Which Macronutrient Is Vital For Every Function Of The Body
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
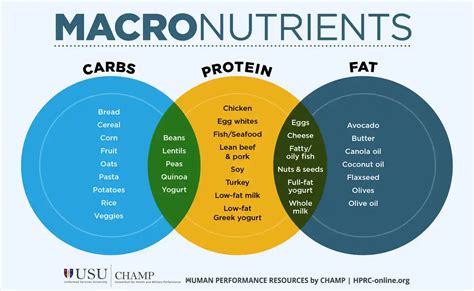
Table of Contents
Which Macronutrient is Vital for Every Function of the Body?
The human body is a complex machine, requiring a constant supply of energy and building blocks to function optimally. We obtain these essential components through our diet, primarily from three macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. While each plays a crucial role in various bodily processes, one stands out as fundamentally vital for every single function: protein.
The Irreplaceable Role of Protein
While carbohydrates provide immediate energy and fats offer stored energy and crucial cellular components, protein uniquely serves as the foundational building block for virtually every aspect of our physiology. This isn't merely a matter of providing energy; protein's significance lies in its role as the primary constituent of our cells, tissues, and organs. Without sufficient protein, the body's ability to repair, rebuild, and maintain itself dramatically diminishes.
Protein: The Body's Construction Material
Think of protein as the bricks and mortar of your body. It's the essential component of:
-
Muscles: From the largest muscles in your legs to the tiny ones in your eyes, protein is the primary structural component, responsible for strength, movement, and overall physical function. Muscle growth and repair are entirely dependent on adequate protein intake.
-
Bones: While calcium and other minerals are crucial for bone density, the structural framework itself is comprised of a protein matrix known as collagen. Without sufficient protein, bone strength and health are compromised.
-
Skin, Hair, and Nails: These structures are largely composed of proteins like collagen and keratin. Protein deficiency leads to brittle nails, thinning hair, and dry, easily damaged skin.
-
Organs: Every organ in your body, from your heart and liver to your kidneys and lungs, relies on proteins for structural integrity and functional capacity. Protein deficiencies can severely impair organ function, leading to a multitude of health problems.
-
Enzymes and Hormones: Enzymes are protein-based catalysts that facilitate countless biochemical reactions essential for life. Hormones, the chemical messengers regulating numerous bodily processes, are also frequently protein-based. Insufficient protein intake directly impacts hormonal balance and overall metabolic function.
-
Antibodies and Immune System: Antibodies, the proteins that fight off infections, are a crucial part of the immune system. A lack of protein weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses.
-
Neurotransmitters: These chemical messengers transmit signals between nerve cells, essential for brain function, mood regulation, and overall neurological health. Many neurotransmitters are protein-derived.
Protein's Diverse Functions Beyond Structure
Beyond its structural roles, protein engages in a vast array of physiological processes. It's involved in:
-
Transporting molecules: Proteins act as carriers, transporting oxygen (hemoglobin), nutrients, and other vital substances throughout the bloodstream.
-
Fluid balance: Proteins in the blood help regulate fluid balance between blood vessels and tissues.
-
Blood clotting: Several proteins are essential for the coagulation cascade, preventing excessive bleeding.
-
Cellular signaling: Proteins play a pivotal role in intercellular communication, ensuring coordinated function across the body's systems.
-
DNA replication and repair: Proteins are involved in the processes of DNA replication, ensuring accurate transmission of genetic information and repair of damaged DNA.
Why Protein Outweighs Carbohydrates and Fats in Overall Necessity
While carbohydrates and fats are essential for energy production and other functions, their roles are less universally fundamental than protein's. A body can temporarily function with reduced carbohydrate or fat intake (though this isn't recommended long-term), but a sustained protein deficiency leads to catastrophic consequences.
Carbohydrates: Primarily provide readily available energy. The body can store some carbohydrates as glycogen, but this is a limited reservoir. The body can also produce glucose through gluconeogenesis (from protein and fat), but this is less efficient.
Fats: Provide a concentrated source of energy, essential fatty acids for cell membranes, and insulation. While essential for numerous functions, the body can, to a certain extent, utilize alternative pathways for energy production and fatty acid synthesis in case of deficiency (though this is not optimal).
Protein: Forms the very fabric of the body. The body cannot synthesize protein at a sufficient rate to replace or repair damaged tissues without adequate dietary intake. Protein deficiency leads to a direct and significant impairment of every cellular and bodily function. The consequences of this deficiency are far-reaching and profoundly affect overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Protein Quality
It's not just about the quantity of protein you consume; the quality is equally critical. Complete proteins, found in animal sources like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy, contain all nine essential amino acids. These essential amino acids cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet. Incomplete proteins, found in plant sources like beans, lentils, and grains, lack one or more essential amino acids. Combining different plant-based protein sources throughout the day can provide all the necessary amino acids.
Determining Your Optimal Protein Intake
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for protein varies depending on factors like age, activity level, and overall health. Consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the optimal protein intake for your individual needs. They can assess your specific requirements and guide you towards a healthy and balanced dietary plan that meets your protein needs.
Signs of Protein Deficiency
Recognizing the signs of protein deficiency is essential for timely intervention. Symptoms can range from subtle to severe and include:
-
Muscle wasting and weakness: Loss of muscle mass and decreased strength.
-
Fatigue and lethargy: Reduced energy levels and persistent tiredness.
-
Edema (swelling): Fluid retention in the body, often seen in the legs and ankles.
-
Brittle nails and hair: Thinning hair, brittle nails, and dry, flaky skin.
-
Slow wound healing: Inability to repair tissue damage efficiently.
-
Increased susceptibility to infections: Weakened immune system and increased risk of illnesses.
-
Delayed growth in children: Stunted growth and developmental delays.
Conclusion: Protein – The Cornerstone of Health
In conclusion, while all macronutrients contribute to overall health and well-being, protein stands out as the macronutrient fundamentally vital for every function of the body. Its role as the primary building block of cells, tissues, and organs, along with its involvement in countless physiological processes, makes it indispensable for life. Prioritizing adequate protein intake, both in quantity and quality, is paramount for maintaining optimal health, supporting athletic performance, ensuring proper immune function, and promoting overall well-being. Don't underestimate the power of protein – it's the true foundation upon which your body's incredible capabilities are built. Consult a healthcare professional to determine your individual protein needs and develop a healthy and balanced dietary plan that prioritizes this essential macronutrient.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Part Of The Patient Record Is Classified As Administrative
May 09, 2025
-
A Recreational Flyer Is A Person Who
May 09, 2025
-
Tremors Hallucinations Delusions And Seizures Are All Symptoms Associated With
May 09, 2025
-
Which Internal Device Has The Largest Nonvolatile Storage Capacity
May 09, 2025
-
A Holder Of A Seller Server Certificate
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Macronutrient Is Vital For Every Function Of The Body . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.