What Is The Role Of Acetylcholinesterase Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
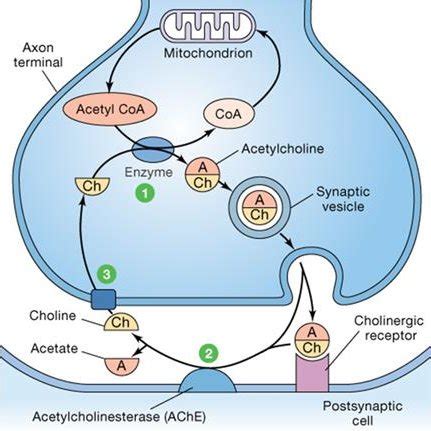
Table of Contents
What is the Role of Acetylcholinesterase? A Deep Dive
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) plays a pivotal role in the nervous system, acting as a critical regulator of cholinergic neurotransmission. Understanding its function is crucial for comprehending a wide range of neurological processes, from muscle contraction to cognitive function. This in-depth article will explore the multifaceted role of AChE, delving into its mechanism of action, its significance in various physiological processes, and the implications of its dysfunction in disease states.
The Mechanism of Acetylcholinesterase: Hydrolyzing the Neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine (ACh), a vital neurotransmitter, mediates crucial signals at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, and in the central nervous system (CNS). However, its action needs to be tightly controlled to prevent continuous stimulation and maintain proper nervous system function. This is where AChE steps in.
AChE is an enzyme that rapidly hydrolyzes ACh, breaking it down into its constituent parts: choline and acetate. This hydrolysis effectively terminates the signal transmitted by ACh, ensuring that the postsynaptic response is brief and precise. The process is incredibly efficient; AChE is one of the fastest enzymes known, capable of hydrolyzing thousands of ACh molecules per second.
The Active Site and Catalytic Mechanism
The active site of AChE contains two crucial components:
- Serine Residue: This amino acid acts as the nucleophile, attacking the carbonyl carbon of ACh.
- Anionic Site: This site, located near the serine residue, binds the quaternary ammonium group of ACh, orienting the substrate for optimal hydrolysis.
The catalytic mechanism proceeds through a two-step process:
- Acylation: The serine hydroxyl group attacks the carbonyl carbon of ACh, forming a covalent acetyl-enzyme intermediate and releasing choline.
- Deacylation: Water then attacks the acetyl-enzyme intermediate, releasing acetate and regenerating the free enzyme.
This rapid hydrolysis ensures that ACh's effects are transient, allowing for precise control of neuronal signaling. The efficiency of AChE is paramount for maintaining proper nervous system function.
The Diverse Roles of Acetylcholinesterase in Physiology
AChE's influence extends far beyond simply breaking down ACh. Its role in various physiological processes highlights its complexity and importance:
1. Neuromuscular Junction: Precise Muscle Control
At the neuromuscular junction, AChE is crucial for ensuring the precise and controlled contraction of skeletal muscles. Following the release of ACh from motor neurons, AChE swiftly hydrolyzes the neurotransmitter, preventing prolonged muscle depolarization and muscle spasms or cramps. Without AChE's rapid action, muscles would remain contracted, leading to paralysis.
2. Autonomic Nervous System: Regulating Involuntary Functions
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiration. AChE plays a significant role in regulating these processes by controlling the duration of ACh's effects at both parasympathetic and sympathetic ganglia. Its action contributes to the finely tuned balance between these two branches of the autonomic nervous system.
3. Central Nervous System: Cognitive Function and Memory
AChE's influence extends to the central nervous system, where it modulates cholinergic neurotransmission in various brain regions. Cholinergic pathways are implicated in several cognitive functions, including learning and memory. The precise regulation of ACh levels by AChE is crucial for optimal cognitive performance. Disruptions to this balance can contribute to cognitive impairments.
