When The Atria Contract Which Of The Following Is True
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
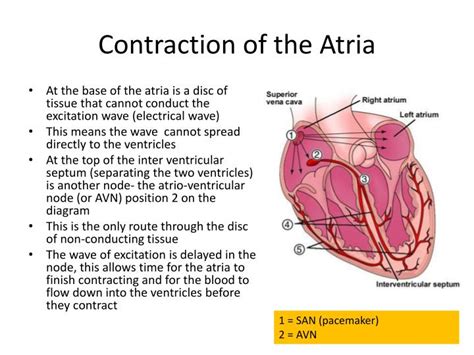
Table of Contents
When the Atria Contract: Which of the Following is True? Understanding Atrial Systole and its Significance
The human heart, a marvel of biological engineering, works tirelessly to pump blood throughout the body. This complex process relies on a precise sequence of contractions and relaxations, and understanding the intricacies of each phase is crucial to grasping the overall functionality of the cardiovascular system. One key phase is atrial systole, the contraction of the atria. When the atria contract, several crucial events occur, making it a pivotal point in the cardiac cycle. This article delves into the details of atrial contraction, exploring what happens during this phase and clarifying common misconceptions.
The Cardiac Cycle: A Brief Overview
Before diving into atrial systole, let's briefly review the cardiac cycle. This cycle represents the sequence of events in a single heartbeat, involving both the atria and ventricles. The cycle typically involves:
- Diastole: This is the relaxation phase where the heart chambers fill with blood. Both atrial and ventricular diastole are part of this.
- Atrial Systole: The contraction of the atria, forcing blood into the ventricles. This is the focus of our discussion.
- Ventricular Systole: The contraction of the ventricles, ejecting blood into the pulmonary artery (right ventricle) and the aorta (left ventricle).
- Complete Cardiac Cycle: The entire sequence, from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next.
Understanding Atrial Systole: What Happens When the Atria Contract?
When the atria contract (atrial systole), the following events take place:
-
Increased Atrial Pressure: The contraction of the atrial muscles significantly increases the pressure within the atria. This pressure increase is essential for efficiently moving blood into the ventricles.
-
Blood Flow into Ventricles: The elevated atrial pressure forces blood through the atrioventricular (AV) valves – the tricuspid valve (right AV valve) and the mitral valve (left AV valve) – into the ventricles. This completes ventricular filling, ensuring the ventricles receive a maximal volume of blood before contraction.
-
Contribution to Ventricular Filling: While the majority of ventricular filling occurs passively during diastole, atrial systole contributes the final 20-30% of the blood volume, a crucial addition for optimal cardiac output.
-
Short Duration: Atrial systole is a relatively short phase compared to other parts of the cardiac cycle, lasting only a fraction of a second. This brevity is essential to maintain the rhythm and efficiency of the entire process.
-
Electrophysiological Events: The contraction of the atria is initiated by the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart's natural pacemaker. The electrical impulse spreads across the atrial muscle, triggering the coordinated contraction. The atria's efficient contraction relies on synchronized electrical activity.
The Significance of Atrial Contraction
The seemingly small contribution of atrial systole to ventricular filling is actually quite significant. Several factors highlight its importance:
-
Optimal Stroke Volume: The extra blood volume delivered by atrial systole contributes directly to stroke volume (the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle per beat). A higher stroke volume translates to more efficient blood circulation.
-
Maintaining Cardiac Output: Cardiac output, the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute, is directly influenced by stroke volume and heart rate. The contribution of atrial systole to stroke volume directly impacts cardiac output and overall circulatory efficiency.
-
Compensation for Reduced Ventricular Filling: In situations where passive ventricular filling is impaired (e.g., due to heart valve problems or reduced venous return), the contribution of atrial systole becomes even more critical in ensuring adequate ventricular filling.
-
Maintaining Systemic Blood Pressure: By optimizing stroke volume, atrial systole helps maintain adequate systemic blood pressure, crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues.
Common Misconceptions about Atrial Systole
Several misconceptions surrounding atrial systole often arise. Addressing these clarifies the true nature of this phase:
-
Atrial Systole as the Primary Filling Mechanism: It's crucial to remember that atrial systole adds to ventricular filling, but it is not the primary mechanism. Most ventricular filling happens passively during diastole due to pressure gradients.
-
Negligible Impact on Cardiac Function: The contribution of atrial systole, while seemingly small, is anything but negligible. It is essential for optimizing cardiac function and maintaining circulatory efficiency. In individuals with impaired atrial function, the lack of this "top-up" can significantly affect cardiac performance.
-
Atrial Systole as an Independent Event: While the SA node initiates the process, atrial systole is intricately linked with other phases of the cardiac cycle. Its timing and effectiveness are tightly regulated to ensure seamless integration with ventricular systole and diastole.
Atrial Fibrillation: A Case Study in Atrial Dysfunction
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common cardiac arrhythmia where the atria contract chaotically and inefficiently. In AFib, the synchronized, coordinated contraction of the atria is disrupted. This significantly reduces the contribution of atrial systole to ventricular filling, leading to several consequences:
-
Reduced Stroke Volume: The disorganized atrial contractions reduce the amount of blood effectively transferred to the ventricles, leading to a lower stroke volume.
-
Decreased Cardiac Output: The combination of a lower stroke volume and potentially altered heart rate impacts cardiac output, affecting overall blood circulation.
-
Increased Risk of Blood Clots: The stagnant blood in the atria due to ineffective contractions increases the risk of blood clot formation, which can lead to stroke or other thromboembolic events.
-
Symptoms: Patients with AFib often experience symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, and dizziness. These symptoms are directly linked to the impaired cardiac function resulting from the inefficient atrial contraction.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Atrial Systole
Atrial systole, while a relatively short phase in the cardiac cycle, plays a crucial role in maintaining efficient cardiovascular function. Its contribution to ventricular filling optimizes stroke volume, thereby influencing cardiac output and systemic blood pressure. Understanding the mechanics and significance of atrial contraction is vital for appreciating the complexities of the heart's workings and recognizing the consequences of atrial dysfunction, as illustrated by the example of atrial fibrillation. This detailed understanding highlights the interconnectedness of each phase in the cardiac cycle and emphasizes the importance of maintaining a healthy heart for optimal circulatory function. Further research into the intricacies of atrial systole continues to refine our understanding of this crucial stage and its implications for overall cardiovascular health. Therefore, understanding when the atria contract and the subsequent events is fundamental to a complete understanding of cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. The efficient functioning of the atria and the precise coordination of atrial systole with other phases of the cardiac cycle are key to optimal heart function and overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Group Of Biologists Is Studying The Competitive Relationships
Mar 27, 2025
-
The Keyword Tyranny In This Poster Is Primarily Used To
Mar 27, 2025
-
Irene Todavia No 1 Of 2 Lista Para Salir
Mar 27, 2025
-
A Bird Building Their Nest In A Tree
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not An Issue With Patching
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When The Atria Contract Which Of The Following Is True . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
