Which Of The Following Events Occurs During Metaphase Of Mitosis
Breaking News Today
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
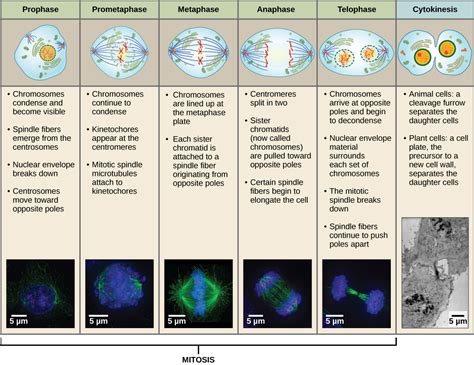
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Events Occurs During Metaphase of Mitosis? A Deep Dive into Cell Division
Mitosis, the process of cell division resulting in two identical daughter cells, is a fundamental aspect of life. Understanding the distinct phases of mitosis, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, is crucial for comprehending cell growth, repair, and reproduction. This article delves into the specifics of metaphase, exploring the key events that occur during this pivotal stage and differentiating it from other phases of mitosis.
Understanding the Stages of Mitosis: A Brief Overview
Before diving into the details of metaphase, let's briefly review the other stages of mitosis:
Prophase: The Preparatory Stage
Prophase marks the beginning of mitosis. During this phase, several crucial events prepare the cell for chromosome separation:
- Chromatin Condensation: The loosely organized chromatin fibers condense into highly organized, visible structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids joined at the centromere.
- Nuclear Envelope Breakdown: The nuclear envelope, which surrounds the nucleus, begins to disintegrate, allowing the chromosomes to move freely within the cytoplasm.
- Spindle Fiber Formation: The centrosomes, which organize microtubules, migrate to opposite poles of the cell. Microtubules begin to assemble, forming the mitotic spindle, a crucial structure for chromosome movement.
Metaphase: Alignment at the Equator
Metaphase is characterized by the precise alignment of chromosomes along the metaphase plate, an imaginary plane equidistant from the two poles of the cell. This alignment is critical for ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete and identical set of chromosomes. We'll explore this in much more detail in the following sections.
Anaphase: Sister Chromatid Separation
In anaphase, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell by the shortening of the kinetochore microtubules. This ensures that each daughter cell receives one copy of each chromosome.
Telophase: The Final Stage
Telophase is the final stage of mitosis. During this phase, the chromosomes arrive at the poles of the cell, the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes, and the chromosomes begin to decondense. This is followed by cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm, resulting in two separate daughter cells.
Metaphase: The Crucial Alignment
Metaphase is a critical checkpoint in the cell cycle. Accurate chromosome alignment is essential for ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete and identical set of chromosomes. If chromosomes fail to align properly, the cell cycle can arrest, preventing the formation of genetically abnormal daughter cells. This checkpoint mechanism is vital for maintaining genomic stability.
Key Events Occurring During Metaphase:
-
Chromosome Congression: Chromosomes are not passively pulled to the metaphase plate; instead, they actively move towards it through a complex process called congression. This involves the dynamic interaction of microtubules with the kinetochores, protein structures located at the centromere of each chromosome. Kinetochore microtubules attach to the kinetochores, and through a process involving motor proteins and microtubule polymerization/depolymerization, the chromosomes are guided to the metaphase plate.
-
Metaphase Plate Alignment: The hallmark of metaphase is the precise alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate. This ensures that each chromosome is equidistant from the two poles of the cell, maximizing the chances of equal chromosome segregation during anaphase. The alignment is not a static event but rather a dynamic equilibrium maintained by the continuous interaction of microtubules with the kinetochores.
