Which Of The Following Scenarios Would Typically Utilize 802.1x Authentication
Breaking News Today
Mar 30, 2025 · 8 min read
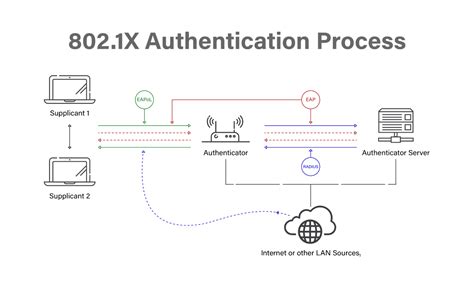
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Scenarios Would Typically Utilize 802.1x Authentication?
802.1X authentication, also known as "Port-based Network Access Control" (PNAC), is a crucial security protocol used to control access to network resources. It's not a standalone technology but rather a framework that leverages other authentication methods like EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) to verify a user or device's identity before granting network access. Understanding when to employ 802.1X is critical for securing your network effectively. Let's delve into various scenarios where 802.1X shines.
Scenario 1: Securing Wireless Networks (Wi-Fi)
High-Security Wireless Networks Require Robust Authentication: 802.1X is a cornerstone of securing Wi-Fi networks, particularly in environments demanding high security. This contrasts with simpler methods like using a pre-shared key (PSK), which offers less granular control and is susceptible to vulnerabilities. With 802.1X, each device connecting to the wireless network undergoes individual authentication. This means that even if one device is compromised, the others remain protected.
How 802.1X Improves Wireless Security:
- Stronger Authentication Methods: 802.1X utilizes various EAP methods (e.g., EAP-TLS, EAP-FAST, PEAP) that provide stronger authentication compared to PSK. These methods often involve digital certificates or strong password-based authentication mechanisms, making it harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Granular Access Control: It enables network administrators to implement fine-grained access control policies. They can restrict access based on user roles, device types, or even time of day. This ensures that only authorized users and devices can connect to the wireless network.
- Enhanced Security Posture: By implementing 802.1X, organizations enhance their overall security posture by minimizing the attack surface. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security incidents. This is especially important in sensitive environments such as healthcare facilities, financial institutions, and government agencies.
Typical Examples:
- Corporate Offices: Protecting sensitive company data from unauthorized access.
- Hospitals: Securing medical devices and patient information on wireless networks.
- Educational Institutions: Controlling student and faculty access to the campus Wi-Fi.
- Government Agencies: Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive government data.
Scenario 2: Securing Wired Networks (Ethernet)
Beyond Wireless: Protecting Wired Connections: While often associated with Wi-Fi, 802.1X authentication can equally secure wired networks using Ethernet connections. This is particularly important in environments where sensitive data is handled or where unauthorized access could have significant consequences. Using 802.1X on wired networks provides a consistent security policy across all network access points.
Benefits of 802.1X on Wired Networks:
- Guest Access Control: Controlling access for temporary users or visitors, ensuring they only have access to designated network segments.
- Device Security: Authenticating devices before granting them access to the network, helping to prevent malicious devices from connecting.
- Enhanced Network Segmentation: Creating isolated network segments based on user authentication, limiting the impact of a security breach.
Typical Examples:
- Data Centers: Controlling access to servers and other critical infrastructure.
- Corporate Offices: Securing workstations and servers connected via Ethernet.
- Financial Institutions: Protecting sensitive financial data from unauthorized access.
- Hotels & Public Spaces: Providing secure wired internet access to guests while maintaining a high level of security.
Scenario 3: Network Access Control (NAC) Implementation
802.1X as the Foundation of NAC: 802.1X forms a critical part of many Network Access Control (NAC) systems. NAC solutions go beyond basic authentication; they often include features like device posture assessment, malware detection, and automated remediation. 802.1X acts as the gateway, controlling initial network access before other NAC checks are performed.
How 802.1X Integrates with NAC:
- Initial Authentication: 802.1X verifies the identity of the user or device attempting to connect to the network.
- Policy Enforcement: After successful authentication, NAC policies are enforced based on the user's role and the device's posture.
- Access Control: The NAC system can grant or deny access to specific network resources based on the outcome of the authentication and posture assessment.
- Remediation: If a device is found to be non-compliant (e.g., lacking antivirus software), the NAC system can automatically remediate the issue or quarantine the device.
Scenario 4: Guest Network Access
Secure and Controlled Guest Access: Providing guest Wi-Fi access is common in many organizations. However, using standard Wi-Fi networks with PSKs for guest access is risky; it exposes the internal network to potential vulnerabilities. 802.1X enables the creation of secure guest networks with controlled access and isolation from the corporate network.
Implementing Secure Guest Wi-Fi with 802.1X:
- Separate VLANs: Assigning guest devices to separate VLANs isolates them from the main corporate network, minimizing the risk of internal network compromise.
