Which Condition Is Associated With Acalculous Cholecystitis Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
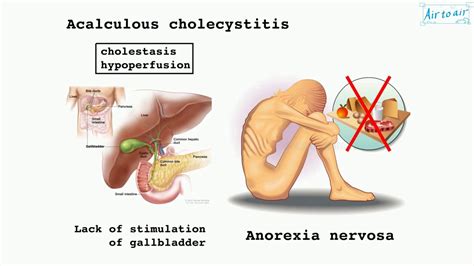
Table of Contents
Acalculous Cholecystitis: Conditions, Causes, and Diagnosis
Acalculous cholecystitis, a severe inflammation of the gallbladder without the presence of gallstones (cholelithiasis), is a serious medical condition requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. While less common than calculous cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation with gallstones), acalculous cholecystitis carries a high morbidity and mortality rate due to its often insidious onset and potential for rapid progression. Understanding the conditions associated with this condition is crucial for early detection and effective management. This comprehensive article will explore the various medical conditions that predispose individuals to acalculous cholecystitis, detailing the underlying mechanisms and highlighting the diagnostic considerations.
Predisposing Factors and Associated Conditions
Several critical illnesses and physiological states significantly increase the risk of developing acalculous cholecystitis. These conditions often impair gallbladder function, leading to stasis, ischemia, and ultimately, inflammation.
1. Severe Illness and Critical Care: The Impact of Systemic Stress
Sepsis: This overwhelming systemic inflammatory response to infection is a major risk factor. The body's intense inflammatory response can disrupt gallbladder blood flow, causing ischemia and necrosis (tissue death) within the gallbladder wall. This ischemic injury is a primary driver of acalculous cholecystitis in critically ill patients. The presence of systemic inflammatory mediators further exacerbates the inflammation within the gallbladder.
Trauma and Burns: Major trauma and extensive burns often lead to hypovolemia (decreased blood volume), hypotension (low blood pressure), and reduced perfusion to the gallbladder. This reduced blood supply contributes to gallbladder ischemia and sets the stage for inflammation.
Post-operative State: Following major surgical procedures, especially those involving the abdomen, the risk of acalculous cholecystitis rises. Several factors contribute to this increased risk: prolonged fasting, bowel dysfunction, use of narcotics, and general stress on the body. These factors may disrupt gallbladder motility and blood flow.
Multi-organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS): Patients suffering from MODS, often a complication of sepsis or severe trauma, experience widespread organ failure. The gallbladder is particularly vulnerable in this context, as reduced blood flow and systemic inflammation exacerbate the risk of acalculous cholecystitis.
2. Gastrointestinal Conditions: Disrupting Gallbladder Function
Parenteral Nutrition: Prolonged administration of parenteral nutrition (feeding intravenously) is associated with an increased incidence of acalculous cholecystitis. The lack of enteral stimulation and the resulting gallbladder stasis are believed to contribute to the development of this condition.
Intestinal Ischemia: Reduced blood supply to the intestines can have secondary effects on the gallbladder. The close anatomical relationship and shared vascular supply between the intestines and gallbladder mean that intestinal ischemia can compromise gallbladder perfusion, leading to inflammation.
Crohn's Disease: While not a direct cause, severe inflammation associated with Crohn's disease can affect the gallbladder indirectly. The systemic inflammatory response and potential for intestinal involvement can impact gallbladder function and increase the risk of acalculous cholecystitis.
3. Underlying Medical Conditions: Systemic Factors at Play
Diabetes Mellitus: Patients with poorly controlled diabetes are at higher risk. Diabetic neuropathy can affect gallbladder motility, leading to bile stasis, and the underlying vascular disease associated with diabetes can further compromise gallbladder perfusion.
Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation, are more susceptible to infections that can trigger acalculous cholecystitis. Their compromised ability to fight off infections increases the risk of sepsis, a major predisposing factor.
4. Medication-Related Factors: The Unintended Consequences
Certain Medications: While not a common direct cause, some medications can indirectly increase the risk. For example, medications that affect bowel motility or cause vasoconstriction can potentially disrupt gallbladder function, leading to increased susceptibility to acalculous cholecystitis.
Pathophysiology: Unraveling the Mechanism of Acalculous Cholecystitis
The pathophysiology of acalculous cholecystitis centers around impaired gallbladder function, leading to stasis, ischemia, and inflammation. The precise mechanisms are not fully understood, but several factors play a crucial role:
-
Gallbladder Stasis: Reduced gallbladder emptying leads to bile concentration and the precipitation of crystals. This creates an environment conducive to inflammation and bacterial growth.
