What Is The Function Of The Blood Testis Barrier Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 7 min read
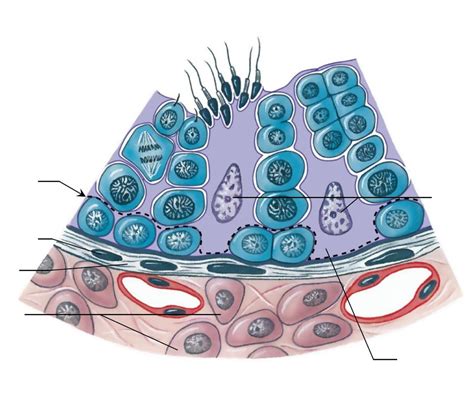
Table of Contents
What is the Function of the Blood-Testis Barrier? A Comprehensive Guide
The blood-testis barrier (BTB) is a crucial structure within the testes, playing a vital role in male fertility and reproductive health. Its primary function is to protect developing germ cells (spermatogonia, spermatocytes, spermatids, and spermatozoa) from the body's immune system and maintain a unique testicular microenvironment. This intricate barrier isn't just a physical wall; it's a dynamic system that adapts and changes throughout spermatogenesis, the process of sperm production. Understanding its intricacies is paramount to comprehending male reproductive biology and the implications of its dysfunction.
The Anatomy of the Blood-Testis Barrier
The BTB is a complex structure composed of several key components working in concert:
1. Sertoli Cells: The Foundation of the Barrier
Sertoli cells are the cornerstone of the BTB. These specialized somatic cells are found within the seminiferous tubules, the site of spermatogenesis. They are interconnected by tight junctions, forming the primary physical barrier that prevents the free passage of molecules and cells between the blood and the seminiferous tubules. These tight junctions are highly regulated and dynamic, exhibiting plasticity in response to hormonal and environmental changes. They are not static structures; they dynamically rearrange to allow for the transit of developing germ cells as they mature. This dynamic regulation is crucial for the proper functioning of the barrier.
2. Tight Junction Proteins: The Gatekeepers
The tight junctions themselves are composed of numerous transmembrane proteins, including claudins, occludins, and junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs). These proteins interact to create a selective seal, controlling what substances can pass through the barrier. The specific composition and organization of these proteins dictate the permeability of the BTB and contribute to its unique properties. Research continues to unravel the precise roles of individual tight junction proteins in BTB function and its regulation.
3. Basal and Adluminal Compartments: Creating Distinct Microenvironments
The BTB divides the seminiferous epithelium into two distinct compartments:
- Basal Compartment: This region lies between the basement membrane of the seminiferous tubules and the tight junctions. It houses spermatogonia, the stem cells that give rise to all other germ cells.
- Adluminal Compartment: This compartment, located inside the tight junctions, is where the meiotic and post-meiotic germ cells (spermatocytes, spermatids, and spermatozoa) develop. This secluded environment is essential for the specialized processes of meiosis and spermiogenesis. The unique composition of this compartment, shielded by the BTB, is crucial for the maturation of sperm cells.
4. Peritubular Myoid Cells: Support and Contractility
While not a direct component of the tight junctions, peritubular myoid cells play a vital supporting role. These cells surround the seminiferous tubules and contribute to the structural integrity of the BTB. Their contractile properties help regulate blood flow and fluid movement within the testes, influencing the overall testicular environment and supporting the function of the barrier.
The Functions of the Blood-Testis Barrier: Protecting and Nurturing Spermatogenesis
The BTB serves several crucial functions, all aimed at ensuring successful spermatogenesis:
1. Immune Privilege: Protecting Developing Germ Cells
The most critical function of the BTB is to prevent the immune system from attacking developing germ cells. During meiosis, germ cells undergo significant genetic changes, expressing novel proteins that the immune system could recognize as foreign. Without the BTB, these haploid cells would be targeted and destroyed by the body's immune defenses, resulting in infertility. The BTB's immune privilege is not absolute; certain immune cells are present, but they play a role in immune tolerance rather than immune attack. The balance of immune cells within the testes is critical to the proper functioning of the BTB.
2. Maintaining a Specialized Microenvironment: Optimal Conditions for Spermatogenesis
The BTB creates a unique environment within the adluminal compartment, crucial for successful spermatogenesis. This compartment maintains specific concentrations of hormones, nutrients, and growth factors essential for the various stages of sperm development. For example, the concentration of testosterone and other factors are meticulously regulated within this space. Any disruption in this delicate balance can have dire consequences for sperm production. This carefully controlled microenvironment is essential for germ cell differentiation and maturation.
