Which Factor Is Considered When Evaluating Someone's Standard Of Living
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
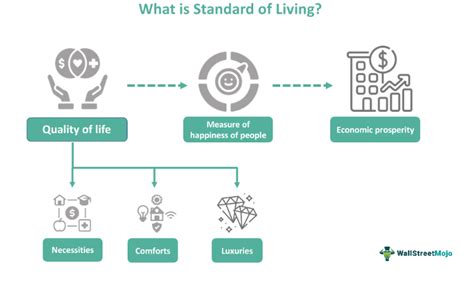
Table of Contents
Which Factors Are Considered When Evaluating Someone's Standard of Living?
Understanding someone's standard of living goes beyond simply looking at their income. It's a multifaceted concept encompassing various economic, social, and environmental factors that contribute to their overall well-being and quality of life. Accurately evaluating this requires a holistic approach, considering a range of indicators that paint a complete picture. This article delves deep into the key factors used to assess an individual's or a population's standard of living.
Material Well-being: The Tangible Indicators
The most readily apparent aspect of standard of living is material well-being, encompassing the tangible goods and services available to individuals. Several key indicators are crucial here:
1. Income and Wealth: The Foundation
Income, representing earnings from employment, investments, or other sources, forms the bedrock of material well-being. A higher income generally translates to greater access to goods and services. However, it's vital to consider income inequality, as a high average income can mask significant disparities within a population. The Gini coefficient, a measure of income inequality, provides valuable context.
Wealth, encompassing assets like property, savings, and investments, offers a longer-term perspective on financial security. Wealth accumulation reflects not just current income but also past savings and investment choices, indicating a greater capacity to withstand economic shocks and access opportunities. Analyzing wealth distribution alongside income helps understand long-term economic stability and opportunity.
2. Access to Goods and Services: Beyond Basic Needs
Beyond basic necessities, the availability and affordability of goods and services significantly impact standard of living. This includes:
- Food Security: Access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food is paramount. Food insecurity, characterized by limited or uncertain access to adequate food, dramatically reduces quality of life and well-being.
- Housing: Adequate and affordable housing is essential. Factors such as housing costs relative to income, housing quality, and access to safe and secure housing all play a role. Overcrowding and substandard housing conditions directly impact health and well-being.
- Healthcare: Access to quality healthcare services is critical. This includes preventative care, treatment for illness and injury, and access to essential medicines. Healthcare affordability and the quality of healthcare infrastructure are key considerations.
- Transportation: Efficient and affordable transportation systems are essential for access to employment, education, and other opportunities. Reliable public transport and access to private vehicles play a significant role.
- Education: Access to quality education at all levels is fundamental to improving standard of living. Education provides individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to participate fully in the economy and society. Literacy rates, school enrollment rates, and educational attainment levels are key indicators.
- Utilities: Access to essential utilities such as electricity, water, and sanitation is vital for a decent standard of living. Reliable access to these services is often taken for granted in developed countries, but their absence can drastically impact life in developing regions.
Social Well-being: The Intangible Assets
Material possessions alone do not define standard of living. Social well-being, encompassing aspects of social interaction, community involvement, and personal fulfillment, plays a crucial role.
1. Social Support Networks: The Strength of Community
Strong social support networks contribute significantly to well-being. This involves the presence of family, friends, and community organizations that offer emotional, practical, and financial support during challenging times. Social isolation and lack of social support can negatively affect mental and physical health.
2. Social Inclusion and Equity: Participation Matters
Social inclusion refers to the degree to which individuals feel valued, respected, and have equal opportunities to participate in society. Factors such as discrimination based on race, gender, religion, or other characteristics significantly impact standard of living. Equity, ensuring fair access to resources and opportunities regardless of background, is crucial for a high standard of living.
3. Safety and Security: Freedom from Fear
Personal safety and security are vital components of a high standard of living. This encompasses freedom from crime, violence, and political instability. A safe and secure environment allows individuals to pursue their goals and aspirations without fear. High crime rates, political unrest, and the fear of violence can significantly impact quality of life.
4. Political Freedom and Participation: A Voice in Society
Political freedom and the ability to participate in political processes are essential for a high standard of living. This includes freedom of speech, assembly, and association, as well as the right to vote and participate in decision-making processes. Political stability and good governance create a more predictable and supportive environment for individuals and communities.
5. Leisure and Recreation: Time for Enjoyment
Access to leisure activities and recreational opportunities is also a significant contributor to a high standard of living. This includes access to parks, recreational facilities, cultural events, and opportunities for relaxation and recreation. These activities contribute to mental and physical well-being and enhance overall quality of life.
Environmental Well-being: The Sustainability Factor
Increasingly, environmental factors are recognized as crucial indicators of standard of living. A healthy environment provides essential resources and contributes to physical and mental well-being.
1. Environmental Quality: Clean Air and Water
Access to clean air and water is fundamental to health and well-being. Air and water pollution can lead to a range of health problems, reducing quality of life and increasing healthcare costs. The quality of the environment directly affects the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
2. Climate Change Resilience: Adapting to Change
The effects of climate change, such as extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and changes in agricultural yields, pose significant threats to standard of living. The ability of communities to adapt to and mitigate the impacts of climate change is a crucial factor. Investing in climate change adaptation measures is essential to safeguarding future well-being.
3. Access to Green Spaces: Nature's Contribution
Access to green spaces, such as parks and natural areas, provides numerous benefits for physical and mental health. These spaces offer opportunities for exercise, relaxation, and social interaction. The availability of green spaces in urban areas is particularly important for enhancing the quality of life in densely populated environments.
Measuring Standard of Living: Indices and Approaches
Various indices and approaches are used to measure standard of living, each with its strengths and limitations.
1. Human Development Index (HDI): A Holistic Approach
The HDI, developed by the United Nations Development Programme, is a widely used composite index that measures standard of living based on life expectancy, education levels, and per capita income. It offers a broader perspective than simply focusing on economic indicators.
2. Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI): Accounting for Sustainability
The GPI attempts to move beyond GDP by incorporating environmental and social factors into the measurement of economic progress. It accounts for factors such as environmental degradation, income inequality, and crime, providing a more nuanced picture of well-being.
3. Happy Planet Index (HPI): Focusing on Well-being
The HPI focuses specifically on well-being, combining life expectancy, experienced well-being, and ecological footprint. It aims to measure how efficiently countries convert environmental resources into long and happy lives.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Perspective
Evaluating someone's standard of living requires a holistic approach, considering a wide range of economic, social, and environmental factors. No single indicator can fully capture the complexity of this concept. By combining various indicators and considering the interconnectedness of these factors, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the quality of life enjoyed by individuals and populations. This nuanced perspective is crucial for informing policy decisions aimed at improving well-being and promoting sustainable development. The ongoing evolution of measurement methodologies reflects the growing understanding of the multifaceted nature of human well-being and the importance of incorporating diverse perspectives into assessments of standard of living.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Functions Of The Nervous System Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
The Goal Of Palliative Care Is To Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Did The Minnesota Study Of Twins Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Would You Describe An Intelligent Workplace Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
Chapter 7 Lord Of The Flies Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Factor Is Considered When Evaluating Someone's Standard Of Living . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
