Which Colour Of The Rainbow Has The Shortest Wavelength
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
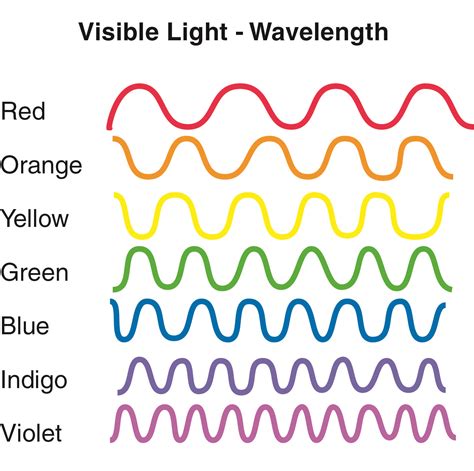
Table of Contents
Which Color of the Rainbow Has the Shortest Wavelength?
The vibrant spectrum of a rainbow, a breathtaking display of nature's artistry, is more than just a pretty sight. It's a physical manifestation of light's properties, specifically its wavelength and frequency. Understanding the relationship between color and wavelength allows us to unravel the mysteries behind this captivating phenomenon. So, which color in the rainbow boasts the shortest wavelength? The answer, as we'll explore in detail, is violet.
Understanding Wavelength and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Before diving into the specifics of rainbow colors, let's establish a foundational understanding of wavelength. Light, though we perceive it as visible color, is actually part of a broader spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. This spectrum encompasses a wide range of wavelengths, from extremely long radio waves to incredibly short gamma rays. Visible light occupies a relatively narrow band within this spectrum, and it's this portion that our eyes are capable of detecting.
Wavelength, denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ), is the distance between two consecutive crests (or troughs) of a wave. It's measured in units like nanometers (nm), where 1 nm is one billionth of a meter. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency (the number of wave cycles passing a point per second). This relationship is inversely proportional: as wavelength decreases, frequency increases, and vice versa.
The Visible Light Spectrum and Rainbow Colors
The visible light spectrum, the portion we can see, is arranged in order of decreasing wavelength (or increasing frequency). This sequence is often remembered by the acronym ROY G. BIV:
- Red: Longest wavelength, lowest frequency.
- Orange:
- Yellow:
- Green:
- Blue:
- Indigo:
- Violet: Shortest wavelength, highest frequency.
It's important to note that the boundaries between these colors are not sharply defined. There's a continuous transition from one color to the next, creating a smooth gradient. The perceived color depends on the dominant wavelength of the light reaching our eyes.
Why Violet Has the Shortest Wavelength
The reason violet possesses the shortest wavelength lies in the interaction of light with our eyes and brain. When sunlight passes through raindrops, it undergoes a process called refraction, bending as it transitions from air to water and back again. This refraction separates the light into its constituent colors based on their different wavelengths. Because violet light has a shorter wavelength, it bends more significantly than red light during refraction. This greater bending is what causes violet to appear on the inner arc of the rainbow, while red is on the outer arc.
Furthermore, the sensitivity of our cone cells (photoreceptor cells in the retina responsible for color vision) plays a role. While our eyes can detect a wide range of wavelengths, they are more sensitive to certain wavelengths than others. Our sensitivity peaks in the green-yellow region, and it tapers off towards both ends of the visible spectrum. While violet has the shortest wavelength, our perception of it might be somewhat less intense than, say, green or yellow, due to this sensitivity curve.
The Subtleties of Indigo: A Matter of Debate
The inclusion of indigo in ROY G. BIV is often a source of debate. Some argue that indigo is not a distinct color but rather a shade of blue or violet. Isaac Newton, who originally identified seven colors in the spectrum, later added indigo, possibly to align with the seven musical notes. In reality, the transition between blue and violet is gradual, making it difficult to draw a precise boundary between these two colors.
Regardless of indigo's status, the fact remains that violet occupies the shortest wavelength end of the visible spectrum. Even if some consider indigo a distinct color, violet still holds the shortest wavelength among commonly recognized rainbow colors.
Beyond the Rainbow: Applications of Wavelength Knowledge
Understanding the relationship between color and wavelength has far-reaching implications beyond the aesthetics of a rainbow. This knowledge is crucial in various scientific and technological fields:
1. Spectroscopy: Analyzing Light and Matter
Spectroscopy is a powerful technique that analyzes the wavelengths of light emitted or absorbed by substances. By studying the spectral lines of an element, scientists can identify its composition. This method finds extensive application in astronomy, chemistry, and materials science.
2. Remote Sensing and Imaging: Studying the Earth and Beyond
Remote sensing technologies utilize different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation to capture images of the Earth's surface, atmosphere, and even other planets. Satellite imagery, for instance, uses different wavelengths to discern various features and properties of land, vegetation, and water bodies.
3. Medical Imaging: Diagnosing and Treating Diseases
Medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays and MRI scans, use different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation to create detailed images of the human body. These images aid in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases and injuries.
4. Communication Technologies: Transmitting Information
Radio waves, microwaves, and infrared radiation, all part of the electromagnetic spectrum, are fundamental to communication technologies. The specific wavelength used determines the range and capacity of the communication system.
5. Color Science and Technology: Creating and Manipulating Colors
The principles of wavelength and color perception are essential in color science and technology. Understanding how different wavelengths of light interact allows designers and engineers to create accurate and vibrant colors in printing, displays, and other applications.
Conclusion: The Violet Enigma and its Significance
The question of which color in the rainbow has the shortest wavelength has led us on a journey through the fascinating world of light and color. We've learned that violet, with its shortest wavelength and highest frequency, is the color that bends the most during refraction, resulting in its placement on the inner arc of the rainbow. While the precise boundaries between colors can be debated, the significance of wavelength in understanding and manipulating light extends far beyond the beauty of a rainbow, influencing diverse fields of science and technology. The next time you see a rainbow, remember that the vibrant violet hue holds the key to understanding a fundamental aspect of light's nature. It’s a testament to the intricate interplay of physics and perception, a spectacle that continues to inspire wonder and curiosity. Understanding the science behind the beauty elevates the appreciation of nature's breathtaking artistry, transforming a simple observation into a profound scientific exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Becoming A Professional Nurse Professional Behaviors In Nursing
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Connective Tissue Has A Liquid Matrix
Apr 02, 2025
-
Nosotros Tenemos Un Perro Es Perro
Apr 02, 2025
-
When People Determine Their Goals For Public Speaking
Apr 02, 2025
-
Acls Precourse Self Assessment And Precourse Work Answers
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Colour Of The Rainbow Has The Shortest Wavelength . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
