Which Of The Following Is Accurate Regarding Status Asthmaticus
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
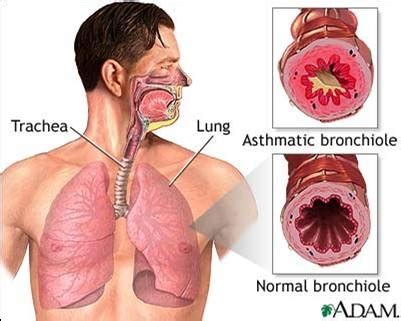
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Is Accurate Regarding Status Asthmaticus
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following is Accurate Regarding Status Asthmaticus?
- Defining Status Asthmaticus: Beyond a Simple Exacerbation
- Key Characteristics Differentiating Status Asthmaticus:
- Accurate Statements Regarding Status Asthmaticus: Dispelling Myths
- Myth 1: "Status asthmaticus is just a severe asthma attack that will resolve on its own."
- Myth 2: "Only long-term asthma sufferers develop status asthmaticus."
- Myth 3: "Once status asthmaticus is resolved, it's unlikely to recur."
- Myth 4: "Treatment solely focuses on bronchodilators in status asthmaticus."
- Myth 5: "Home treatment is sufficient for managing status asthmaticus."
- Accurate Statements Regarding Diagnosis and Treatment: A Closer Look
- Accurate Statement 1: Diagnosis relies on clinical presentation and response to treatment.
- Accurate Statement 2: Treatment involves a multi-pronged approach.
- Accurate Statement 3: Early recognition and rapid intervention are crucial for improving outcomes.
- Accurate Statement 4: Long-term management is essential to prevent recurrence.
- Conclusion: Understanding Status Asthmaticus for Improved Outcomes
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following is Accurate Regarding Status Asthmaticus?
Status asthmaticus is a life-threatening condition characterized by a severe, prolonged asthma exacerbation that is unresponsive to standard treatment. Understanding its nuances is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals with asthma alike. This article delves deep into the accurate statements regarding status asthmaticus, debunking common misconceptions and clarifying critical aspects of this medical emergency.
Defining Status Asthmaticus: Beyond a Simple Exacerbation
Status asthmaticus is not simply a severe asthma attack. While it presents with similar symptoms, its defining characteristic lies in its duration and resistance to treatment. A typical asthma exacerbation usually responds to bronchodilators within a reasonable timeframe. In status asthmaticus, however, bronchospasm persists despite aggressive treatment, leading to a potentially fatal deterioration of respiratory function. The crucial distinction lies in the unresponsiveness to initial therapy, highlighting the need for immediate escalation of care.
Key Characteristics Differentiating Status Asthmaticus:
-
Duration: The most crucial defining factor is the prolonged nature of the episode. While the exact timeframe isn't rigidly defined, most medical professionals agree that an exacerbation lasting more than 12 hours despite treatment warrants strong consideration for status asthmaticus.
-
Severity: The severity of symptoms is significantly heightened. Patients experience extreme shortness of breath, wheezing that may be absent (silent chest, a grave sign), use of accessory muscles for breathing, and a potentially life-threatening decrease in oxygen saturation levels.
-
Unresponsiveness to Treatment: This is the hallmark of status asthmaticus. Standard treatments like inhaled beta-agonists (e.g., albuterol) and ipratropium bromide provide minimal or no relief. This lack of response necessitates a rapid escalation of treatment strategies.
Accurate Statements Regarding Status Asthmaticus: Dispelling Myths
Many misconceptions surround status asthmaticus. Let's address some common inaccurate statements and replace them with factual information:
Myth 1: "Status asthmaticus is just a severe asthma attack that will resolve on its own."
Fact: Status asthmaticus is a medical emergency requiring immediate and aggressive intervention. It will not resolve spontaneously and can rapidly lead to respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and death if left untreated. Early recognition and prompt treatment are paramount.
Myth 2: "Only long-term asthma sufferers develop status asthmaticus."
Fact: While individuals with a history of poorly controlled asthma are at higher risk, anyone with asthma can experience status asthmaticus, including those with previously mild disease. Factors like respiratory infections, allergens, or environmental triggers can precipitate the condition even in individuals with seemingly well-controlled asthma.
