What Action By The Nurse Best Encompasses The Preoperative Phase
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
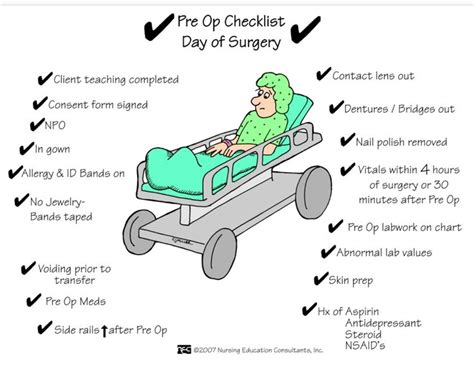
Table of Contents
What Actions by the Nurse Best Encompass the Preoperative Phase?
The preoperative phase, the period between a patient's decision to undergo surgery and the actual procedure, is a critical time requiring meticulous attention to detail and comprehensive nursing care. A nurse's actions during this phase directly impact the patient's safety, comfort, and overall surgical outcome. This article will delve into the multifaceted role of the nurse in the preoperative phase, highlighting key actions that ensure a smooth and successful surgical experience.
Assessment: The Cornerstone of Preoperative Care
The preoperative assessment forms the bedrock of effective nursing intervention. A thorough assessment encompasses several key areas:
Medical History:
-
Identifying Risk Factors: The nurse meticulously reviews the patient's medical history, identifying potential risk factors that could complicate the surgery or recovery. This includes allergies (especially medication allergies!), previous surgical experiences, chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, respiratory issues, and bleeding disorders. Detailed documentation is paramount. Any family history of malignant hyperthermia or adverse reactions to anesthesia should be noted.
-
Current Medications: A complete list of current medications, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, is crucial. Many medications can interact negatively with anesthetics or impact the surgical outcome. This information should be clearly communicated to the anesthesiologist.
-
Review of Systems: A systematic review of each body system helps identify any existing problems that might be exacerbated by surgery or anesthesia. This includes assessing cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, gastrointestinal, renal, and integumentary systems.
Psychological Assessment:
-
Anxiety and Fear Management: Surgery is often a stressful event. The nurse assesses the patient's level of anxiety and fear, employing active listening and empathetic communication to address concerns. Providing clear, concise explanations about the procedure and postoperative expectations can significantly alleviate anxiety. Referral to a psychologist or social worker might be necessary in cases of significant anxiety.
-
Understanding Patient Expectations: Understanding the patient's expectations about the surgery, recovery, and outcomes is crucial. Addressing any misconceptions and managing unrealistic expectations proactively is vital.
Physical Assessment:
-
Baseline Vital Signs: Accurate recording of vital signs (temperature, pulse, blood pressure, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation) provides a baseline for comparison post-operatively. Any abnormalities should be reported to the surgeon and anesthesiologist.
-
Nutritional Status: The nurse assesses the patient's nutritional status, as proper nutrition is essential for healing. Patients with malnutrition may require nutritional supplementation before surgery.
-
Skin Assessment: Careful examination of the skin, particularly at the surgical site, helps identify any potential infections or skin breakdown. This is crucial to prevent postoperative wound complications.
-
Respiratory Assessment: Assessment of respiratory function, including lung sounds and respiratory effort, is critical, especially for patients with pre-existing respiratory conditions. This helps determine the need for pre-operative pulmonary hygiene measures, such as deep breathing exercises and incentive spirometry.
-
Cardiovascular Assessment: Thorough assessment of the cardiovascular system, including heart rate, rhythm, blood pressure, and peripheral pulses, helps identify potential cardiovascular risks and guide appropriate interventions.
Preoperative Teaching: Empowering the Patient
Effective preoperative teaching empowers the patient and facilitates a smoother recovery. This includes:
Surgical Procedure Explanation:
-
Clear and Concise Information: The nurse provides clear and concise explanations of the surgical procedure, including its purpose, the anticipated duration, and potential risks and benefits. Using simple, non-medical jargon is essential.
-
Addressing Patient Concerns: The nurse patiently addresses all patient concerns and questions, fostering a sense of trust and collaboration.
Postoperative Care Instructions:
-
Pain Management: The nurse explains the different methods of pain management available post-operatively, encouraging patients to communicate their pain levels effectively.
-
Mobility and Deep Breathing Exercises: Teaching deep breathing exercises, coughing techniques, and leg exercises helps prevent respiratory and circulatory complications.
