Which Clinical Manifestations Are Characteristic Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
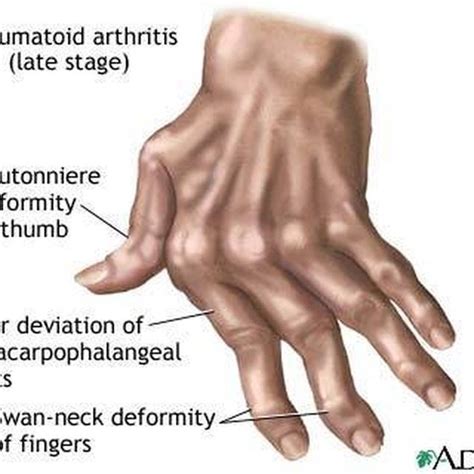
Table of Contents
- Which Clinical Manifestations Are Characteristic Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Quizlet
- Table of Contents
- Which Clinical Manifestations are Characteristic of Rheumatoid Arthritis? A Comprehensive Guide
- 1. Joint Pain (Arthralgia) and Inflammation (Arthritis):
- 2. Specific Joint Involvement:
- 3. Systemic Symptoms:
- 1. Rheumatoid Nodules:
- 2. Vasculitis:
- 3. Pulmonary Manifestations:
- 4. Cardiac Manifestations:
- 5. Ocular Manifestations:
- 6. Renal Manifestations:
- 7. Hematologic Manifestations:
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Clinical Manifestations are Characteristic of Rheumatoid Arthritis? A Comprehensive Guide
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. Understanding its characteristic clinical manifestations is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide explores the key symptoms, signs, and extra-articular manifestations of RA, providing a detailed overview often found in study resources like Quizlet, but with significantly more depth and context.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Before diving into the clinical manifestations, it's essential to grasp the underlying pathology of RA. It's an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the joints. This attack leads to inflammation, pain, swelling, and ultimately, joint destruction if left untreated. The disease process isn't limited to the joints; it can affect various organ systems, leading to a wide range of clinical presentations.
I. Classic Joint Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
The hallmark of RA is inflammatory arthritis, affecting predominantly the small joints of the hands and feet, often symmetrically. This means both sides of the body are usually affected equally.
1. Joint Pain (Arthralgia) and Inflammation (Arthritis):
- Pain: Often described as a deep, aching pain, worse in the mornings and after periods of rest. The pain is often accompanied by stiffness. The intensity of pain can fluctuate significantly.
- Swelling: Joints become visibly swollen due to inflammation of the synovium and accumulation of fluid within the joint capsule. This swelling is usually accompanied by warmth and tenderness to the touch.
- Stiffness: Morning stiffness is a hallmark symptom, often lasting for more than 30 minutes. This stiffness can also occur after periods of inactivity. The stiffness can range from mild discomfort to significant restriction of movement.
- Limited Range of Motion: Inflammation and pain restrict the normal movement of affected joints. This can lead to difficulty performing everyday tasks like buttoning clothes or opening jars.
2. Specific Joint Involvement:
- Hands and Feet: Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints of the hands are most commonly affected. The wrists, ankles, and metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints of the feet are also frequently involved.
- Symmetrical Involvement: The disease typically affects joints on both sides of the body equally. For example, if the right hand's MCP joints are inflamed, the left hand's MCP joints will likely be similarly affected.
- Joint Deformities: Over time, chronic inflammation can lead to joint destruction and deformities. These can include ulnar deviation (drifting of the fingers toward the ulnar side), boutonniere deformity (flexion of the PIP joint and hyperextension of the DIP joint), and swan neck deformity (hyperextension of the PIP joint and flexion of the DIP joint).
3. Systemic Symptoms:
While joint involvement is the primary feature, RA can also present with systemic symptoms, reflecting the body's overall inflammatory response.
- Fatigue: Persistent and debilitating fatigue is a common complaint among patients with RA. It can significantly impact their daily activities and quality of life.
- Fever: Low-grade fever is possible, especially during periods of active disease flares.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss is another possible symptom, often associated with the chronic inflammatory process and decreased appetite.
- Malaise: A general feeling of unwellness or discomfort, often accompanied by fatigue and weakness.
II. Extra-Articular Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
RA's impact extends beyond the joints. Extra-articular manifestations involve various organ systems and can significantly impact a patient's overall health.
1. Rheumatoid Nodules:
Subcutaneous nodules, or rheumatoid nodules, are firm, painless lumps that can develop under the skin, particularly over bony prominences like the elbows, knees, and fingers. They are composed of inflammatory cells and are often a sign of more severe disease.
2. Vasculitis:
Inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) can occur in RA, leading to complications such as:
- Raynaud's phenomenon: Episodic discoloration of the fingers and toes in response to cold or stress.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Damage to nerves in the hands and feet, causing numbness, tingling, or pain.
- Mononeuritis multiplex: Inflammation of multiple individual peripheral nerves.
3. Pulmonary Manifestations:
- Pleuritis: Inflammation of the lining of the lungs (pleura), causing chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Interstitial lung disease: Inflammation and scarring of the lung tissue, leading to progressive shortness of breath.
- Rheumatoid lung nodules: Similar to subcutaneous nodules but located in the lungs.
4. Cardiac Manifestations:
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the lining of the heart (pericardium), causing chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Valvulitis: Inflammation of the heart valves, potentially leading to heart failure.
- Coronary artery disease: Increased risk of atherosclerosis and heart attack.
5. Ocular Manifestations:
- Scleritis: Inflammation of the white part of the eye (sclera), causing severe pain and redness.
- Episcleritis: Inflammation of the tissue overlying the sclera, typically less severe than scleritis.
6. Renal Manifestations:
- Amyloidosis: Accumulation of abnormal protein deposits in the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
7. Hematologic Manifestations:
- Anemia: Reduction in red blood cell count, often due to chronic inflammation.
- Thrombocytosis: Increased platelet count.
III. Diagnostic Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Diagnosis of RA relies on a combination of clinical findings, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria are widely used for diagnosis. These criteria incorporate various factors, such as:
- Joint involvement: Number of affected joints and their location.
- Serology: Presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA).
- Duration of symptoms: Symptoms must be present for at least 6 weeks.
- Acute-phase reactants: Elevated levels of inflammatory markers like ESR and CRP.
IV. Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment:
Early diagnosis and treatment of RA are crucial for preventing irreversible joint damage and managing systemic complications. Effective treatment strategies, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic therapies, can significantly slow the progression of the disease and improve patient outcomes.
V. Conclusion:
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune disorder characterized by a wide range of clinical manifestations. Understanding these manifestations—from the classic joint symptoms to the less common extra-articular manifestations—is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management. Early intervention with appropriate treatment significantly improves patient outcomes and prevents long-term disability. This detailed overview provides a comprehensive understanding surpassing the typical information found on quick-reference sites, enabling deeper learning and a more holistic approach to understanding this complex disease. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Who Helps Pip Learn To Read And Write
Mar 26, 2025
-
Explain The Goals Of The World Resources Simulation Center
Mar 26, 2025
-
Worksheet On Dna Rna And Protein Synthesis
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is Not A Function Of Cerumen
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Scientific Study Of Life Is Known As
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Clinical Manifestations Are Characteristic Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
