reflex With Its Description
Apr 09, 2025
-
One Of Your Tables Flags You Down
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about To Develop Psychographic Segments The Marketer Must Understand Consumers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.