What Is Abraham Maslow Best Known For Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
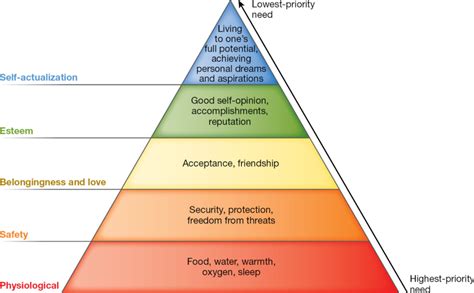
Table of Contents
What is Abraham Maslow Best Known For? A Deep Dive into His Hierarchy of Needs
Abraham Maslow, a prominent figure in humanistic psychology, is best known for his hierarchy of needs. This influential theory, often depicted as a pyramid, profoundly impacted various fields, from psychology and business to education and self-improvement. While Maslow's work encompassed a broader range of topics, his hierarchy remains his most enduring and recognizable contribution. This article will explore the nuances of Maslow's hierarchy, delve into its applications, examine criticisms levied against it, and ultimately answer the question: what is Abraham Maslow best known for?
Understanding Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's hierarchy proposes that human needs are arranged in a five-tiered pyramid, with basic physiological needs forming the foundation and self-actualization at the apex. Individuals must satisfy lower-level needs before progressing to higher ones. Let's break down each level:
1. Physiological Needs: These are the most fundamental requirements for human survival. They include:
- Air: The necessity of breathing for survival.
- Water: Essential for bodily functions.
- Food: Providing energy and nutrients.
- Shelter: Protection from the elements.
- Sleep: Crucial for physical and mental restoration.
- Homeostasis: Maintaining a stable internal environment.
Without these basic needs met, an individual's focus will primarily be on securing them, making higher-level needs largely unattainable.
2. Safety Needs: Once physiological needs are adequately addressed, safety needs come into focus. These include:
- Personal Security: Freedom from violence and threats.
- Financial Security: Stability and resources for the future.
- Health and Well-being: Protection from illness and injury.
- Property: Ownership and protection of possessions.
A sense of security provides a foundation for psychological growth and allows individuals to move towards fulfilling higher-order needs.
3. Love and Belonging Needs: These needs relate to our innate desire for connection and social acceptance. This level encompasses:
- Friendship: Developing meaningful relationships with others.
- Family: Creating and maintaining strong family bonds.
- Intimacy: Developing close, personal relationships.
- Sense of connection: Feeling part of a community or group.
The absence of love and belonging can lead to feelings of loneliness, isolation, and depression.
4. Esteem Needs: Once social needs are met, individuals strive for esteem, which is comprised of two components:
- Self-esteem: Confidence, achievement, independence, and freedom.
- Respect from others: Recognition, appreciation, and status.
Achieving esteem boosts self-confidence and motivates further personal growth.
5. Self-Actualization Needs: This is the pinnacle of Maslow's hierarchy. Self-actualization refers to the realization of one's full potential and the pursuit of personal growth. It involves:
- Creativity: Expressing oneself through art, innovation, or other creative pursuits.
- Problem-solving: Approaching challenges with a sense of purpose and ingenuity.
- Acceptance of facts: Facing reality objectively and without denial.
- Spontaneity: Embracing authenticity and expressing oneself freely.
- Autonomy: Self-governance and independence.
Self-actualized individuals are often characterized by their deep understanding of themselves, their compassion for others, and their pursuit of a meaningful life.
Applications of Maslow's Hierarchy
Maslow's hierarchy has found widespread application across various disciplines.
In Business: Understanding employee needs is crucial for fostering a productive and engaged workforce. By addressing employees' physiological needs (fair wages, safe working conditions), safety needs (job security, benefits), love and belonging needs (teamwork, social events), esteem needs (recognition, promotion opportunities), and self-actualization needs (challenging work, opportunities for growth), organizations can enhance motivation and job satisfaction.
In Education: Educators can utilize the hierarchy to understand students' needs and tailor their teaching methods accordingly. Addressing basic needs like hunger and safety creates a learning environment where students can focus on academics and personal growth. Fostering a sense of belonging and encouraging self-esteem can improve student engagement and academic performance.
In Marketing: Marketers can use Maslow's hierarchy to target consumer needs and create effective marketing campaigns. For instance, advertising that emphasizes safety and security (e.g., home security systems) appeals to a different consumer segment than advertising that focuses on self-actualization (e.g., luxury travel experiences).
Criticisms of Maslow's Hierarchy
Despite its widespread influence, Maslow's hierarchy has faced several criticisms:
- Lack of Empirical Evidence: Critics argue that there's insufficient empirical evidence to fully support the hierarchical structure. Individuals may prioritize needs differently depending on their circumstances and cultural background.
- Cultural Bias: The hierarchy reflects a Western, individualistic perspective. Collectivist cultures may prioritize social needs over individual needs.
- Oversimplification: The hierarchy simplifies the complexity of human motivation. Needs are often intertwined and not always sequentially fulfilled.
- Difficulty in Measurement: Precisely measuring the degree to which an individual has satisfied each level is challenging.
Maslow's Other Contributions
While the hierarchy of needs is his most famous work, Maslow's contributions extend beyond this single theory. He also explored concepts such as:
- Self-Transcendence: A stage beyond self-actualization where individuals focus on helping others and contributing to something larger than themselves.
- Peak Experiences: Moments of intense joy, wonder, and fulfillment.
- Metamotivation: The motivation of self-actualized individuals, driven by intrinsic values and a desire for personal growth, contrasting with the deficiency-based motivations of lower levels.
Conclusion: What is Abraham Maslow Best Known For?
In conclusion, Abraham Maslow is best known for his hierarchy of needs, a groundbreaking theory that continues to influence various fields. While criticisms exist, the enduring impact of his work on our understanding of human motivation and personal growth is undeniable. His insightful exploration of human needs, from the most basic physiological requirements to the pinnacle of self-actualization, provides a valuable framework for understanding human behavior and fostering personal development. His legacy extends beyond the hierarchy, encompassing broader concepts that continue to enrich our understanding of the human condition. Therefore, while he contributed to several areas within psychology, it's his hierarchy of needs that has cemented his place as one of the most influential figures in humanistic psychology. Understanding Maslow's work is crucial for anyone interested in human motivation, personal growth, and the pursuit of a fulfilling life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Can Be Controlled By Copyright
Mar 25, 2025
-
An Organism That Is Eaten By Another Organism
Mar 25, 2025
-
Managers Who Redo Budgets Rethink Processes Or Revise Policies Are
Mar 25, 2025
-
Today Patients With Cystic Fibrosis Are Surviving To
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Best Explains The Evolution Of Gymnosperm Plants
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Abraham Maslow Best Known For Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
