When A Client Expresses Anxiety About Being Given Anesthesia
Breaking News Today
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
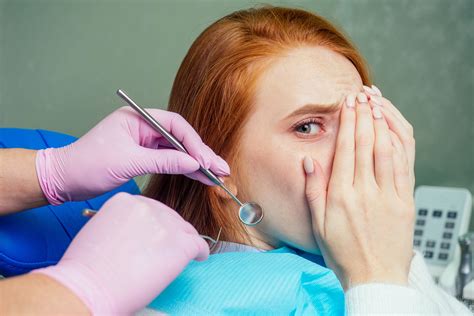
Table of Contents
When a Client Expresses Anxiety About Being Given Anesthesia: A Comprehensive Guide
Anesthesia is a cornerstone of modern surgery and medical procedures, allowing for painless and safe interventions. However, it's not uncommon for clients to experience anxiety about receiving anesthesia. This anxiety can stem from a multitude of sources, ranging from a fear of needles to concerns about loss of control or potential complications. Understanding these anxieties and addressing them effectively is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure patient comfort and a successful procedure. This comprehensive guide explores the common causes of anesthesia-related anxiety, effective communication strategies, and techniques to alleviate patient concerns.
Understanding the Roots of Anesthesia Anxiety
Anxiety surrounding anesthesia is a multifaceted issue, influenced by personal experiences, cultural background, and individual personality traits. Several factors contribute to this apprehension:
1. Fear of the Unknown:
Perhaps the most prevalent source of anxiety is the inherent unknown surrounding the anesthetic experience. Patients may worry about losing consciousness, experiencing pain during the process, or not waking up. The feeling of vulnerability and lack of control can be particularly overwhelming.
2. Negative Past Experiences:
Previous negative experiences with medical procedures, including those involving injections or sedation, can significantly amplify anxiety related to anesthesia. These experiences, even if seemingly minor, can create a powerful association linking medical interventions with fear and discomfort.
3. Learned Behaviors and Social Influences:
Anxiety surrounding anesthesia can be learned through observation or relayed experiences. Hearing negative stories from friends, family members, or even media portrayals can fuel apprehension and create unrealistic expectations. Cultural beliefs and societal narratives surrounding medical procedures also play a vital role.
4. Pre-existing Anxiety Disorders:
Individuals with pre-existing anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder or panic disorder, may exhibit heightened sensitivity to the stresses associated with medical interventions, including anesthesia. These conditions amplify the perception of threat and magnify feelings of vulnerability.
5. Specific Fears:
Some patients have specific anxieties related to certain aspects of anesthesia. These may include:
- Needle phobia: The fear of needles is extremely common and can be a significant barrier to undergoing procedures requiring anesthesia.
- Loss of control: The feeling of relinquishing control during the procedure can be deeply unsettling for some individuals.
- Respiratory complications: Concerns about breathing difficulties during or after anesthesia are often expressed.
- Adverse reactions: The possibility of allergic reactions or unexpected complications can heighten anxiety.
- Post-operative nausea and vomiting (PONV): The fear of experiencing nausea and vomiting after surgery is a common concern.
Effective Communication: The Cornerstone of Anxiety Management
Open and empathetic communication is paramount in addressing a patient's anesthesia-related anxiety. Healthcare professionals need to actively listen, validate their concerns, and provide clear, accurate information.
1. Active Listening and Empathy:
Creating a safe and trusting environment begins with truly listening to the patient's concerns without interruption or judgment. Acknowledging and validating their feelings is crucial. Phrases like, "I understand this is a worrying time," or "It's perfectly normal to feel anxious about this procedure," can significantly ease a patient's apprehension.
2. Providing Clear and Concise Information:
Explaining the anesthesia process in simple, straightforward terms is essential. Avoid using overly technical jargon that might confuse or further alarm the patient. Using visual aids, such as diagrams or videos, can enhance understanding and reduce anxiety.