- Limited Access: Restricting access to only specific network resources, such as the internet, prevents guests from accessing sensitive company data.
- Time-Based Access: Setting time limits for guest access, ensuring that users are not granted continuous access.
- Authentication Methods: Utilizing simpler EAP methods such as EAP-TTLS or EAP-PEAP for guest access to balance security and ease of use.
Scenario 5: Securing Voice over IP (VoIP) Phones
Protecting VoIP Infrastructure: VoIP systems are increasingly used for communication, and their security is critical. 802.1X can protect these systems from unauthorized access and eavesdropping. Authenticating VoIP phones ensures only legitimate devices can access the network and participate in calls.
802.1X in VoIP Security:
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: Only authenticated VoIP phones are permitted to connect to the network, thus preventing unauthorized users from making or intercepting calls.
- Network Security: Protecting the VoIP infrastructure from malicious attacks and ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
- Quality of Service (QoS): 802.1X can be integrated with QoS policies, providing priority to VoIP traffic to ensure call quality.
Scenario 6: Protecting IoT Devices
Securing the Internet of Things: The proliferation of IoT devices presents significant security challenges. Many IoT devices lack robust security features, making them vulnerable to attacks. 802.1X helps to control access to the network for these devices.
802.1X in IoT Security:
- Device Authentication: Verifying the identity of each IoT device before granting access.
- Access Control: Limiting access to specific network segments or resources based on the device's role and security posture.
- Policy Enforcement: Enforcing security policies, such as encryption and firmware updates, to improve the overall security of IoT devices.
Scenario 7: VPN Access Control
Improving VPN Security: While VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) provide secure remote access, they can be vulnerable if not properly secured. 802.1X can enhance VPN security by integrating authentication methods into the VPN access process, ensuring only authenticated users can establish a VPN connection. This adds an extra layer of security beyond just username and password authentication.
Benefits of 802.1X with VPN:
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Combining 802.1X with other multi-factor authentication methods like smart cards or one-time passwords enhances security.
- Centralized Authentication: Using a central authentication server to manage user credentials simplifies administration and improves security.
- Enhanced Security Posture: Provides a more robust security layer to VPN access, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Scenario 8: Healthcare Environments (HIPAA Compliance)
Meeting HIPAA Regulations: Healthcare organizations must adhere to stringent security regulations like HIPAA. 802.1X plays a key role in achieving HIPAA compliance by controlling access to electronic protected health information (ePHI). Strong authentication and access control measures implemented through 802.1X help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
802.1X for HIPAA Compliance:
- Data Confidentiality: Protecting ePHI from unauthorized access by ensuring that only authorized users and devices can connect to the network.
- Data Integrity: Preventing unauthorized modification of ePHI through strong authentication and access control measures.
- Data Availability: Ensuring that ePHI is available to authorized users when needed, while maintaining security.
Scenario 9: Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) Access
Securing Access to Virtual Desktops: VDI environments provide users with virtual desktops accessed remotely. 802.1X can secure access to these virtual desktops, ensuring only authorized users can connect and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
802.1X in VDI Security:
- Authentication Before Access: Only authenticated users are allowed to connect to their virtual desktops.
- Device Posture Check: Verifying the security posture of the client device before granting access to the virtual desktop, further improving security.
- Compliance with Security Policies: Ensuring that users are only granted access to the virtual desktop based on pre-defined security policies.
Choosing the Right EAP Method
The effectiveness of 802.1X depends heavily on the chosen EAP method. There are various options, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Common EAP methods include:
- EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security): A highly secure method using digital certificates for both the client and the server. It provides strong mutual authentication but requires certificate management, which can be complex.
- PEAP (Protected EAP): Encapsulates other EAP methods within a TLS tunnel, providing strong security without the certificate management complexity of EAP-TLS.
- EAP-FAST (Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling): Developed by Cisco, it offers strong security similar to PEAP but with simplified certificate management.
- EAP-TTLS (Tunneled TLS): Provides strong security with reduced certificate requirements compared to EAP-TLS, only requiring a server-side certificate.
In conclusion, 802.1X authentication is a versatile and powerful tool for securing network access in a wide range of scenarios. Its ability to integrate with various authentication methods and network access control systems makes it an essential component of any robust security strategy. Selecting the appropriate EAP method and carefully configuring the system are vital to maximizing its effectiveness. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different scenarios and authentication methods, organizations can effectively leverage 802.1X to safeguard their networks and protect sensitive data.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
King Uses The Check And Promissory Note Metaphors To
Apr 01, 2025
-
Poor Maintenance Of Home Poor Personal Care
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Statement Is True About The Factors Affecting Physical Fitness
Apr 01, 2025
-
Economic Efficiency In A Competitive Market Is Achieved When
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Does Catherine Tell Nick About Gatsby
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Scenarios Would Typically Utilize 802.1x Authentication . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
