Which Of The Following Corresponds To A Single Fascicle
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
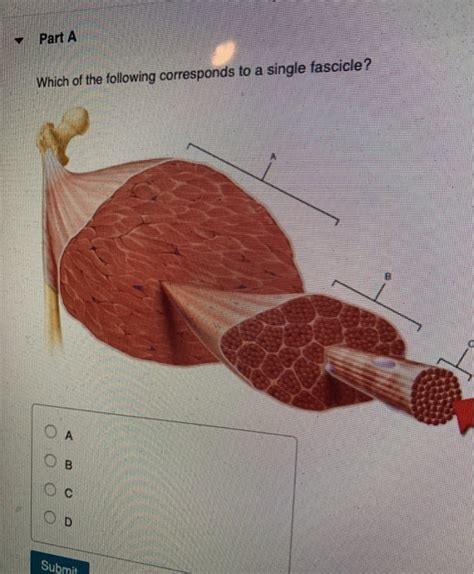
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Corresponds to a Single Fascicle? Exploring the Anatomy of Muscle Fiber Bundles
Understanding muscle anatomy is crucial for comprehending how our bodies move and function. Within the intricate structure of skeletal muscles lies a hierarchical organization of muscle fibers, culminating in the fascicle. This article delves into the precise definition of a fascicle, differentiating it from other muscle components, and clarifying which structures among a given set would accurately correspond to a single fascicle.
Understanding Muscle Structure: From Myofibrils to Muscle Belly
Before we pinpoint the structure corresponding to a single fascicle, let's build a foundational understanding of the hierarchical organization of skeletal muscle tissue:
1. Myofibrils: The Fundamental Units
The smallest functional units of a muscle fiber are myofibrils. These cylindrical structures are packed with repeating units called sarcomeres, which are the actual contractile units of the muscle. Myofibrils are comprised of actin and myosin filaments, the proteins responsible for muscle contraction through the sliding filament theory.
2. Muscle Fibers (Muscle Cells): Bundles of Myofibrils
Myofibrils are bundled together within individual muscle fibers, also known as muscle cells. Each muscle fiber is a long, cylindrical cell containing many myofibrils, mitochondria (for energy production), and other organelles necessary for muscle function. Muscle fibers are surrounded by a delicate connective tissue sheath called the endomysium.
3. Fascicles: Bundles of Muscle Fibers
Several muscle fibers are grouped together to form a fascicle. This is a distinct bundle of muscle fibers, a crucial intermediate organizational level within the muscle. The fascicles are themselves wrapped in a thicker layer of connective tissue called the perimysium. The arrangement of fascicles within a muscle significantly contributes to the overall shape and function of that muscle.
4. Muscle Belly (Muscle Body): The Whole Muscle
Finally, multiple fascicles are bundled together to create the muscle belly, also known as the muscle body – the entire muscle itself. The muscle belly is enclosed by a tough outer layer of connective tissue called the epimysium. Tendons, which attach muscles to bones, extend from the epimysium.
Distinguishing a Fascicle from Other Muscle Components
It's essential to differentiate a fascicle from other components of muscle tissue. Consider these key distinctions:
-
Fascicle vs. Myofibril: A fascicle contains numerous muscle fibers, each of which contains countless myofibrils. Myofibrils are significantly smaller and are the basic contractile units within a muscle fiber.
-
Fascicle vs. Muscle Fiber: A fascicle is a bundle of multiple muscle fibers. A muscle fiber is a single, elongated cell containing many myofibrils.
-
Fascicle vs. Muscle Belly: The muscle belly is the whole muscle, comprised of many fascicles grouped together. A fascicle is a smaller, distinct bundle within the muscle belly.
-
Fascicle vs. Perimysium: The perimysium is the connective tissue surrounding the fascicle. The fascicle is the bundle of muscle fibers itself. The perimysium provides structural support and facilitates the transmission of force.
Identifying a Single Fascicle: A Case Study
Let's imagine we have a microscopic image or a diagram showing different structures within a muscle. To identify a single fascicle, we'd look for a distinct, bundled grouping of muscle fibers. This bundle would be surrounded by the perimysium. We would not identify a single muscle fiber or myofibril as a fascicle. Likewise, the entire muscle belly wouldn't represent a single fascicle, but rather a collection of many fascicles.
Consider a scenario where we are presented with the following options:
A. A single muscle fiber B. A collection of myofibrils C. A bundle of muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium D. The entire muscle belly E. A single myofibril
The correct answer is C. Only option C accurately describes a single fascicle: a bundle of muscle fibers enclosed within the perimysium.
The Significance of Fascicle Arrangement
The arrangement of fascicles within a muscle is not random; it directly impacts the muscle's overall function and power. Different types of fascicle arrangements exist, including:
-
Parallel: Muscle fibers run parallel to the long axis of the muscle, generating considerable force over a long distance. Examples include the sartorius muscle and the rectus abdominis muscle.
-
Pennate: Muscle fibers attach obliquely (at an angle) to a central tendon. This arrangement maximizes the number of muscle fibers within a given space, resulting in greater power but less range of motion. There are different types of pennate arrangements, including unipennate, bipennate, and multipennate.
-
Convergent: Muscle fibers converge from a broad origin to a narrower insertion. This arrangement allows for a wide range of motion but often generates less force compared to parallel arrangements. The pectoralis major muscle is a good example of a convergent muscle.
-
Circular: Muscle fibers are arranged in concentric rings, encircling an opening. These muscles primarily function as sphincters, controlling the opening and closing of orifices. The orbicularis oculi (eye muscle) is a classic example.
Understanding these different fascicle arrangements is vital for understanding the unique functional capabilities of individual muscles and the musculoskeletal system as a whole.
Clinical Relevance: Fascicles and Muscle Injuries
Damage to fascicles can result in various muscle injuries, including strains and tears. The severity of the injury depends on the extent of damage to the fascicles and surrounding connective tissue. Clinicians use imaging techniques such as ultrasound and MRI to assess the degree of muscle damage, including identifying tears within specific fascicles. Understanding fascicle structure is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of muscle injuries.
Further Exploration: Advanced Microscopic Techniques
Advanced microscopic techniques, including electron microscopy, provide detailed visualization of fascicle structure at the ultrastructural level. These techniques allow researchers to examine the precise organization of muscle fibers within the fascicle, the distribution of connective tissue, and the intricate relationships between muscle fibers and the surrounding vasculature and nerves. This level of detail is crucial for advancing our understanding of muscle physiology and pathology.
Conclusion: The Fascicle - A Key Component of Muscle Architecture
The fascicle is a fundamental structural unit of skeletal muscle, representing a bundle of muscle fibers bound together by the perimysium. Understanding the organization of muscle tissue from the myofibril level to the fascicle and ultimately the muscle belly is critical for comprehending muscle function, contractility, and the mechanisms of various muscle injuries. By recognizing the characteristics that distinguish a fascicle from other muscle components, we can better appreciate the complexity and efficiency of the musculoskeletal system. The fascicle, therefore, stands as a crucial piece in the intricate puzzle of human movement and physiology. Continued research using advanced microscopic and imaging techniques promises to further illuminate the structure and function of this vital component of our muscular system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Floors Walls Ceiling Shelves And Racks
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Vehicle Uses The Chademo Standard Charging Port
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Do Master Regulatory Genes Function In Cell Differentiation
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is Abbot Suger Holding In The Image Below
Mar 25, 2025
-
Wellness And Self Care Stress Causes Effects And Management
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Corresponds To A Single Fascicle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
