Which Of The Following Transfer Rates Is The Fastest
Breaking News Today
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
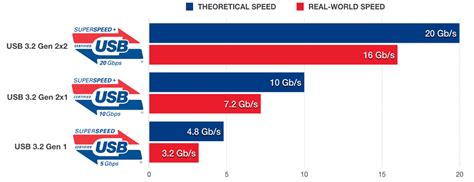
Table of Contents
Which of the following transfer rates is the fastest? A Deep Dive into Data Transfer Speeds
The question "which of the following transfer rates is fastest?" is deceptively simple. The answer depends entirely on what is being transferred, how it's being transferred, and the specific technologies involved. There's no single universally fastest transfer rate. This article will delve into the complexities of data transfer speeds, comparing various technologies and explaining the factors influencing their performance.
Understanding Data Transfer Units and Rates
Before comparing speeds, let's establish a common understanding of measurement units. Data transfer rates are typically expressed in:
- Bits per second (bps): The fundamental unit, representing the number of individual bits transferred per second.
- Kilobits per second (kbps): 1,000 bps (although sometimes 1024 bps is used).
- Megabits per second (Mbps): 1,000,000 bps.
- Gigabits per second (Gbps): 1,000,000,000 bps.
- Bytes per second (Bps): A more practical unit for file sizes, where 1 byte = 8 bits.
- Kilobytes per second (KBps): 1,000 Bps.
- Megabytes per second (MBps): 1,000,000 Bps.
- Gigabytes per second (GBps): 1,000,000,000 Bps.
It's crucial to differentiate between bits (b) and bytes (B), as a factor of eight often separates reported speeds. A connection advertised as 1 Gbps will transfer data at approximately 125 MBps (1,000,000,000 bits/second / 8 bits/byte).
Comparing Transfer Technologies: A Hierarchy of Speeds
Let's compare some common data transfer technologies, ranging from slower to faster:
1. Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology primarily used for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and speakers. Its transfer speed varies considerably depending on the version and the devices involved. Older versions (e.g., Bluetooth 2.0) offer speeds in the low Mbps range. Modern versions like Bluetooth 5.0 can reach speeds significantly higher, exceeding 2 Mbps in some cases. However, compared to other technologies, it remains relatively slow. Bluetooth is best suited for low-bandwidth applications, not large file transfers.
2. Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a ubiquitous wireless technology for connecting devices to a network. Speeds vary greatly based on the standard (802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax), the router's capabilities, and network congestion. Older Wi-Fi standards offered speeds in the tens of Mbps, while modern Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax) can achieve speeds in the gigabit range (several Gbps theoretically, though real-world speeds are often lower). Wi-Fi is a good balance between convenience and speed for many applications, but performance can be unpredictable.
3. Ethernet
Ethernet is a wired networking technology providing significantly faster and more reliable data transfer speeds than Wi-Fi. Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) is a common standard, capable of transferring data at around 125 MBps. 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps), offering around 1.25 GBps, is increasingly prevalent in high-performance networks and data centers. Ethernet offers consistent and high speeds, making it ideal for demanding tasks like large file transfers and online gaming.
4. Thunderbolt
Thunderbolt is a high-speed interface developed by Intel, offering significantly higher bandwidth than USB. Thunderbolt 3 and 4 can reach speeds up to 40 Gbps, while Thunderbolt 4 is optimized for enhanced performance and compatibility. Thunderbolt is primarily used for connecting external storage devices, displays, and other peripherals requiring high bandwidth.
5. Fiber Channel
Fiber Channel is a high-speed networking technology primarily used in storage area networks (SANs) and data centers. It boasts transfer rates far exceeding other technologies discussed thus far, reaching multi-Gbps speeds and even exceeding 100 Gbps in advanced implementations. Fiber Channel is a specialized technology optimized for high-throughput data transfer in enterprise environments.
6. Infiniband
Infiniband is a high-performance interconnect technology often employed in high-performance computing (HPC) clusters and data centers. It provides extremely high bandwidth and low latency, enabling incredibly fast data transfers within these environments. Speeds can reach hundreds of Gbps, significantly surpassing other technologies discussed. Infiniband's complexity and cost make it unsuitable for typical consumer applications.
Factors Affecting Transfer Speeds
Several factors can influence the actual transfer speeds experienced, even with the fastest technologies:
- Network Congestion: High network traffic can significantly reduce transfer speeds on any network.
- Hardware Limitations: The speed of storage devices (hard drives, SSDs), network interface cards (NICs), and other hardware components can limit the overall transfer rate.
- Protocol Overhead: Network protocols add overhead to data packets, reducing the effective transfer speed.
- Distance: Signal attenuation over longer distances can reduce transfer speeds in wired and wireless networks.
- Data Compression: Compressing data before transfer can significantly increase effective transfer speed by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted.
- Encryption: Encrypting data adds processing overhead, which can slightly reduce the transfer rate.
Real-World Examples and Considerations
Let's consider some practical scenarios:
- Copying a large video file: Using a Thunderbolt 4 external drive will generally be much faster than transferring the same file over Wi-Fi or even Gigabit Ethernet.
- Streaming high-definition video: A fast and stable internet connection (with high Mbps speeds) is crucial for smooth streaming. Wi-Fi 6 or a wired Ethernet connection is typically recommended.
- Backing up a large server: A Fiber Channel SAN or Infiniband network might be necessary for very large and high-speed backups.
It's important to remember that theoretical maximum speeds are rarely achieved in real-world scenarios. Many factors contribute to reducing the actual transfer rates observed.
Choosing the Right Technology
The "fastest" transfer rate depends entirely on your specific needs and context. Consider the following:
- Budget: Higher speeds generally come with higher costs.
- Application: Different applications have different bandwidth requirements.
- Distance: Wired connections are generally faster and more reliable over longer distances.
- Ease of Use: Some technologies are easier to set up and use than others.
For most consumers, a combination of Gigabit Ethernet for wired connections and high-speed Wi-Fi for wireless needs will provide adequate performance for the majority of tasks. Professionals in fields like video editing, data science, or high-performance computing may require more advanced technologies like Thunderbolt, Fiber Channel, or Infiniband.
Conclusion
There's no single answer to the question of which transfer rate is the fastest. The optimal choice depends on the specific application, budget constraints, and desired level of performance. Understanding the different technologies and the factors that influence their speeds is crucial for selecting the best solution for your particular needs. By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the technology that provides the best balance of speed, reliability, and cost-effectiveness for your data transfer requirements. This comprehensive understanding will empower you to make informed decisions when dealing with data transfer, optimizing your workflow and ensuring efficient data management.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Concept Of Limited Government Holds That
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Drawback Of Planning Is That It
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True About Fake News
Apr 01, 2025
-
When Recording Progress Notes The Specific Chief Complaint Should Be
Apr 01, 2025
-
You Are Providing Bag Mask Ventilations To A Patient
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Transfer Rates Is The Fastest . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
