To Record A Sale On Account The Company Should Debit
Breaking News Today
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
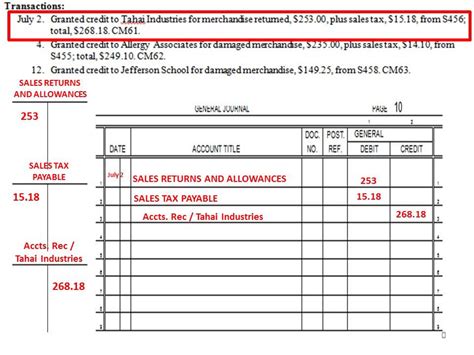
Table of Contents
To Record a Sale on Account, the Company Should Debit: A Comprehensive Guide to Accounts Receivable
Selling goods or services on account, also known as extending credit to customers, is a common practice in many businesses. Understanding how to accurately record these transactions is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring smooth business operations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the accounting treatment of sales on account, focusing specifically on the debit entry required. We'll explore the underlying principles, provide practical examples, and address common misconceptions.
Understanding the Accounting Equation
Before diving into the specifics of recording sales on account, let's review the fundamental accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Every accounting transaction must maintain the balance of this equation. When a sale on account occurs, both the asset and equity sides of the equation are affected.
The Debit Entry: Accounts Receivable
When a company sells goods or services on account, it's essentially extending credit to the customer. This creates an asset for the company – an amount of money owed to the company by the customer. This asset is recorded as Accounts Receivable. To increase the balance of this asset account, we use a debit entry.
Why Debit?
The debit/credit system is based on the principle of double-entry bookkeeping. Assets have a normal debit balance, meaning that increases in assets are recorded with a debit. Since Accounts Receivable is an asset, increasing it requires a debit entry.
The Credit Entry: Sales Revenue
Simultaneously, the sale itself increases the company's revenue. Revenue is part of equity (specifically, retained earnings), and increases in revenue are recorded as credits. Therefore, a credit entry is made to the Sales Revenue account.
Example: Recording a Sale on Account
Let's illustrate with a concrete example. Suppose ABC Company sells $1,000 worth of goods to a customer, XYZ Corp., on account. The journal entry would be:
| Date | Account Name | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oct 26, 2024 | Accounts Receivable | $1,000 | |
| Sales Revenue | $1,000 | ||
| To record sale on account to XYZ Corp. |
This entry increases the Accounts Receivable (asset) by $1,000 and increases Sales Revenue (equity) by $1,000, maintaining the balance of the accounting equation.
The Importance of Accurate Recording
Accurate recording of sales on account is vital for several reasons:
- Financial Reporting: Accurate records are crucial for generating reliable financial statements, including the income statement and balance sheet. Inaccurate recording can lead to misstated revenue and assets.
- Credit Management: Tracking Accounts Receivable allows businesses to monitor outstanding payments and manage credit risk effectively. This includes identifying customers who are consistently late with payments or those with a high risk of default.
- Cash Flow Forecasting: Accurate accounts receivable data is essential for predicting future cash inflows. This helps in making informed decisions about budgeting, investments, and operational expenses.
- Debt Collection: Properly recorded accounts receivable data streamlines the debt collection process. It facilitates timely follow-ups with customers and the efficient management of outstanding invoices.
- Tax Compliance: Accurate accounting records are essential for filing accurate tax returns. Misreporting revenue can lead to significant penalties and legal issues.
Other Considerations When Recording Sales on Account
While the basic journal entry is straightforward, several other factors can influence the recording process:
Sales Taxes
In many jurisdictions, sales taxes are levied on sales transactions. When sales are made on account, the sales tax must be recorded separately. This typically involves crediting a "Sales Tax Payable" account.
Example with Sales Tax:
Assume a 6% sales tax rate on the $1,000 sale to XYZ Corp. The journal entry would be:
| Date | Account Name | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oct 26, 2024 | Accounts Receivable | $1,060 | |
| Sales Revenue | $1,000 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable | $60 | ||
| To record sale on account to XYZ Corp. including sales tax |
Discounts
Businesses may offer discounts to customers for early payment (e.g., a 2/10, n/30 discount). These discounts need to be accounted for at the time of payment, not when the sale is initially recorded. If the discount is taken, a reduction in Accounts Receivable and a debit to Sales Discounts are recorded.
Bad Debts
Not all accounts receivable will be collected. Businesses need to account for the possibility of bad debts (uncollectible accounts). This is typically done through an allowance for doubtful accounts, which is a contra-asset account that reduces the net realizable value of accounts receivable.
Sales Returns and Allowances
If a customer returns goods or receives an allowance for damaged goods, the Accounts Receivable balance needs to be adjusted. This involves debiting Sales Returns and Allowances and crediting Accounts Receivable.
Using Accounting Software
Modern accounting software simplifies the process of recording sales on account. Most systems automatically generate the necessary journal entries based on the invoice data entered. Features like automated invoicing, accounts receivable management, and reporting tools significantly streamline the process and reduce the risk of errors. However, a fundamental understanding of the underlying accounting principles remains essential for effective use and interpretation of the software's output.
Reconciling Accounts Receivable
Regularly reconciling accounts receivable is crucial to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies. This involves comparing the balance in the Accounts Receivable account with the amounts owed by customers, as reflected in individual customer invoices and payment records. Any discrepancies need to be investigated and resolved promptly.
Analyzing Accounts Receivable Turnover
The Accounts Receivable Turnover ratio is a key performance indicator that measures how efficiently a company is collecting its receivables. It indicates the number of times, on average, that accounts receivable are collected during a period. A high turnover ratio suggests efficient credit management, while a low ratio could indicate problems with collecting payments.
Impact on Financial Statements
Sales on account directly impact both the income statement and the balance sheet:
- Income Statement: Sales revenue is reported on the income statement, reflecting the increase in revenue generated from credit sales. Any sales discounts or returns are also reflected in the income statement, reducing the net sales revenue.
- Balance Sheet: Accounts Receivable is reported as a current asset on the balance sheet, representing the amount of money owed to the company by its customers. The allowance for doubtful accounts will reduce the reported value of accounts receivable.
Conclusion: Mastering the Debit Entry for Sales on Account
Understanding the debit entry for sales on account is fundamental to accurate financial reporting and effective business management. By correctly recording these transactions and diligently managing accounts receivable, businesses can ensure financial stability, improve cash flow, and make informed decisions based on reliable financial data. This detailed guide provides a solid foundation for managing sales on account and maintaining accurate financial records. Remember, while accounting software can automate much of the process, a thorough grasp of the underlying principles remains critical for sound financial management. Continuously review and update your understanding of accounting practices to adapt to changes in business environments and regulations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Adhd Is A Disorder That Is Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Statement Concerning Rare Threatened Or Endangered Species Is True
Mar 31, 2025
-
Defining Research With Human Subjects Citi Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Company Sold A Machine For 15000 Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Congress Passed The Domestic Violence Act In Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about To Record A Sale On Account The Company Should Debit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