3. Selective Transport: Providing Necessary Substances
The BTB is not an impenetrable wall; it allows the selective passage of specific molecules needed for spermatogenesis. This transport is highly regulated, involving various carrier proteins and channels embedded in the Sertoli cell membranes. Essential nutrients, hormones, and growth factors are actively transported across the barrier, while potentially harmful substances are excluded. This controlled transport system is essential for the support and nourishment of the developing germ cells.
4. Preventing the Escape of Antigens: Maintaining Systemic Immune Tolerance
The BTB prevents the release of antigens from the seminiferous tubules into the bloodstream. This prevents the immune system from being exposed to potentially immunogenic materials, such as germ cell-specific proteins, which could trigger an autoimmune response. The barrier's role in maintaining systemic immune tolerance is vital for preventing autoimmune disorders targeting the male reproductive system. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for managing autoimmune infertility.
Dysfunction of the Blood-Testis Barrier: Implications for Male Infertility
Disruptions to the integrity of the BTB can lead to several issues, often resulting in male infertility:
1. Autoimmune Infertility: Attack on Germ Cells
Breaches in the BTB can expose the immune system to developing germ cells, triggering an autoimmune response. Autoantibodies target these cells, causing damage and impairing spermatogenesis. This can lead to reduced sperm count, poor sperm quality, or even complete azoospermia (absence of sperm in semen). Autoimmune responses are a significant cause of infertility, highlighting the crucial role of the BTB in protecting developing germ cells.
2. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Damaging the Testicular Environment
Inflammation within the testes can disrupt the integrity of the BTB, leading to further damage. This can be triggered by infections, trauma, or other factors. Oxidative stress, an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body's ability to neutralize them, can also compromise the barrier's function and harm developing germ cells. The delicate balance within the testes is readily disrupted, leading to substantial issues in fertility.
3. Environmental Factors: Toxins and Exposure
Exposure to environmental toxins and pollutants can negatively impact the BTB's integrity. Certain chemicals can disrupt the function of tight junction proteins, weakening the barrier and increasing its permeability. This compromises the barrier's protective function and can expose germ cells to harmful substances. Research continues to identify environmental factors that impact male reproductive health and the BTB.
4. Genetic Factors: Inherited Conditions
Genetic mutations affecting the genes encoding BTB components, such as claudins and occludins, can lead to congenital defects in the barrier's structure and function. These genetic conditions can result in infertility or other reproductive problems. Understanding the genetic basis of BTB dysfunction is critical for developing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research focuses on several key areas related to the BTB:
- Identifying novel BTB-associated proteins: Discovering and characterizing new proteins involved in BTB structure and function will provide a deeper understanding of its mechanisms.
- Investigating the regulation of BTB permeability: Exploring the molecular mechanisms that regulate the opening and closing of the BTB during spermatogenesis is crucial.
- Developing therapies to restore BTB integrity: Research aims to develop treatments that can repair or strengthen a compromised BTB in cases of infertility.
- Understanding the effects of environmental factors on the BTB: Continued research will identify and characterize environmental toxins that impact BTB function and male reproductive health.
- Exploring the role of the BTB in disease: Investigating the involvement of BTB dysfunction in various diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune disorders, will help develop targeted therapies.
Conclusion
The blood-testis barrier is a remarkable structure essential for male fertility. Its multifaceted functions, ranging from immune privilege to the maintenance of a specialized microenvironment, are critical for successful spermatogenesis. Disruptions to the BTB can lead to significant reproductive problems, highlighting its importance in maintaining male reproductive health. Continued research is crucial for a more comprehensive understanding of the BTB and the development of innovative strategies to address its dysfunction and its impact on male infertility. Understanding the intricate mechanisms of the BTB allows for a more comprehensive approach towards improving diagnosis, treatment, and ultimately, prevention of male infertility. The intricacies of the BTB continue to be a fascinating area of ongoing research, with implications reaching far beyond basic reproductive biology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When The Simcell Membrane In The Cell O Scope
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Shaft Of A Long Bone Is The
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Image Seen In A Plane Mirror Is Located
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lokes Was Thrilled When She Found A Low Cost Airfare
Mar 18, 2025
-
Credit Accident And Health Plans Are Designed To
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Function Of The Blood Testis Barrier Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
