Which One Of These Is An Amino Group
Breaking News Today
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
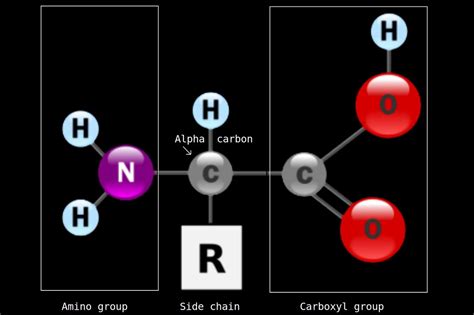
Table of Contents
Which One of These is an Amino Group? A Deep Dive into Organic Chemistry
Understanding functional groups is fundamental to organic chemistry. Among the many crucial functional groups, the amino group holds a prominent position, playing a vital role in the structure and function of a vast array of biologically important molecules, including amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. This article delves deep into the characteristics of the amino group, distinguishing it from other functional groups and exploring its significance in various chemical contexts.
What is a Functional Group?
Before we pinpoint the amino group, let's establish a clear understanding of what functional groups are. In organic chemistry, a functional group is a specific atom or group of atoms within a molecule that is responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of that molecule. These groups dictate the molecule's properties, influencing its reactivity, polarity, and overall behavior. Different functional groups impart different properties, enabling a vast diversity of chemical compounds and their associated functionalities. The presence or absence of specific functional groups determines whether a molecule behaves as an acid, base, or something else entirely.
Identifying the Amino Group: -NH₂
The amino group, denoted as -NH₂, is a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. This simple yet crucial functional group is characterized by its basic properties. The nitrogen atom, possessing a lone pair of electrons, readily accepts a proton (H⁺), exhibiting its basic nature. This proton acceptance leads to the formation of an ammonium ion (-NH₃⁺).
Key Features of the Amino Group:
- Nitrogen Atom: The central atom, nitrogen, is the key player. Its electronegativity and lone pair are crucial for the group's reactivity.
- Two Hydrogen Atoms: These hydrogen atoms are directly bonded to the nitrogen. The number of hydrogens can vary in substituted amino groups (discussed later).
- Basic Nature: The presence of the lone pair makes the amino group a Lewis base, capable of donating electron pairs and forming bonds. This leads to its characteristic reactions, especially with acids.
- Polarity: The N-H bonds are polar due to the electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen, imparting polarity to the molecule containing the amino group.
- Hydrogen Bonding: The polar N-H bonds can participate in hydrogen bonding, affecting the physical properties of the molecule, such as boiling point and solubility.
Distinguishing the Amino Group from Other Functional Groups
Several functional groups share similarities with the amino group, making it crucial to understand their distinctions. Let's compare the amino group with some commonly confused functional groups:
1. Amide Group (-CONH₂):
The amide group, often confused with the amino group, contains a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a nitrogen atom. The key difference lies in the presence of the carbonyl group. Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acids and exhibit different chemical properties compared to amines (compounds containing the amino group). Amides are significantly less basic than amines due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group.
2. Nitro Group (-NO₂):
The nitro group contains a nitrogen atom bonded to two oxygen atoms. Unlike the amino group, the nitro group is electron-withdrawing, making it an acidic functional group rather than a basic one. It has very different chemical reactivities and imparts unique properties to the molecules it's part of.
3. Imine Group (-C=N-):
The imine group consists of a carbon-nitrogen double bond. While both contain nitrogen, the imine group lacks the hydrogen atoms directly bonded to the nitrogen found in the amino group. This difference results in differing reactivity and properties.
4. Nitrile Group (-C≡N):
The nitrile group features a carbon-nitrogen triple bond. Similar to the imine group, it lacks the characteristic two hydrogens directly attached to the nitrogen, setting it apart from the amino group. Its properties are significantly different from the amino group's.
Importance of the Amino Group in Biological Molecules
The amino group is ubiquitous in biological systems, playing a crucial role in the structure and function of many vital molecules:
1. Amino Acids:
Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, are characterized by the presence of both an amino group (-NH₂) and a carboxyl group (-COOH). The amino group's basic nature and ability to form peptide bonds are essential for protein synthesis. The specific side chain (R group) attached to the α-carbon atom varies amongst the 20 standard amino acids, dictating the unique properties of each amino acid and influencing the overall structure and function of the resulting protein.
2. Proteins:
Proteins are polymers formed from amino acids linked together via peptide bonds. These peptide bonds are formed through a condensation reaction between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another. The amino group's involvement in peptide bond formation is critical to the creation of the protein's primary structure and its subsequent folding into higher-order structures (secondary, tertiary, and quaternary).
3. Nucleic Acids:
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, contain nitrogenous bases that possess amino groups. These amino groups participate in hydrogen bonding between base pairs, which is crucial for maintaining the double helix structure of DNA and the stability of RNA. The specific arrangement of these bases, dictated by their amino and other functional groups, determines the genetic code.
4. Neurotransmitters:
Several neurotransmitters, chemicals that transmit signals between nerve cells, contain amino groups. For instance, dopamine and serotonin, critical for mood regulation and other neurological functions, are amines and therefore contain this crucial functional group. The presence of the amino group affects their interactions with receptor sites in the brain.
Chemical Reactions Involving the Amino Group
The amino group's basic nature makes it highly reactive, participating in various chemical reactions:
1. Acid-Base Reactions:
The amino group readily accepts a proton (H⁺) from an acid, forming an ammonium ion (-NH₃⁺). This is a crucial property in various biological processes and chemical syntheses.
2. Acylation:
Acylating agents can react with the amino group, forming amides. This reaction is vital in peptide bond formation, the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, and the modification of proteins.
3. Alkylation:
Alkyl halides can react with the amino group, leading to the formation of substituted amines. This process is frequently used in organic synthesis to introduce alkyl groups onto the nitrogen atom.
4. Diazotization:
Amino groups can react with nitrous acid (HNO₂) to form diazonium salts. Diazonium salts are highly reactive intermediates used in various organic syntheses, particularly in the formation of azo dyes.
Conclusion: The Amino Group's Significance
The amino group, though seemingly a simple functional group, plays a pivotal role in the chemical world and particularly in biological systems. Its basic nature, reactivity, and ability to form hydrogen bonds contribute significantly to the diversity and functionality of organic molecules. Understanding its characteristics is crucial for comprehending the structure, properties, and reactions of a wide array of biologically important compounds, from amino acids and proteins to neurotransmitters and nucleic acids. The information presented here serves as a comprehensive guide to help you confidently identify and appreciate the amino group's critical role in chemistry and biology. The study of functional groups, particularly the amino group, is essential for anyone pursuing a deeper understanding of organic chemistry and its applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of These Is The Best Reason For Proper Nutrition
Apr 01, 2025
-
True Or False Acetaminophen Poisoning Is An Acute Illness
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Correct Match
Apr 01, 2025
-
The End Of Big Trees Commonlit Answers
Apr 01, 2025
-
All Of The Following People Should Receive W 2 Forms Except
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which One Of These Is An Amino Group . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
