Which Of The Following Is True About Type 1 Diabetes
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 7 min read
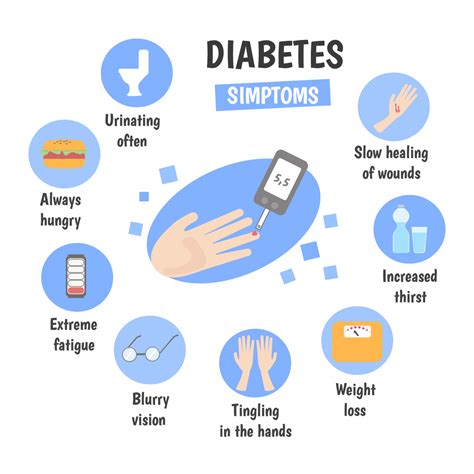
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is True About Type 1 Diabetes? Demystifying the Facts
Type 1 diabetes, often referred to as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects how your body regulates blood sugar. Understanding the nuances of this condition is crucial for effective management and preventing long-term complications. Let's delve into the common misconceptions surrounding Type 1 diabetes and clarify which statements are truly accurate.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes: Separating Fact from Fiction
Before we tackle the "true or false" aspects, let's establish a foundational understanding of Type 1 diabetes. In this condition, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone essential for transporting glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream into the body's cells, where it's used for energy. Without sufficient insulin, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). This hyperglycemia can cause a cascade of severe health problems if left unmanaged.
Key Characteristics of Type 1 Diabetes:
- Autoimmune Disease: The immune system's attack on pancreatic beta cells is the hallmark of Type 1 diabetes. This is a crucial distinction from Type 2 diabetes, which is primarily characterized by insulin resistance.
- Insulin Dependence: Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to survive. This is because their bodies cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar effectively.
- Onset Typically in Childhood or Adolescence: While Type 1 can develop at any age, it most commonly manifests during childhood or adolescence, hence the term "juvenile diabetes." However, it can also develop in adults.
- Genetic Predisposition: While not directly inherited, there's a genetic component influencing susceptibility to Type 1 diabetes. Having a family history increases the risk, but it doesn't guarantee development of the condition.
- No Cure: Currently, there is no cure for Type 1 diabetes. However, advancements in research offer hope for future treatments, including immunotherapy and stem cell therapy.
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Type 1 Diabetes
Now, let's tackle some frequently encountered statements about Type 1 diabetes and determine their accuracy:
1. "Type 1 diabetes is caused by eating too much sugar."
FALSE. This is a pervasive myth. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, not a result of dietary choices. The immune system's attack on the pancreas is the underlying cause, regardless of an individual's diet. While a healthy diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels in Type 1 diabetes, it doesn't cause the condition.
2. "People with Type 1 diabetes can manage their condition through diet and exercise alone."
FALSE. While diet and exercise are crucial for managing Type 1 diabetes, they are insufficient on their own. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy to survive. Diet and exercise help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health, but they cannot replace the essential role of insulin.
3. "Type 1 diabetes is contagious."
FALSE. Type 1 diabetes is not contagious. It's an autoimmune disease, not an infection. It cannot be spread through contact with an individual who has the condition.
4. "People with Type 1 diabetes can't live long, healthy lives."
FALSE. With proper management, people with Type 1 diabetes can enjoy long, healthy lives. This involves diligent monitoring of blood sugar levels, adhering to an individualized treatment plan (including insulin therapy), maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and receiving regular medical care. Advancements in technology, such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps, have significantly improved the quality of life for individuals with Type 1 diabetes.
5. "Type 1 diabetes is more common in overweight individuals."
FALSE. Type 1 diabetes is not directly linked to obesity. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes has a strong association with obesity and insulin resistance. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks its own insulin-producing cells.
6. "All symptoms of Type 1 diabetes are obvious and easily noticeable."
FALSE. The symptoms of Type 1 diabetes can be subtle and easily overlooked in the initial stages. While some individuals experience classic symptoms such as excessive thirst (polydipsia), frequent urination (polyuria), unexplained weight loss, and increased hunger (polyphagia), others may have less noticeable symptoms or even be asymptomatic. This is why regular health checkups are important, particularly for those with a family history of diabetes.