-
Ischemia: Decreased blood supply to the gallbladder results in tissue hypoxia (lack of oxygen), leading to cell damage and necrosis. This damage triggers an inflammatory cascade.
-
Inflammation: The damaged gallbladder tissue releases inflammatory mediators, attracting immune cells and further exacerbating the inflammatory process. Bacterial infection can further enhance the inflammation.
-
Bacterial Infection: While not always present, bacterial infection frequently accompanies acalculous cholecystitis, amplifying the inflammatory response and leading to worsening symptoms.
Clinical Presentation: Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
The clinical presentation of acalculous cholecystitis can be variable, making early diagnosis challenging. However, some common symptoms include:
-
Right upper quadrant pain: This is a hallmark symptom, often accompanied by tenderness to palpation.
-
Fever: The presence of infection often leads to fever.
-
Nausea and vomiting: These gastrointestinal symptoms are frequent.
-
Leukocytosis: An elevated white blood cell count in the blood reflects the body's inflammatory response.
-
Positive Murphy's Sign: This is a positive finding where deep palpation in the right upper quadrant elicits pain during inspiration.
Diagnosis: Confirming the Suspicion
Diagnosing acalculous cholecystitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Imaging plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis and ruling out other conditions.
-
Ultrasound: This is the initial imaging modality of choice. It can reveal gallbladder wall thickening, distension, and pericholecystic fluid (fluid surrounding the gallbladder), all suggestive of acalculous cholecystitis.
-
CT Scan: A CT scan may provide more detailed information about the extent of inflammation and identify complications such as perforation or abscess formation.
-
HIDA Scan (Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid Scan): This nuclear medicine study assesses gallbladder function and can help differentiate between acalculous cholecystitis and other conditions. A non-visualizing gallbladder on HIDA scan is highly suggestive of acalculous cholecystitis.
-
Laboratory Tests: Complete blood count (CBC) shows leukocytosis (elevated white blood cell count), indicative of inflammation. Liver function tests may also be abnormal. Blood cultures are sometimes performed to identify the causative bacteria.
Treatment: Addressing the Inflammation and Underlying Causes
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause and controlling the inflammation. The cornerstone of management is surgical intervention:
-
Cholecystectomy: Surgical removal of the gallbladder is the preferred treatment. This eliminates the source of infection and prevents complications. The approach may be laparoscopic (minimally invasive) or open, depending on the patient's condition and the surgeon's preference.
-
Antibiotics: Broad-spectrum antibiotics are usually administered to combat bacterial infection, although this is not always necessary in all cases. The choice of antibiotics depends on the suspected pathogen.
-
Supportive Care: Intravenous fluids, pain management, and nutritional support are crucial components of supportive care. Maintaining adequate fluid balance and addressing pain are important aspects of patient management.
Prognosis and Prevention: Looking Ahead
The prognosis for acalculous cholecystitis is generally good with prompt diagnosis and treatment. Early surgical intervention significantly reduces morbidity and mortality. However, delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to serious complications such as gallbladder perforation, peritonitis (infection of the abdominal cavity), and sepsis.
Preventing acalculous cholecystitis is challenging since many predisposing factors are beyond individual control. However, effective management of underlying medical conditions such as diabetes and sepsis, along with prompt treatment of infections, can significantly reduce the risk.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Condition Requiring Comprehensive Understanding
Acalculous cholecystitis is a complex condition arising from a confluence of factors leading to gallbladder inflammation in the absence of gallstones. Understanding the underlying pathophysiology and associated conditions is paramount for early diagnosis and effective management. Prompt recognition of symptoms, appropriate diagnostic imaging, and timely surgical intervention are crucial for a favorable prognosis. Furthermore, managing underlying medical conditions and preventing severe infections can play a vital role in reducing the risk of this serious complication. This comprehensive understanding underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to the management of acalculous cholecystitis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In A Resting State Sodium Is At A Higher Concentration
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Are The Functions Of The Structure Seen Here
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Best Describes Earths Magnetic Field Lines
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Complications Did Michelangelo Face While Painting The Sistine Chapel
Mar 25, 2025
-
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Natural Selection Answer Key
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Condition Is Associated With Acalculous Cholecystitis Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