-
Spindle Checkpoint Activation: The cell possesses a sophisticated surveillance mechanism known as the spindle checkpoint, also called the metaphase-to-anaphase transition checkpoint. This checkpoint monitors the attachment of kinetochore microtubules to chromosomes. If a chromosome is not properly attached to the spindle, the checkpoint signals prevent the cell from proceeding to anaphase, preventing aneuploidy (abnormal chromosome number) in daughter cells. This checkpoint involves several proteins that detect unattached kinetochores and inhibit the activation of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), a crucial enzyme complex that triggers the onset of anaphase.
-
Tension at the Kinetochores: Proper attachment of kinetochore microtubules to the chromosomes results in tension at the kinetochores. This tension is essential for proper chromosome segregation and is detected by the spindle checkpoint. The tension is generated by the pulling forces exerted by the microtubules from opposite poles of the cell. Lack of tension is a signal to the spindle checkpoint that the chromosome is not correctly attached.
-
Preparation for Anaphase: Metaphase serves as a critical preparatory phase for anaphase. The precise alignment and attachment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate ensures that sister chromatids will be efficiently separated and distributed to daughter cells during anaphase. The activation of the APC/C at the end of metaphase is the signal that initiates the separation of sister chromatids and the onset of anaphase.
Differentiating Metaphase from Other Mitotic Phases
It's crucial to distinguish metaphase from other mitotic phases to accurately understand the sequence of events during cell division.
Metaphase vs. Prophase:
| Feature | Prophase | Metaphase |
|---|---|---|
| Chromosomes | Condensing; not yet fully condensed | Fully condensed; aligned at metaphase plate |
| Nuclear Envelope | Intact or beginning to disintegrate | Completely disintegrated |
| Spindle Fibers | Forming | Fully formed; chromosomes attached |
| Chromosome Alignment | No alignment | Aligned at metaphase plate |
Metaphase vs. Anaphase:
| Feature | Metaphase | Anaphase |
|---|---|---|
| Sister Chromatids | Joined at the centromere | Separated and moving to opposite poles |
| Chromosome Movement | No movement of chromosomes | Sister chromatids separating; moving to poles |
| Spindle Fibers | Attached to kinetochores; under tension | Shortening; pulling chromatids to poles |
Metaphase vs. Telophase:
| Feature | Metaphase | Telophase |
|---|---|---|
| Chromosomes | Aligned at metaphase plate | Arriving at poles; decondensed |
| Nuclear Envelope | Absent | Reforming around chromosomes |
| Spindle Fibers | Present; fully functional | Disassembling |
The Importance of Accurate Metaphase: Consequences of Errors
Accurate chromosome segregation during metaphase is paramount for maintaining genomic integrity. Errors in metaphase can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Aneuploidy: An abnormal number of chromosomes in daughter cells. This can result in developmental abnormalities, cancer, and other genetic disorders. Aneuploidy is a significant driver of tumorigenesis.
- Chromosomal Instability: Increased propensity for chromosomal rearrangements, such as translocations and deletions. This can further contribute to genomic instability and increase the risk of cancer.
- Cell Death: If errors in metaphase are severe, the cell may undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death) to prevent the propagation of genetically damaged daughter cells. This is a safeguard mechanism to prevent the development of abnormal cells.
Conclusion: Metaphase – A Precise and Regulated Process
Metaphase is a highly regulated and precisely orchestrated stage of mitosis. The accurate alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate and the subsequent separation of sister chromatids are essential for generating genetically identical daughter cells. The spindle checkpoint plays a crucial role in ensuring the fidelity of chromosome segregation, preventing the propagation of errors that could have disastrous consequences for the organism. Understanding the intricate details of metaphase provides valuable insights into the fundamental mechanisms of cell division and its vital role in maintaining genomic stability. Disruptions in this carefully choreographed process can have profound implications for health and disease, highlighting the importance of this often-overlooked stage of mitosis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Function Of Skin
Mar 31, 2025
-
Anything That Takes Up Space And Has Mass
Mar 31, 2025
-
An Example Of A Latent Viral Infection Is Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Why Are Olfaction And Gustation Called Chemical Senses
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Does International Trade Lead To Specialization Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Events Occurs During Metaphase Of Mitosis . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