7. "Type 1 diabetes only affects children."
FALSE. While it's more common in children and adolescents, Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age. While the onset in adulthood is less frequent, it's important to remember that adults can also be diagnosed with this condition.
8. "Stress can cause Type 1 diabetes."
FALSE. Stress itself doesn't cause Type 1 diabetes. While stress can exacerbate existing conditions and potentially affect blood sugar control in those with Type 1 diabetes, it's not the underlying cause of the autoimmune attack on the pancreas. The precise cause of Type 1 diabetes is still under investigation, but it's linked to genetic predisposition and environmental factors, not solely stress.
9. "Once diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes, your life is drastically altered."
FALSE. While diagnosis requires significant lifestyle adjustments, it doesn't necessarily mean a drastic alteration of one's life. With proper management, education, support systems, and technological advancements, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can maintain active, fulfilling lives. The key is proactive management and a focus on overall well-being.
10. "There is no hope for a cure for Type 1 diabetes."
FALSE. While there's no cure currently available, extensive research is underway to find a cure or effective preventative measures. Several promising avenues of research include immunotherapy, stem cell therapy, and islet cell transplantation. While a cure may not be immediately available, ongoing research offers significant hope for the future.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes: Strategies for Effective Management
Managing Type 1 diabetes effectively involves a multifaceted approach that requires dedication and commitment. Here are some key strategies:
1. Insulin Therapy: The Cornerstone of Management
Insulin therapy is essential for survival in Type 1 diabetes. This can involve various methods, including multiple daily injections (MDI), continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) using an insulin pump, or a combination of both. The type and dosage of insulin are tailored to individual needs and are adjusted based on blood sugar monitoring and lifestyle factors.
2. Blood Glucose Monitoring: Staying Informed
Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for understanding how blood sugar levels respond to insulin, food, and activity. This information allows for adjustments to insulin doses and lifestyle choices to maintain optimal blood sugar control. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time glucose data and can significantly simplify blood sugar monitoring.
3. Healthy Diet: Fueling Your Body
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is vital for managing blood sugar levels. This involves carefully monitoring carbohydrate intake and understanding how different foods affect blood sugar. Working with a registered dietitian specializing in diabetes can be incredibly helpful in developing a personalized meal plan.
4. Regular Physical Activity: Keeping Active
Regular physical activity is beneficial for overall health and can improve insulin sensitivity. This doesn't necessarily mean intense workouts; moderate exercise like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling can have a positive impact on blood sugar control. Consult your doctor before starting a new exercise regimen.
5. Medical Check-ups and Professional Support: Ongoing Care
Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring long-term complications associated with diabetes. This includes monitoring kidney function, eye health, and nerve health. Developing a strong relationship with your healthcare team, including your doctor, diabetes educator, and dietitian, is crucial for effective management and support.
6. Emotional Wellbeing: Addressing Psychological Aspects
Living with a chronic condition like Type 1 diabetes can take an emotional toll. It's important to prioritize mental health and seek support when needed. This might involve talking to a therapist, joining a support group, or finding healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress and anxiety.
Conclusion: Living Well with Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a significant health challenge, but it's not a life sentence. With proper management, individuals can live long, healthy, and fulfilling lives. Understanding the facts, dispelling misconceptions, and proactively managing the condition are vital for achieving optimal health outcomes. Remember to seek guidance from healthcare professionals to develop a personalized management plan tailored to your specific needs and lifestyle. The ongoing advancements in diabetes research continue to offer hope for a brighter future for those living with Type 1 diabetes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Decidimos Venir A Este Restaurante Porque Mi Jefe
Apr 02, 2025
-
Skills Module 3 0 Intravenous Medication Administration Posttest
Apr 02, 2025
-
America The Story Of Us Episode 9 Bust
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Did Kuba Artists Decorate Their Ngady Amawaash Masks
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Research Study Using Naturalistic Observation Entails
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is True About Type 1 Diabetes . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
