What Is The Bitrate Of A System
Breaking News Today
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
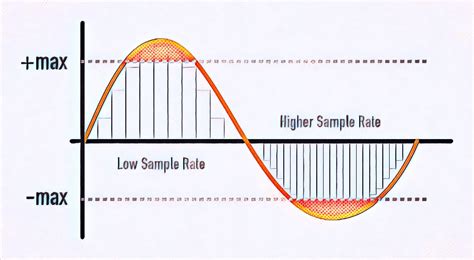
Table of Contents
What is the Bitrate of a System? A Deep Dive into Data Transfer Rates
Understanding bitrate is crucial for anyone working with digital data, whether you're a gamer, video editor, audiophile, or network engineer. It's a fundamental concept that dictates the quality and efficiency of digital transmission and storage. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of bitrate, exploring its meaning, how it's measured, its impact on various systems, and the common misconceptions surrounding it.
Understanding the Basics: What is Bitrate?
Simply put, bitrate refers to the rate at which data is transferred or processed. It's measured in bits per second (bps), indicating the number of bits transmitted or processed within a single second. Higher bitrates generally translate to higher quality, but also demand more bandwidth and storage space.
Think of it like a water pipe: a larger pipe (higher bitrate) allows more water (data) to flow through per second, while a smaller pipe (lower bitrate) restricts the flow. This analogy helps visualize the impact of bitrate on various applications.
Key Differences: Bitrate vs. Bandwidth
While often used interchangeably, bitrate and bandwidth are distinct concepts. Bandwidth refers to the capacity of a communication channel, representing the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted within a given time. Bitrate, on the other hand, is the actual rate of data transfer occurring at a specific moment. A system can have a high bandwidth but a low bitrate if the data transfer is inefficient or if the source is limited.
Think of bandwidth as the size of the highway, and bitrate as the speed of the cars driving on it. A wide highway (high bandwidth) can support many fast cars (high bitrate), but it can also support a low number of slow cars (low bitrate).
Bitrate in Different Contexts:
Bitrate’s importance varies across different applications. Let's explore its impact in key areas:
1. Audio Bitrate: The Sound of Quality
In audio, bitrate determines the fidelity and quality of sound reproduction. Higher bitrates result in richer, more detailed sound with a wider dynamic range. Lower bitrates often lead to compression artifacts, such as a loss of clarity, and a reduction in the overall quality of the audio. Common audio bitrates include:
- Low Bitrate (e.g., 64 kbps): Suitable for podcasts or applications where storage space or bandwidth is severely limited. Audio quality is significantly compressed.
- Medium Bitrate (e.g., 128-192 kbps): A reasonable compromise between quality and file size. Suitable for most casual listening scenarios.
- High Bitrate (e.g., 256 kbps and above): Offers superior sound quality, approaching near lossless audio. Ideal for audiophiles and professional applications.
- Lossless Audio (e.g., FLAC, WAV): These formats maintain the original audio data without any compression, resulting in the highest possible fidelity but significantly larger file sizes. They typically have variable bitrates depending on the complexity of the audio.
2. Video Bitrate: The Visual Feast
Video bitrate plays a crucial role in determining the video quality, especially in terms of resolution, color depth, and motion clarity. High bitrate videos offer sharper images, smoother motion, and vibrant colors. Lower bitrates might lead to pixelation, blockiness, and artifacts, particularly noticeable during fast-paced scenes.
The required bitrate for video is heavily influenced by:
- Resolution: Higher resolutions (e.g., 4K) require significantly higher bitrates than lower resolutions (e.g., 720p).
- Frame Rate: Higher frame rates (e.g., 60fps) demand more data to be processed and transmitted, leading to a higher bitrate requirement.
- Encoding Method: Different video codecs (e.g., H.264, H.265/HEVC) have varying compression efficiencies. More efficient codecs can achieve higher quality at lower bitrates.
