Which Of These Equations Best Summarizes Photosynthesis
Breaking News Today
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
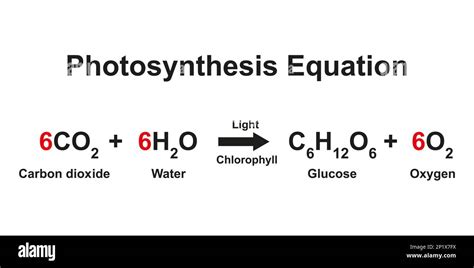
Table of Contents
Which of These Equations Best Summarizes Photosynthesis? A Deep Dive into the Chemistry of Life
Photosynthesis, the remarkable process by which plants and other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, is a cornerstone of life on Earth. Understanding its intricacies requires delving into the various chemical equations that attempt to represent this complex biochemical pathway. While numerous simplified equations exist, none perfectly encapsulate the entire process. This article explores several common equations, compares their strengths and weaknesses, and ultimately argues for the equation that best represents the overall essence of photosynthesis.
The Simplified Equation: A Starting Point
The most commonly encountered equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation depicts the overall transformation: six molecules of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and six molecules of water (H₂O) react in the presence of light energy to produce one molecule of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), a simple sugar, and six molecules of oxygen (O₂). This equation is useful for a basic understanding of the inputs and outputs. It clearly shows that carbon dioxide is consumed, water is consumed, light energy drives the reaction, and glucose and oxygen are produced.
Strengths:
- Simplicity: Its simplicity makes it easily memorizable and understandable, even for those without a strong science background.
- Overall Representation: It accurately reflects the net transformation of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Weaknesses:
- Oversimplification: This equation drastically simplifies a complex multi-step process. It omits the numerous intermediate compounds and reactions involved in the light-dependent and light-independent stages of photosynthesis.
- Misleading Oxygen Source: The equation implies that all the oxygen produced comes from water. While the majority does, a small amount is derived from carbon dioxide during specific photosynthetic pathways.
- Ignoring Energy Transfer: It doesn't explicitly show the conversion of light energy into chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucose.
A More Detailed Equation: Acknowledging the Role of ATP and NADPH
To gain a more nuanced understanding, we need to incorporate the crucial intermediate molecules: adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). These energy-carrying molecules are produced during the light-dependent reactions and are essential for the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle). A more comprehensive equation would incorporate these:
6CO₂ + 12H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ + 6H₂O
This equation still simplifies the process, but it recognizes that the water utilized is not only for the production of oxygen but also plays a crucial role in the Calvin cycle.
Strengths:
- Acknowledgement of Water's Dual Role: It better represents the role of water in both oxygen production and the Calvin cycle.
- Improved Accuracy: It provides a slightly more accurate reflection of the overall stoichiometry than the highly simplified equation.
Weaknesses:
- Still Oversimplified: It still ignores the multitude of intermediate steps, enzymes, and chemical reactions.
- ATP and NADPH Absence: The most important energy-carrying molecules are still absent, failing to convey the essential energy transfer aspect of photosynthesis.
The Importance of ATP and NADPH: The Energy Currency of Photosynthesis
The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are primarily responsible for converting light energy into the chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH. These molecules act as energy carriers, supplying the necessary energy to drive the reactions of the Calvin cycle. The Calvin cycle uses this energy to fix carbon dioxide and synthesize glucose. Therefore, a more accurate representation must explicitly include these crucial components. While a single equation encompassing the entire pathway is impractical due to its complexity, we can highlight the importance of ATP and NADPH with two separate equations:
Light-dependent Reactions: Several equations exist to describe this stage, depending on the specific details being emphasized. A simplified version might be:
H₂O + Light Energy → ATP + NADPH + O₂
Light-independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): This stage utilizes ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions. A simplified representation is:
6CO₂ + ATP + NADPH → C₆H₁₂O₆
Strengths:
- Highlights Energy Transfer: This approach clearly shows the conversion of light energy into chemical energy (ATP and NADPH) and then the utilization of this energy for glucose synthesis.
- Focus on Key Intermediates: It emphasizes the pivotal role of ATP and NADPH, providing a more realistic picture of the energy flow within the photosynthetic process.
Weaknesses:
- Two Equations Required: Two equations are needed rather than a single, concise one. This can be less convenient for some purposes.
- Simplification of Each Stage: Each equation still simplifies a complex series of reactions within its respective stage.
Which Equation Best Summarizes Photosynthesis?
Considering the strengths and weaknesses of each equation presented, the most informative approach is to combine the simplified overview with the two-stage approach highlighting ATP and NADPH. While a single equation cannot fully capture the intricate details of photosynthesis, this combination offers a balance between simplicity and accuracy.
The simplified equation:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
provides a helpful overview, easily understandable by a broad audience. Then, by subsequently explaining the role of ATP and NADPH through separate equations for the light-dependent and light-independent reactions, you provide a deeper understanding of the process without overwhelming readers with unnecessary complexity.
This combined approach successfully conveys the essential features of photosynthesis:
- The overall transformation of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- The crucial role of light energy as the driving force.
- The importance of ATP and NADPH as energy carriers.
Therefore, this approach serves as the most effective method of summarizing photosynthesis, catering to both a general audience and those seeking a deeper understanding of the biological process.
Beyond the Equations: The Importance of Context
It's vital to remember that equations are merely tools to represent complex biological processes. A comprehensive understanding of photosynthesis extends beyond these simplified models. Factors like:
- Different photosynthetic pathways: C3, C4, and CAM pathways exhibit variations in their approach to carbon fixation.
- Environmental factors: Light intensity, temperature, water availability, and carbon dioxide levels influence photosynthetic efficiency.
- Enzyme involvement: Numerous enzymes catalyze the myriad reactions within photosynthesis.
are crucial aspects that must be considered. The equations should serve as a foundation upon which a more holistic understanding of photosynthesis is built, incorporating these vital elements and the dynamic nature of this essential life process.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Approach to Understanding Photosynthesis
Ultimately, no single equation perfectly encapsulates the complexity of photosynthesis. However, using a combination of the simplified overview equation along with the separate equations highlighting ATP and NADPH strikes the best balance between simplicity, accuracy, and comprehension. This multifaceted approach allows for a clear, yet nuanced, understanding of this fundamental biological process, laying the foundation for further exploration of its fascinating intricacies. Remember to emphasize the role of the numerous intermediate steps and environmental factors for a truly complete picture. This multi-pronged approach respects the complexity of the subject while ensuring easy understanding for various learning levels.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Purpose Of Isoo Cui Registry
Mar 19, 2025
-
If Records Are Inadvertently Destroyed Who Should You Contact Immediately
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is Depicted In The Image Above
Mar 19, 2025
-
Have Properties Of Both Metals And Non Metals
Mar 19, 2025
-
Dna Is Composed Of Building Blocks Called
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of These Equations Best Summarizes Photosynthesis . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