-
Wound Care: The nurse provides instructions on wound care, emphasizing the importance of keeping the wound clean and dry.
-
Dietary Restrictions: The nurse explains any necessary dietary restrictions before and after surgery, such as NPO (nothing by mouth) status before the procedure.
-
Medication Regimen: The nurse provides clear instructions on any postoperative medications, including their purpose, dosage, and potential side effects.
Preoperative Preparation: Ensuring Safety and Comfort
Preoperative preparation involves several crucial actions:
Informed Consent:
-
Verification and Witnessing: The nurse verifies that the patient has received and understands the information provided in the informed consent form and witnesses the patient's signature. It's vital to ensure the patient is fully alert and capable of making informed decisions.
-
Addressing Patient Questions: The nurse should address any remaining questions or concerns about the informed consent process.
Hygiene and Skin Preparation:
-
Showering and Hygiene: The nurse guides the patient in following appropriate hygiene protocols, such as showering with antiseptic soap, to reduce the risk of infection.
-
Hair Removal: If necessary, the nurse assists with hair removal at the surgical site, using appropriate techniques to minimize skin irritation and infection risk.
Bowel and Bladder Preparation:
-
Bowel Preparation: If required by the surgical procedure, the nurse assists with bowel preparation using prescribed laxatives or enemas.
-
Bladder Emptying: Ensuring the bladder is emptied before surgery is crucial to prevent bladder injury.
Prophylactic Measures:
-
Prophylactic Antibiotics: The nurse may administer prophylactic antibiotics as prescribed by the surgeon to reduce the risk of postoperative infection.
-
Anticoagulants: The nurse may administer prophylactic anticoagulants to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Documentation: A Critical Component
Meticulous documentation throughout the preoperative phase is essential for legal and medical reasons. The nurse meticulously documents:
-
Assessment Findings: All assessment findings, including medical history, physical examination results, and psychological status, are accurately documented.
-
Preoperative Teaching: Documentation of preoperative teaching confirms that the patient received the necessary information.
-
Informed Consent: Documentation confirms that informed consent was obtained, including the date, time, and witness signature.
-
Preoperative Medications: Accurate documentation of any administered pre-operative medications, including the dosage, route, and time of administration, is vital.
-
Any Abnormalities: Any abnormalities detected during the assessment should be promptly reported and documented, along with any interventions taken.
Collaboration and Communication: A Team Effort
Effective communication and collaboration with the surgical team, including the surgeon, anesthesiologist, and other healthcare professionals, are crucial for optimal patient care. The nurse:
-
Communicates Assessment Findings: The nurse accurately communicates all assessment findings to the surgical team.
-
Collaborates on Treatment Plan: The nurse actively participates in developing and implementing the preoperative treatment plan.
-
Addresses Concerns and Questions: The nurse addresses any concerns or questions raised by the surgical team.
-
Maintains Open Communication with Patient and Family: The nurse maintains open communication with the patient and their family, addressing their anxieties and providing emotional support.
Beyond the Basics: Addressing Specific Needs
The preoperative phase is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Nurses must adapt their actions to meet the specific needs of each patient, considering factors like:
-
Age: Elderly patients may require more extensive assessment and individualized care due to increased susceptibility to complications.
-
Cognitive Impairment: Patients with cognitive impairment may require simplified explanations and modified teaching strategies.
-
Cultural Considerations: The nurse respects the patient's cultural beliefs and practices while providing care.
-
Language Barriers: Appropriate interpreters should be used when dealing with patients with language barriers.
In conclusion, the nurse's role in the preoperative phase is multifaceted and crucial for the patient's safety and well-being. From meticulous assessment and thorough teaching to diligent preparation and seamless collaboration, every action taken by the nurse contributes to a successful surgical outcome. The unwavering commitment to comprehensive care, individualized attention, and exceptional communication defines the nurse’s contribution to this critical phase of the surgical journey. The depth of this involvement underscores the vital role of nursing in optimizing patient care and ensuring the best possible results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Pharmacology Made Easy 4 0 The Neurological System Part 2
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Sentence Best Describes The Logic Of Scientific Inquiry
Mar 22, 2025
-
Liability For Illegal Alcohol Sales Can Be
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Does The Term New Woman Mean
Mar 22, 2025
-
Empareja Cada Pregunta Con Su Respuesta Correcta Y Logica
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Action By The Nurse Best Encompasses The Preoperative Phase . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
