Which Cocom Has A Problem With Trafficking
Breaking News Today
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
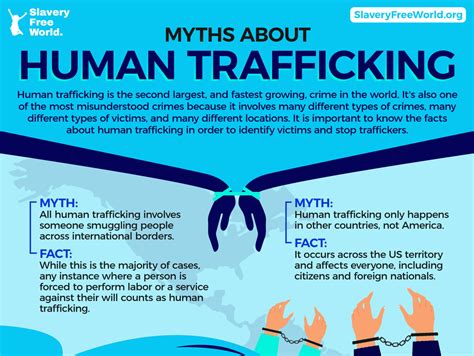
Table of Contents
Which Coco Crops Have a Problem with Trafficking? Combating Exploitation in the Chocolate and Coconut Industries
The idyllic image of sun-drenched cocoa plantations and swaying coconut palms often belies a dark reality: human trafficking and exploitation are significant problems within both industries. While the focus often lands on cocoa, the coconut industry, too, grapples with similar challenges, albeit with less public awareness. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities within each crop and the interconnected nature of these issues is crucial to effective intervention and ethical sourcing.
The Bitter Truth: Human Trafficking in the Cocoa Industry
The cocoa industry, the primary ingredient in chocolate, has been widely documented for its association with child labor and human trafficking. West Africa, specifically Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana, are the world's largest cocoa producers, and unfortunately, also the epicenter of this exploitation. Several factors contribute to this complex problem:
Poverty and Lack of Educational Opportunities:
Poverty is a fundamental driver. Desperate families often send their children to work on cocoa farms, viewing it as a necessary evil to ensure survival. The lack of educational opportunities further exacerbates this, trapping children in a cycle of poverty and labor. The children are often lured with false promises of education or better opportunities, only to find themselves subjected to grueling work and abuse.
Weak Governance and Enforcement:
Weak governance and law enforcement are significant obstacles. Corruption and a lack of resources hinder effective monitoring and enforcement of child labor laws. This allows exploitative practices to thrive unchecked. Many farms operate in remote areas, making it difficult to monitor and regulate their activities.
Complex Supply Chains:
The complex and opaque nature of the cocoa supply chain makes it challenging to trace cocoa beans back to their origin. This lack of traceability makes it difficult to identify and hold accountable those involved in human trafficking. Large multinational companies often rely on complex networks of intermediaries and smaller farmers, making it difficult to ensure ethical sourcing throughout the entire supply chain.
Demand-Driven Exploitation:
The insatiable global demand for chocolate fuels this cycle of exploitation. The relentless pursuit of cheap cocoa by chocolate manufacturers inadvertently incentivizes unethical practices on the ground. While many companies have implemented sustainability initiatives and ethical sourcing programs, the scale of the problem remains immense.
The Hidden Struggle: Trafficking in the Coconut Industry
While less prominently featured in the media than the cocoa industry, the coconut industry also faces significant challenges related to human trafficking and exploitation. The issues are often less visible, but equally devastating.
Migrant Workers and Exploitation:
Large coconut plantations, particularly in Southeast Asia, often rely on migrant workers. These workers are frequently vulnerable to exploitation, including human trafficking, due to their precarious legal status and lack of access to legal protections. They are often subjected to long hours, poor working conditions, and low wages, with little recourse to redress grievances.
Debt Bondage and Forced Labor:
In some regions, coconut farmers and workers become trapped in cycles of debt bondage. They are forced to work to pay off debts, often incurred through recruitment fees or advances. This can lead to conditions akin to forced labor, with little or no freedom to leave the plantation.
Lack of Transparency and Traceability:
Similar to the cocoa industry, the lack of transparency and traceability in the coconut supply chain makes it difficult to monitor working conditions and identify instances of human trafficking. The extensive use of intermediaries and complex supply networks obscures the true origins of many coconut products.
Environmental Degradation and its Impact:
Environmental degradation linked to intensive coconut cultivation can further marginalize communities and increase their vulnerability to human trafficking. Loss of livelihoods due to environmental damage can push people into exploitative labor arrangements as they desperately seek alternative income sources.
Combating Trafficking: Shared Strategies for Cocoa and Coconut
Addressing human trafficking in both the cocoa and coconut industries requires a multi-faceted approach focusing on several key areas:
Strengthening Legal Frameworks and Enforcement:
Robust legislation that specifically addresses child labor and human trafficking is essential, coupled with strong enforcement mechanisms to hold perpetrators accountable. This includes regular inspections of farms and plantations, prosecution of offenders, and effective redress mechanisms for victims.
Improving Traceability and Transparency:
Enhanced traceability systems can help track products from origin to consumer, allowing for greater accountability throughout the supply chain. This involves investing in technologies such as blockchain and developing more transparent supply chain management practices.
Empowering Local Communities:
Supporting local communities through education, job creation, and economic development initiatives can help break the cycle of poverty that drives many into exploitative labor. This includes investing in education, healthcare, and infrastructure in cocoa and coconut-growing regions.
Promoting Ethical Sourcing and Consumer Awareness:
Consumers play a vital role by demanding ethically sourced products and supporting companies committed to fair labor practices. Increased awareness of the issues surrounding human trafficking in these industries can drive demand for ethically produced cocoa and coconut products, incentivizing better practices across the supply chain.
Collaboration and Partnerships:
Effective solutions require collaboration between governments, businesses, NGOs, and consumers. Strong partnerships are needed to effectively monitor farms, implement ethical sourcing initiatives, and support community development programs.
Investing in Technology and Innovation:
Technology can play a significant role in improving transparency and traceability. Blockchain technology, for instance, can help track products throughout the supply chain, ensuring that they are ethically sourced. Remote sensing technology can also be used to monitor farms and plantations for signs of human trafficking.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Ethical Production
Combating human trafficking in the cocoa and coconut industries is a complex challenge that demands a concerted and sustained effort. While the challenges are immense, significant progress can be made through a combination of stronger legal frameworks, improved traceability and transparency, empowering local communities, promoting ethical sourcing, and fostering effective partnerships. Ultimately, the goal is to create a more just and ethical system where the production of cocoa and coconuts does not come at the cost of human dignity and freedom. By raising awareness, supporting ethical businesses, and demanding accountability throughout the supply chain, we can all contribute towards a future where these delicious crops are produced sustainably and ethically.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Most Damaged Topsoil And Farming Equipment During The 1930s
Apr 06, 2025
-
Tb Control Training Must Be Completed Monthly
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Do You Call The Answer To A Multiplication Problem
Apr 06, 2025
-
If The Pond Is Resampled A Year Later
Apr 06, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is True About Information Systems
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Cocom Has A Problem With Trafficking . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