4. Development and Synaptic Plasticity: Shaping Neural Circuits
Emerging research suggests that AChE also plays a role in neuronal development and synaptic plasticity. It is implicated in axon guidance, synapse formation, and the refinement of neuronal circuits during development. Furthermore, AChE's activity can influence the strength and stability of synaptic connections, contributing to learning and memory processes throughout life.
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Therapeutic Applications and Implications
The crucial role of AChE makes it a prime target for pharmacological intervention. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) are drugs that block the activity of AChE, increasing the concentration of ACh at the synapse. This has implications for treating various conditions:
1. Myasthenia Gravis: Improving Muscle Strength
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease characterized by muscle weakness due to impaired neuromuscular transmission. AChEIs are used to treat myasthenia gravis by increasing the availability of ACh at the neuromuscular junction, improving muscle strength and reducing symptoms.
2. Alzheimer's Disease: Enhancing Cognitive Function
In Alzheimer's disease, cholinergic neurons are significantly affected, leading to cognitive decline. AChEIs are commonly used to treat the cognitive symptoms of Alzheimer's disease by increasing ACh levels in the brain, potentially improving memory and cognitive function. However, the benefits are often modest and may not be sustained over the long term.
3. Other Neurological Conditions: Exploring Potential Applications
AChEIs are also being investigated for their potential in treating other neurological conditions, including Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and certain types of cognitive impairment. Research continues to explore the therapeutic potential of these inhibitors in a wider range of neurological disorders.
The Consequences of Acetylcholinesterase Dysfunction: Neurological Diseases
Disruptions in AChE activity, whether due to genetic mutations, autoimmune diseases, or exposure to toxins, can lead to various neurological disorders:
1. Myasthenia Gravis: Autoimmune Attack on Neuromuscular Junction
Myasthenia gravis, as previously mentioned, is an autoimmune disease where antibodies attack the acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Although not a direct AChE dysfunction, the resulting decrease in effective ACh signaling is similar to AChE overactivity.
2. Organophosphate Poisoning: Inhibition Leading to Paralysis
Organophosphates, found in certain pesticides and nerve agents, are potent AChE inhibitors. Exposure to organophosphates leads to a buildup of ACh, resulting in excessive stimulation of cholinergic receptors, potentially leading to muscle paralysis, respiratory failure, and even death.
3. Genetic Mutations: Rare but Significant Effects
Rare genetic mutations affecting AChE can lead to a range of neurological symptoms, highlighting the enzyme's critical role in normal nervous system development and function. These mutations often result in altered AChE activity, leading to imbalances in cholinergic neurotransmission.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase plays a pivotal role in the nervous system, acting as a critical regulator of cholinergic neurotransmission. Its rapid hydrolysis of ACh ensures the precise and controlled transmission of signals at various synapses throughout the body. Understanding AChE's function is fundamental to comprehending neurological processes, developing therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders, and understanding the consequences of its dysfunction. Further research continues to unravel the complexities of this essential enzyme and its multifaceted roles in health and disease. The ongoing study of AChE remains a critical area in the pursuit of novel treatments for neurological disorders and a deeper understanding of the intricacies of the nervous system. The diverse roles of AChE, from muscle control to cognitive function, underline its significance in maintaining overall health and well-being. Its influence extends to development and synaptic plasticity, shaping the very architecture of our neural circuitry. The therapeutic applications of AChE inhibitors further underscore the enzyme's importance as a target for pharmacological interventions. The devastating consequences of AChE dysfunction, particularly in cases of organophosphate poisoning, highlight the critical need for appropriate safety measures and effective treatments.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Transmission Characteristic Is Never Fully Achieved
May 09, 2025
-
Are You Smarter Than A 2nd Grader
May 09, 2025
-
The Hazcom Program Must Be Written And Available To Employees
May 09, 2025
-
Which Is Not An Essential Aim Of Existential Humanistic Therapy
May 09, 2025
-
Tamara Rajavi One Of You Will Fail
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Role Of Acetylcholinesterase Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.