What Type Of Information Does This Personnel Roster Represent
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
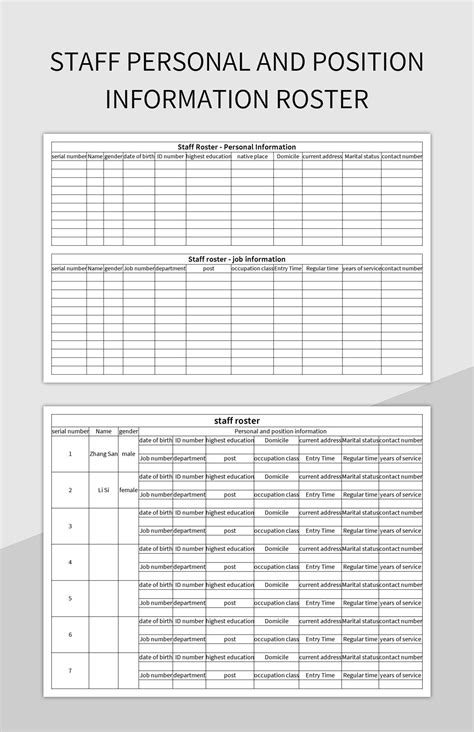
Table of Contents
What Type of Information Does This Personnel Roster Represent? Deciphering the Data Within
A personnel roster, at its core, seems simple enough: a list of employees. However, the information contained within a seemingly straightforward roster can be surprisingly complex and multifaceted, revealing much more than just names and titles. The type of information represented depends heavily on the organization's needs and the purpose for which the roster is created. This article delves deep into the various types of data a personnel roster might contain, exploring its applications and the insights it can provide.
Beyond Names and Titles: Unveiling the Richness of Personnel Roster Data
A basic personnel roster will, at minimum, include employee names and job titles. However, a comprehensive roster serves as a valuable repository of information crucial for numerous organizational functions. Let's explore the diverse data points that might be included:
1. Essential Employee Information:
- Full Name: This seems obvious, but consistency is key. Using standardized formats (e.g., Last Name, First Name, Middle Initial) ensures data accuracy and simplifies searches.
- Employee ID: A unique identifier, essential for payroll, performance tracking, and other administrative processes.
- Job Title/Position: Clearly defining roles and responsibilities. This can include department, team, and reporting structure.
- Contact Information: Work email, work phone number, and sometimes personal contact information (depending on company policy and employee consent). This is vital for communication and emergency contact purposes.
- Department/Division: Indicates the employee's area of responsibility within the organization's structure.
- Hire Date: Tracks employee tenure and contributes to workforce planning and analysis.
- Date of Birth (DOB): Often included for payroll, benefits administration, and compliance with age-related regulations. Privacy considerations are paramount here, and data protection laws must be strictly adhered to.
2. Compensation and Benefits Data:
- Salary/Wage: Information about an employee's compensation, often kept confidential and accessible only to authorized personnel. This data is crucial for payroll processing, budgeting, and compensation analysis.
- Benefits Eligibility: Details about health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off (PTO), and other benefits offered to the employee. This information is essential for benefits administration and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Pay Frequency: Specifies whether the employee is paid weekly, bi-weekly, monthly, etc. This data is critical for payroll accuracy.
- Tax Information: This includes tax withholding information, social security number (SSN), and other necessary tax-related data. Strict confidentiality and compliance with tax laws are crucial.
3. Performance and Training Data:
- Performance Reviews: Summaries of employee performance evaluations, highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. This information is crucial for performance management and employee development.
- Training and Certifications: A record of completed training courses, workshops, and certifications, demonstrating the employee's skills and qualifications. This helps identify skill gaps and inform training needs.
- Performance Metrics: Quantifiable data related to an employee's output, such as sales figures, project completion rates, or customer satisfaction scores. This is essential for performance appraisal and objective assessment.
- Skill Set: Listing of the employee's key skills and abilities, contributing to talent management and project assignments.
