Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Proteins
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
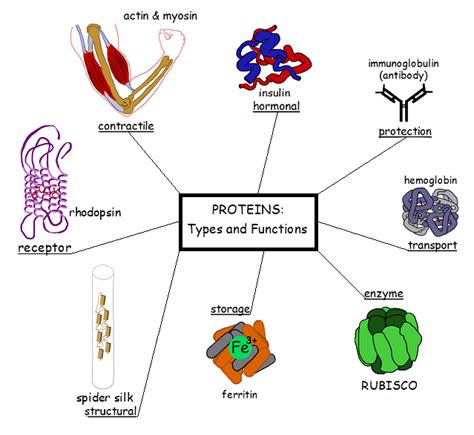
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Function of Proteins? A Deep Dive into the Amazing World of Proteins
Proteins: the workhorses of the cell. These complex molecules are fundamental to virtually every biological process, performing a myriad of functions essential for life. Understanding their diverse roles is crucial to comprehending the intricacies of biology and the mechanisms behind health and disease. This comprehensive article delves into the multifaceted functions of proteins, answering the question: which of the following is a function of proteins? We’ll explore numerous protein functions, highlighting their significance and providing examples.
The Amazing Versatility of Proteins: A Multitude of Roles
Proteins are not a single entity, but rather a vast family of molecules, each with a unique structure and function. Their versatility stems from their ability to fold into complex three-dimensional shapes, dictated by their amino acid sequence. This precise folding allows proteins to interact specifically with other molecules, mediating countless biological processes.
Let's explore some of the key functional categories of proteins:
1. Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life
Perhaps the most well-known function of proteins is their role as enzymes. Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate the rate of chemical reactions within cells. Without enzymes, many essential metabolic processes would occur far too slowly to sustain life. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed.
Examples:
- Amylase: Breaks down starch into sugars.
- Lactase: Breaks down lactose (milk sugar).
- DNA polymerase: Synthesizes DNA.
- Proteases: Break down proteins.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats.
Keywords: enzymes, catalysts, metabolism, biochemical reactions, activation energy
2. Structural Proteins: Providing Support and Shape
Structural proteins provide support and shape to cells and tissues. They are often fibrous in nature and possess high tensile strength.
Examples:
- Collagen: A major component of connective tissues like skin, tendons, and cartilage. Provides strength and elasticity.
- Elastin: Allows tissues to stretch and recoil, found in lungs and blood vessels.
- Keratin: Forms the protective outer layer of skin, hair, and nails.
- Actin and Myosin: Contractile proteins responsible for muscle movement.
- Tubulin: Forms microtubules, part of the cytoskeleton providing cell shape and support.
Keywords: structural proteins, collagen, elastin, keratin, cytoskeleton, connective tissue, muscle contraction
3. Transport Proteins: Facilitating Movement
Transport proteins facilitate the movement of molecules across cell membranes. Some act as channels or pores, allowing specific molecules to pass through, while others bind to molecules and carry them across the membrane.
Examples:
- Hemoglobin: Carries oxygen in the blood.
- Membrane transport proteins: Facilitate the movement of ions and small molecules across cell membranes (e.g., glucose transporters, ion channels).
- Lipoproteins: Transport lipids in the blood.
Keywords: transport proteins, hemoglobin, membrane transport, ion channels, glucose transporters, lipoproteins
4. Hormones: Chemical Messengers
Many hormones are proteins. These chemical messengers are secreted by glands and travel through the bloodstream to target cells, influencing their activity.
Examples:
- Insulin: Regulates blood glucose levels.
- Growth hormone: Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
- Glucagon: Increases blood glucose levels.
Keywords: hormones, insulin, growth hormone, glucagon, endocrine system, chemical messengers
5. Receptor Proteins: Receiving Signals
Receptor proteins are embedded in cell membranes or located within cells. They bind to specific signaling molecules (ligands), triggering a cellular response. This is crucial for cell communication and regulation.
Examples:
- Neurotransmitter receptors: Bind to neurotransmitters at synapses, transmitting nerve impulses.
- Hormone receptors: Bind to hormones, initiating specific cellular responses.
- Growth factor receptors: Bind to growth factors, regulating cell growth and differentiation.
Keywords: receptor proteins, ligands, cell signaling, neurotransmitters, hormones, growth factors
6. Defense Proteins: Protecting the Body
Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are a type of protein that plays a critical role in the immune system. They recognize and bind to foreign substances (antigens), neutralizing them and marking them for destruction.
Examples:
- Antibodies (Immunoglobulins): Recognize and neutralize pathogens.
- Complement proteins: Enhance the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promoting inflammation, and attacking the pathogen's cell membrane.
Keywords: defense proteins, antibodies, immunoglobulins, immune system, antigens, complement proteins
7. Storage Proteins: Storing Essential Molecules
Storage proteins bind and store essential molecules, releasing them when needed.
Examples:
- Ferritin: Stores iron in the liver and other tissues.
- Casein: A milk protein that stores amino acids for infant development.
Keywords: storage proteins, ferritin, casein, iron storage, amino acid storage
8. Motor Proteins: Generating Movement
Motor proteins generate movement within cells and tissues. They use ATP (energy) to move along cytoskeletal filaments, transporting cargo or causing cellular structures to change shape.
Examples:
- Myosin: Involved in muscle contraction and intracellular transport.
- Kinesin and Dynein: Transport organelles and vesicles along microtubules.
Keywords: motor proteins, myosin, kinesin, dynein, intracellular transport, muscle contraction, ATP
9. Gene Regulatory Proteins: Controlling Gene Expression
These proteins bind to DNA, regulating the transcription of genes. This controls which genes are expressed and when, influencing cellular development and function.
Examples:
- Transcription factors: Bind to DNA and regulate gene transcription.
- Repressors: Inhibit gene expression.
- Activators: Enhance gene expression.
Keywords: gene regulatory proteins, transcription factors, repressors, activators, gene expression, DNA binding proteins
10. Other Important Protein Functions:
Proteins are also involved in numerous other critical processes, including:
- Blood clotting: Proteins like fibrinogen are essential for blood clot formation.
- Cell adhesion: Proteins mediate cell-cell interactions and adhesion to the extracellular matrix.
- Signal transduction: Proteins relay signals from the cell surface to the interior, triggering specific responses.
- Chaperones: Help other proteins fold correctly.
The Importance of Protein Structure-Function Relationship
The remarkable diversity of protein function is directly linked to their unique three-dimensional structures. The amino acid sequence determines how a protein folds, and this folding creates specific binding sites and functional domains. Even small changes in the amino acid sequence can significantly alter a protein's structure and function, leading to disease.
This relationship between structure and function is crucial in understanding how proteins work and how mutations or other alterations can disrupt their function.
Conclusion: Proteins – The Cornerstones of Life
This comprehensive exploration reveals the staggering versatility of proteins. From catalyzing biochemical reactions as enzymes to providing structural support, transmitting signals, defending against pathogens, and regulating gene expression, proteins are the fundamental building blocks and operational machinery of life. Understanding their diverse roles is critical for advancements in medicine, biotechnology, and our fundamental understanding of biology itself. The answer to "Which of the following is a function of proteins?" is essentially, almost anything essential for life. They are the true workhorses of the cellular world, and their intricate functions continue to fascinate and inspire scientific investigation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Select The Issues Of Development Among The Following
Apr 01, 2025
-
For Adults Adolescents You Should Call Activate
Apr 01, 2025
-
Renin Is Released In Response To
Apr 01, 2025
-
Your Company Manufactures 72 Hour Emergency Kit
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Incident Commander Establishes Incident Objectives That Include
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Proteins . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