3. Addressing Specific Concerns:
Directly addressing the patient's specific fears is crucial. For instance, if a patient is anxious about needles, discuss techniques to minimize discomfort, such as using smaller needles or applying numbing cream. If concerns revolve around loss of control, emphasize the monitoring and support provided throughout the procedure.
4. Collaborative Decision-Making:
Involving the patient in the decision-making process can empower them and alleviate anxiety. Discussing different anesthesia options, explaining the risks and benefits of each, and allowing the patient to express their preferences can foster a sense of control.
5. Realistic Expectations and Debunking Myths:
Addressing misconceptions and providing realistic expectations about the anesthesia experience is crucial. Many myths and misinformation surround anesthesia, leading to unwarranted anxiety. It's vital to debunk these myths using evidence-based information. For example, clarifying that loss of consciousness is temporary and that monitoring ensures patient safety can effectively alleviate apprehension.
Techniques to Alleviate Anesthesia Anxiety
Beyond effective communication, various techniques can further alleviate a client's anxiety:
1. Pre-operative Counseling and Education:
Providing detailed information about the anesthesia process and answering questions comprehensively can reduce anxiety significantly. This can be done through individual consultations, group sessions, or printed materials.
2. Relaxation Techniques:
Teaching patients relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery, can help them manage anxiety before and during the procedure. These techniques can be practiced at home and incorporated into pre-operative routines.
3. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT is a highly effective approach to managing anxiety disorders. It helps patients identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs associated with anesthesia, replacing them with more realistic and positive perspectives.
4. Medication:
In cases of severe anxiety, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms. Anesthesiologists or psychiatrists can assess the need for medication and determine the appropriate dosage and type. This should be carefully considered and discussed with the patient.
5. Support Systems:
Encouraging patients to bring a trusted friend or family member to the pre-operative consultation and to be present during the procedure can provide significant emotional support and reduce anxiety.
6. Mindfulness and Meditation:
Mindfulness and meditation practices can enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation, enabling patients to better cope with anxiety-provoking situations. These techniques involve focusing on the present moment and accepting feelings without judgment.
The Role of the Anesthesiologist and Surgical Team
The anesthesiologist and the entire surgical team play a pivotal role in managing a client's anxiety. Their expertise, compassion, and collaborative approach significantly contribute to a positive patient experience.
1. Pre-operative Assessment:
A thorough pre-operative assessment is crucial to identify risk factors for anesthesia-related anxiety and tailor the management approach accordingly. This involves assessing the patient's medical history, current medications, and psychological status.
2. Personalized Anesthesia Plan:
Based on the patient's individual needs and preferences, the anesthesiologist should develop a personalized anesthesia plan that minimizes discomfort and anxiety. This might involve using specific anesthetic techniques or medications to address the patient's specific concerns.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Support:
Throughout the procedure, the anesthesiologist monitors the patient's vital signs and provides continuous support to ensure their safety and comfort. This constant attention and reassurance can significantly alleviate anxiety.
4. Post-operative Care:
Effective post-operative care extends beyond the immediate recovery period. Addressing any lingering concerns or complications promptly can prevent anxiety from escalating.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Approach to Conquer Anesthesia Anxiety
Anesthesia-related anxiety is a significant concern for many patients undergoing medical procedures. However, with a collaborative approach involving open communication, evidence-based techniques, and a compassionate healthcare team, this anxiety can be effectively managed. By addressing the underlying causes, providing clear and accurate information, and offering appropriate support, healthcare professionals can empower patients to navigate the anesthesia experience with greater confidence and reduced distress, ensuring a positive and safe outcome. Remember, a patient's comfort and peace of mind are paramount to the success of any medical procedure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2019 International Practice Exam Mcq Apush Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Ati Health Promotion Wellness And Disease Prevention Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Credit Card Is A Type Of Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Whistleblower Is A Person Who Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
All Of The Following Are Steps In Derivative Classification
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When A Client Expresses Anxiety About Being Given Anesthesia . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