4. Emergency Contact and Personal Data (with consent):
- Emergency Contact Information: Details of a person to contact in case of an emergency, including name, relationship, and contact information. This is vital for employee safety and well-being.
- Address: Employee's residential or mailing address, which might be required for various purposes, such as sending paychecks or important communications. This requires strict privacy protection.
- Marital Status: Might be relevant for certain benefits or legal purposes.
- Dependents: Information on spouses and children, often relevant for benefits enrollment and tax purposes.
5. Other Relevant Information:
- Employee Status: Indicates whether the employee is full-time, part-time, temporary, or a contractor. This determines eligibility for various benefits and employment rights.
- Work Location: Specifies the employee's primary work location, which may be an office, remote location, or a combination of both. This is important for facilities management and resource allocation.
- Security Clearance (if applicable): Indicates the level of security clearance an employee possesses, if applicable. This is vital for security-sensitive organizations and ensures compliance with security protocols.
- Union Membership (if applicable): Indicates whether the employee is a member of a labor union. This is important for labor relations and compliance with collective bargaining agreements.
The Purpose and Application of Personnel Rosters
The type of information included in a personnel roster significantly depends on its intended purpose. Here are some key applications:
- Payroll and Compensation: Rosters serve as the foundation for payroll processing, ensuring accurate calculation and distribution of salaries and wages. They provide the necessary data for tax withholding, benefits deductions, and other payroll-related tasks.
- Human Resources Management: HR professionals rely on rosters for various tasks, including recruitment, onboarding, performance management, employee relations, and compliance. A comprehensive roster allows for efficient tracking of employee data, identification of talent gaps, and strategic workforce planning.
- Emergency Response: In case of emergencies, the roster provides essential contact information, enabling rapid communication with employees and facilitating emergency response measures.
- Security and Access Control: Rosters can be integrated with security systems to control access to facilities and sensitive information. Employee IDs and security clearances, if included, play a vital role in this function.
- Compliance and Reporting: Rosters help organizations comply with various legal and regulatory requirements, including labor laws, tax regulations, and data privacy regulations. They provide the data needed for generating various reports required by government agencies.
- Project Management: Detailed skill sets and expertise within a roster aids in effective resource allocation during project planning.
Data Security and Privacy: A Critical Consideration
The sensitive nature of personnel data necessitates robust security measures. Organizations must comply with data privacy regulations (such as GDPR, CCPA) and implement measures to protect the information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. This includes:
- Access Control: Restricting access to the roster to authorized personnel only.
- Data Encryption: Protecting the data through encryption methods to prevent unauthorized access even if the data is intercepted.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular audits to identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary improvements.
- Employee Training: Educating employees on data security best practices and their responsibilities in protecting sensitive information.
- Data Retention Policies: Establishing clear policies on how long the data will be retained and how it will be disposed of securely once it is no longer needed.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of the Personnel Roster
The personnel roster has evolved from a simple list of employees to a dynamic and comprehensive database that plays a critical role in various organizational functions. Its value lies in its ability to provide a centralized, accessible, and secure repository of employee information, enabling informed decision-making, efficient HR management, and enhanced organizational effectiveness. By understanding the diverse types of information a roster can represent and the importance of data security and privacy, organizations can leverage the power of their personnel data to drive success. The future of personnel rosters likely involves further integration with other systems, enabling enhanced analytics, automated processes, and even more insightful workforce management. This evolution will further solidify the personnel roster's vital role in the modern workplace.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Vehicles Have Their Own Exclusive Traffic Signals
Apr 02, 2025
-
All Of The Following Are True About Sql Except
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Release Of A Tendon From Adhesions
Apr 02, 2025
-
Are You Smarter Than A Fourth Grader
Apr 02, 2025
-
An 8 Month Old Infant Is Eating And Suddenly Begins To Cough
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Type Of Information Does This Personnel Roster Represent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