Myth 3: "Once status asthmaticus is resolved, it's unlikely to recur."
Fact: Status asthmaticus significantly increases the risk of future episodes. Patients who have experienced status asthmaticus require aggressive, long-term management to prevent recurrence. This typically involves optimizing asthma control plans, regular monitoring, and potentially adjusting medication regimens.
Myth 4: "Treatment solely focuses on bronchodilators in status asthmaticus."
Fact: While bronchodilators remain a cornerstone of treatment, status asthmaticus management necessitates a multimodal approach. This includes high-dose inhaled and systemic corticosteroids to reduce airway inflammation, intravenous fluids to maintain hydration, and oxygen therapy to address hypoxemia. In severe cases, mechanical ventilation might be necessary.
Myth 5: "Home treatment is sufficient for managing status asthmaticus."
Fact: Status asthmaticus is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate hospitalization and intensive care. Home treatment is inadequate and potentially dangerous. Delaying professional medical assistance significantly increases the risk of morbidity and mortality.
Accurate Statements Regarding Diagnosis and Treatment: A Closer Look
Let's delve into the accurate aspects of diagnosing and managing status asthmaticus:
Accurate Statement 1: Diagnosis relies on clinical presentation and response to treatment.
Status asthmaticus lacks a definitive diagnostic test. The diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on:
- Persistent and severe symptoms despite treatment.
- Prolonged duration of the exacerbation (typically >12 hours).
- Objective measurements: Arterial blood gas analysis revealing hypoxemia and hypercapnia, and peak expiratory flow (PEF) readings significantly below predicted values.
- Clinical signs: Use of accessory muscles for breathing, tachypnea, tachycardia, and potentially decreased or absent breath sounds (silent chest).
Accurate Statement 2: Treatment involves a multi-pronged approach.
Treatment focuses on reversing bronchospasm and reducing airway inflammation. Key interventions include:
- High-dose inhaled and systemic corticosteroids: To decrease inflammation.
- High-flow oxygen therapy: To improve oxygenation.
- Nebulized beta-agonists: To relax airway smooth muscles.
- Ipratropium bromide: To further relax airways.
- Magnesium sulfate: An IV medication with bronchodilating effects.
- Intravenous fluids: To maintain hydration.
- Mechanical ventilation: In severe cases requiring respiratory support.
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of vital signs, oxygen saturation, and arterial blood gases.
Accurate Statement 3: Early recognition and rapid intervention are crucial for improving outcomes.
Delaying treatment significantly increases the risk of complications, including respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and death. Immediate recognition of the condition and prompt initiation of treatment are critical for optimizing patient outcomes.
Accurate Statement 4: Long-term management is essential to prevent recurrence.
Following recovery from status asthmaticus, long-term management is crucial to prevent future episodes. This often involves:
- Regular monitoring: Frequent follow-up appointments with a physician.
- Optimized asthma control plan: Adjustments to medication and lifestyle factors.
- Education: Patient education on asthma triggers, medication use, and recognition of worsening symptoms.
- Allergy testing: To identify and avoid potential triggers.
- Peak flow monitoring: To track lung function and identify early signs of exacerbation.
Conclusion: Understanding Status Asthmaticus for Improved Outcomes
Status asthmaticus is a serious medical emergency demanding immediate and aggressive intervention. Understanding the accurate information about this condition is vital for both healthcare professionals and individuals with asthma. Early recognition, prompt treatment, and diligent long-term management are critical factors in preventing the devastating consequences of this life-threatening condition. The key takeaway is that status asthmaticus is not simply a severe asthma attack; it's a distinct clinical entity requiring specialized care to improve chances of survival and prevent long-term complications. This information should empower individuals with asthma to seek immediate medical attention if they experience prolonged, severe symptoms unresponsive to standard treatment, thus ensuring better health outcomes and potentially saving lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Ati Pn Pharmacology Proctored Exam 2023 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Difference Between Viruses And Bacterial Infections Is Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
2018 International Practice Exam Mcq Apush Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are The Terrorism Threat Levels Regional And Local Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Your Niece Is Politically Active In The Climate Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Accurate Regarding Status Asthmaticus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
