Which Criterion Is Used To Functionally Classify Neurons
Breaking News Today
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
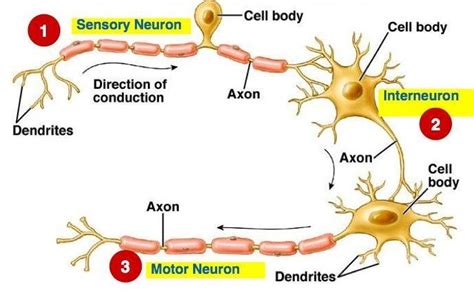
Table of Contents
Which Criterion is Used to Functionally Classify Neurons?
The human nervous system, a marvel of biological engineering, comprises billions of neurons, each playing a specific role in information processing. Understanding how these neurons function and interact is crucial to comprehending brain activity, behavior, and neurological disorders. While structural classifications of neurons exist based on morphology (e.g., unipolar, bipolar, multipolar), functional classification focuses on a neuron's role within a neural circuit. This classification is multifaceted and doesn't rely on a single, universally accepted criterion. Instead, it utilizes a combination of criteria to categorize neurons based on their diverse functions.
Key Criteria for Functional Neuron Classification
Several key criteria are employed to functionally classify neurons, often in conjunction with one another. These include:
1. Neurotransmitter Released:
This is perhaps the most common and readily understood criterion. Neurons are classified based on the primary neurotransmitter they release at their synapses. For example:
-
Cholinergic neurons: Release acetylcholine. These are prevalent in the neuromuscular junction, playing a vital role in muscle contraction. Dysfunction in cholinergic neurons is implicated in Alzheimer's disease.
-
GABAergic neurons: Release gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. They play a crucial role in regulating neuronal excitability and preventing runaway neuronal firing. Imbalances in GABAergic function are associated with anxiety and epilepsy.
-
Glutamatergic neurons: Release glutamate, the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. They are involved in a vast array of brain functions, including learning and memory. Excessive glutamate activity can lead to excitotoxicity, damaging neurons.
-
Dopaminergic neurons: Release dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in reward, motivation, and motor control. Degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra is the hallmark of Parkinson's disease.
-
Serotonergic neurons: Release serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation, sleep, and appetite. Imbalances in serotonin are implicated in depression and anxiety disorders.
-
Noradrenergic neurons: Release norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter involved in alertness, attention, and the fight-or-flight response. Dysregulation of noradrenergic systems can contribute to anxiety and PTSD.
It's important to note that many neurons can release multiple neurotransmitters, complicating this classification system. However, the primary neurotransmitter released often dictates the neuron's primary functional role.
2. Effect on Postsynaptic Neuron:
Neurons can be classified based on their effect on the postsynaptic neuron. This boils down to whether they excite or inhibit the postsynaptic neuron.
-
Excitatory neurons: Increase the likelihood of the postsynaptic neuron firing an action potential. Glutamatergic neurons are a prime example.
-
Inhibitory neurons: Decrease the likelihood of the postsynaptic neuron firing an action potential. GABAergic neurons are a classic example.
This criterion often overlaps with the neurotransmitter released, but it's not always a direct correlation. Some neurotransmitters can have both excitatory and inhibitory effects depending on the receptor subtype present on the postsynaptic neuron.
3. Projection Target:
The location of a neuron's axon terminals – its projection target – provides another functional classification. This criterion considers the range and location of neuronal influence within the nervous system:
-
Projection neurons: These neurons have long axons that project to distant brain regions. They are essential for long-range communication within the brain, connecting different cortical areas or subcortical structures. Pyramidal neurons in the cortex are a prime example.
-
Interneurons: These neurons have short axons that connect to nearby neurons within the same brain region. They act as local circuit processors, modulating activity within a specific area. Interneurons are crucial for fine-tuning neural activity and shaping complex patterns of neural processing. The various types of interneurons in the cortex exhibit highly diverse functional roles.
-
Sensory neurons: These neurons transmit sensory information from peripheral receptors to the central nervous system (CNS). They are specialized to detect specific types of stimuli, such as light, sound, touch, or temperature.
-
Motor neurons: These neurons transmit signals from the CNS to muscles and glands, controlling movement and other effector functions. Their projections target skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, or glands.
This classification is crucial for understanding how information is integrated and processed within the nervous system.
4. Firing Pattern:
The temporal pattern of action potentials fired by a neuron can also be a defining characteristic for functional classification:
-
Regular-spiking neurons: These neurons fire action potentials at a relatively constant rate.
-
Fast-spiking neurons: These neurons fire action potentials very rapidly, often exhibiting high-frequency bursts.
-
Bursting neurons: These neurons fire action potentials in bursts, interspersed with periods of silence.
These different firing patterns reflect the neuron's intrinsic properties and can influence its contribution to network dynamics. The timing of action potentials is crucial for information processing, and different firing patterns can lead to different functional outcomes.
5. Electrophysiological Properties:
Electrophysiological techniques, such as patch-clamp recordings, can reveal detailed information about the neuron's membrane properties, which can inform its functional classification:
-
Voltage-gated ion channel subtypes: The types and densities of voltage-gated ion channels expressed in a neuron's membrane profoundly influence its excitability and firing pattern.
-
Synaptic integration properties: How a neuron sums and integrates synaptic inputs can determine its response to various stimuli.
-
Intrinsic excitability: This reflects the neuron's propensity to generate action potentials, influenced by its resting membrane potential, membrane resistance, and the presence of different ion channels.
Overlap and Complexity
It's crucial to understand that these criteria are not mutually exclusive. A single neuron can be classified according to multiple criteria. For instance, a neuron might be classified as a glutamatergic, excitatory projection neuron with a regular-spiking pattern and specific electrophysiological properties. This layered classification allows for a more nuanced understanding of neuronal function within complex neural circuits. The interplay of these factors generates the vast diversity of neuronal function observed in the nervous system.
The Future of Functional Neuron Classification
Ongoing research using advanced techniques like optogenetics, calcium imaging, and connectomics is continually refining our understanding of neuronal function and refining the classification systems used. These new technologies allow for detailed investigations into the dynamic interactions of neurons within complex networks. Furthermore, the growing appreciation of glial cell function and their interactions with neurons is adding another dimension to our understanding of neuronal classification and function. Future research will likely lead to more precise and comprehensive classifications that reflect the intricate complexity of neuronal roles within the nervous system. A truly complete understanding will integrate structural, functional, and connectomic data to paint a comprehensive picture of neuronal diversity and function.
This integrated approach will be crucial for developing effective treatments for neurological disorders, which often arise from disruptions in specific neuronal circuits and the complex interactions between different neuronal subtypes. By refining our understanding of neuronal functional classification, we can move closer to developing more targeted and effective therapies for these conditions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Paraphrase This Passage To Explain What A Hero Stands For
Mar 13, 2025
-
Which Statement Describes The Size Of The Inner Planets
Mar 13, 2025
-
A Nurse Is Preparing To Administer Dextrose 5 In Water
Mar 13, 2025
-
James Is Goal As Monarch Was To
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Happens When You Format A Filesystem On A Partition
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Criterion Is Used To Functionally Classify Neurons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
