What Is Meant By Light Rays Being Divergent
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
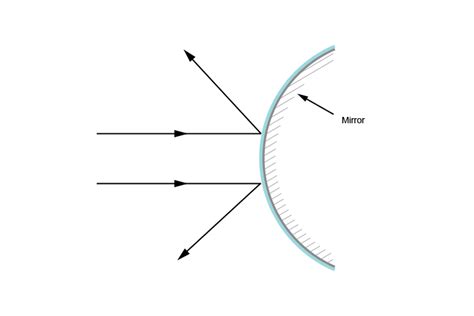
Table of Contents
What is Meant by Light Rays Being Divergent?
Divergent light rays, also known as diverging rays or diverging beams, describe a beam of light where the rays spread outwards from a common point. Understanding this fundamental concept in optics is crucial for grasping how lenses, mirrors, and the human eye function. This article delves deep into the nature of divergent light, exploring its origins, properties, and applications across various optical systems.
Understanding the Nature of Divergent Light Rays
Imagine a light source, like a light bulb. Light emanates from this source in all directions. These light rays, originating from a single point, move outwards, gradually spreading apart. This spreading phenomenon is precisely what defines divergent light. Unlike parallel rays, which travel in a straight line without spreading, divergent rays progressively increase their separation as they propagate.
The Point Source and its Significance
The key characteristic of divergent light is its origin from a point source. This point source doesn't necessarily have to be infinitesimally small; it can be a relatively small light emitting area from which rays appear to diverge. The apparent divergence is more pronounced when the source is smaller relative to the distance the light travels. Consider a flashlight: while the bulb itself isn't a perfect point source, the light emerging from its aperture appears to diverge as it travels into the surrounding space.
Contrast with Convergent and Parallel Rays
To fully grasp divergent light, it's essential to compare it with its counterparts: convergent and parallel rays.
- Convergent Rays: These rays converge towards a single point, typically after interacting with a converging lens or mirror. They effectively "come together."
- Parallel Rays: These rays travel in the same direction, maintaining a constant distance between them. They don't spread or converge. This is an idealized condition often used in theoretical optics, and is approximated in practice using collimating lenses.
The Origin of Divergent Light
Divergent light rays primarily originate from:
- Point sources: Any light source that can be approximated as a point emits divergent light. This includes incandescent bulbs, LEDs, and even the sun (though at very long distances, sunlight can appear almost parallel).
- Scattering: When light interacts with a rough surface, it scatters in various directions, resulting in divergent light. This is why you can see light reflected from a piece of paper from many angles.
- Refraction: Light passing from a denser medium to a rarer medium (e.g., from water to air) can diverge depending on the angles of incidence and refraction. This is often seen when light passes from a fish tank into the air.
- Diffraction: When light passes through a small aperture or around an obstacle, it bends, resulting in a diverging beam. This phenomenon is a key component of wave optics.
How Divergent Light Affects Optical Systems
Understanding how divergent light interacts with optical elements like lenses and mirrors is critical in designing and analyzing optical systems.
Interaction with Converging Lenses
When divergent light rays encounter a converging lens, the lens attempts to converge these rays. However, the resulting image is virtual and upright, meaning it appears to be behind the lens rather than formed on a screen. The lens effectively reduces the divergence, but doesn't completely eliminate it unless the rays originate from the lens's focal point.
Interaction with Diverging Lenses
A diverging lens further increases the divergence of already spreading light rays. The light rays emerge from a diverging lens even more spread out than they were before. This results in a virtual, diminished, and upright image.
Interaction with Mirrors
Similar principles apply to mirrors. A concave mirror (converging mirror) will attempt to converge divergent rays, forming a real or virtual image depending on the object's distance from the mirror. A convex mirror (diverging mirror) will reflect the divergent rays, further increasing their divergence, and always producing a virtual, diminished, and upright image.
Applications of Divergent Light
Despite often being treated as a challenge in imaging systems, divergent light plays a crucial role in several applications:
- Illumination: Many lighting systems utilize divergent light sources to spread illumination over a wide area. Flashlights, streetlights, and room lighting are all examples of this. The design of the reflector and lens system controls the extent of the divergence.
- Holography: Holography relies on the interference patterns created by coherent (typically laser) divergent beams to record a three-dimensional image.
- Optical Fiber Communication: While focused light is guided within the fiber core, some divergence inevitably occurs at the input and output ends.
- Microscopy: Specialized microscopes utilize techniques that deal with divergent light to achieve high resolution.
- Laser Scanning: In some laser scanning systems, intentionally divergent beams are used to cover larger areas quickly.
Measuring and Controlling Divergence
The extent of divergence is often quantified by the divergence angle. This angle is the angle between the outermost rays of the beam. A smaller divergence angle indicates a more collimated beam. The divergence angle can be affected by factors like the source size, wavelength of light, and the optical elements used to shape the beam.
Methods for controlling divergence include:
- Collimating lenses: These lenses are used to reduce the divergence of a light beam, making it more parallel.
- Apertures: By restricting the beam's diameter, you can indirectly control divergence. A smaller aperture reduces divergence, while a larger aperture increases it.
- Spatial filters: These filters remove unwanted light rays, effectively reducing the beam's divergence.
Divergence in the Human Eye
The human eye itself deals with divergent light. Objects at different distances produce light rays with varying degrees of divergence. The eye's lens adjusts its focal length through a process called accommodation, allowing it to focus both near and distant objects by converging these divergent rays onto the retina. Problems with the eye's focusing mechanism (e.g., myopia, hyperopia) are directly related to the eye's ability to correctly handle divergent light.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
The concept of divergent light extends to various advanced topics in optics, including:
- Gaussian beam propagation: This describes the propagation of a laser beam, which is inherently divergent, using Gaussian functions.
- Diffraction theory: This provides a more rigorous description of how light spreads out due to diffraction phenomena.
- Non-imaging optics: This field deals with efficiently transferring light energy without creating a well-defined image, often using reflective surfaces to manage divergent light.
- Adaptive optics: This technique is used to correct for atmospheric turbulence that causes divergence in astronomical observations.
Conclusion
Understanding divergent light is fundamental to comprehending various aspects of optics, from basic illumination to complex imaging systems. This article provided a comprehensive overview of divergent light, covering its origin, properties, interaction with optical components, and practical applications. By mastering this concept, one gains a significant foundation in the fascinating world of optics and its vast implications across science and technology. Further exploration into the advanced topics mentioned above will lead to a deeper and more nuanced understanding of this crucial optical phenomenon.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Quickly Should You Move During Resistance Training
Mar 15, 2025
-
Hazmat Familiarization And Safety In Transportation Module 04 Exam
Mar 15, 2025
-
Creating Two Departments And Placing One Manager Over Each
Mar 15, 2025
-
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Anki Deck Dirty Medicine
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Statement Accurately Describes The Inner Planets
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Meant By Light Rays Being Divergent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