- Complexity of the Scene: Scenes with rapid motion or detailed textures need higher bitrates to maintain quality.
Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing video encoding settings to achieve a balance between quality and file size.
3. Network Bitrate: The Backbone of Connectivity
In networking, bitrate signifies the speed at which data travels across a network connection, such as your internet connection or local area network (LAN). It directly impacts the speed of downloads, uploads, streaming, and online gaming. Network bitrates are often expressed in:
- Kbps (kilobits per second): Used for slower connections.
- Mbps (megabits per second): Common for broadband internet connections.
- Gbps (gigabits per second): Used for high-speed connections like fiber optics.
The advertised bitrate of your internet connection is usually the maximum rate achievable under ideal conditions. Actual speeds can be lower due to network congestion, distance from the server, and various other factors.
4. Storage Bitrate: The Capacity Conundrum
While not directly referred to as "bitrate" in the context of storage, the concept is fundamentally the same: the rate at which data can be read or written. Fast storage devices (SSDs) boast higher bitrates than slower ones (HDDs), allowing for faster data access and transfer speeds. The performance difference between these storage technologies directly impacts the speed of applications and overall system responsiveness.
Calculating and Measuring Bitrate:
Calculating bitrate involves dividing the amount of data (in bits) by the time (in seconds) taken to transfer or process it. The formula is simple:
Bitrate = Data (bits) / Time (seconds)
For example, if 10 megabytes of data are transferred in 10 seconds, the bitrate can be calculated as follows:
- 1 megabyte = 8 megabits
- 10 megabytes = 80 megabits = 80,000,000 bits
- Bitrate = 80,000,000 bits / 10 seconds = 8,000,000 bps = 8 Mbps
However, in practice, measuring bitrate isn't always straightforward. Specialized tools and software are often required for accurate measurements of audio, video, and network bitrates. These tools provide real-time analysis of data transfer rates, allowing for efficient monitoring and optimization of various systems.
Common Misconceptions About Bitrate:
Several misconceptions surround the concept of bitrate. Let's clarify some of them:
- Higher Bitrate Always Equals Better Quality: While generally true, this isn't always the case. Poorly compressed high-bitrate audio or video might still sound or look bad. The encoding method and the source material also heavily influence the final quality.
- Bitrate is the Only Factor Determining Quality: Many factors influence the final quality, including compression algorithms, resolution, and source material. Bitrate is just one piece of the puzzle.
- All Systems Have the Same Bitrate: Different systems have different capabilities and limitations, leading to varying bitrates. The bitrate of your internet connection, for example, will differ significantly from that of a high-end audio interface.
Optimizing Bitrate for Your Needs:
Optimizing bitrate involves finding the right balance between quality and efficiency. Consider the following factors:
- Intended Use: Are you creating a high-quality video for professional purposes, or a casual video for social media?
- Storage Space: How much storage space do you have available?
- Bandwidth: What is the bandwidth capacity of your network?
- Target Devices: Consider the capabilities of the devices that will be used to play the audio or video.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select an appropriate bitrate that delivers the desired quality without unnecessary resource consumption.
Conclusion: Bitrate – A Critical Component of Digital Systems
Bitrate is a fundamental concept in the digital world, impacting the quality, efficiency, and performance of various systems. Understanding its meaning, how it's measured, and its influence on different applications is crucial for anyone dealing with digital data. By optimizing bitrate for your specific needs, you can ensure high-quality output without compromising on efficiency or resource utilization. Remember that bitrate is only one factor in achieving optimal digital performance; always consider other aspects of your system for a holistic approach.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Water Food And Sleep Are Examples Of
Apr 04, 2025
-
When Writers Use Long Paragraphs In Business Messages It
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Safest Technique Used For Steering Wheel Control Is
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Indication For Mouth To Mouth Rescue Breaths
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Quienes Les Escribiste Las Postales A Ellos
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Bitrate Of A System . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
