Which One Of These Is Not A Physical Security Feature
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
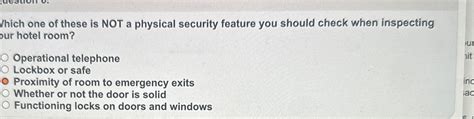
Table of Contents
Which One of These is NOT a Physical Security Feature? A Deep Dive into Security Measures
Physical security is the bedrock of any robust security strategy. It encompasses the tangible measures designed to protect assets, personnel, and facilities from unauthorized access, damage, or theft. But understanding what isn't a physical security feature is just as crucial as knowing what is. This article delves into the key characteristics of physical security, explores various features commonly associated with it, and ultimately identifies which among a selection of options does not fall under this category.
Defining Physical Security: The Tangible Shield
Before we dissect the question at hand, let's establish a clear understanding of physical security. It's primarily concerned with the physical aspects of protection. This includes everything from barriers and locks to surveillance systems and response plans. The core objective is to deter, detect, and respond to threats that involve physical interaction with the protected entity. Think of it as the tangible, visible layer of your overall security architecture.
Key Elements of Physical Security:
-
Access Control: This involves restricting entry to authorized individuals only. This is achieved through various methods, like keycard systems, biometric scanners, and security personnel. The aim is to create a controlled environment where only legitimate access is permitted.
-
Perimeter Security: This forms the first line of defense. It encompasses all measures designed to protect the perimeter of a facility or area. This could include fences, walls, gates, lighting, and intrusion detection systems. A strong perimeter makes it more difficult for intruders to gain entry.
-
Surveillance Systems: These systems act as a deterrent and provide crucial evidence in case of an incident. They typically include CCTV cameras, motion detectors, and alarm systems. The recorded footage can help identify perpetrators and assist in investigations.
-
Environmental Controls: This aspect focuses on protecting the physical environment itself. This might involve climate control to protect sensitive equipment, fire suppression systems to mitigate fire risks, and backup power generators to ensure continuous operation during power outages.
-
Response Planning and Training: This crucial element involves developing comprehensive plans for handling security incidents, including emergency procedures and staff training. A well-prepared response team can significantly minimize the impact of a breach.
Differentiating Physical from Logical Security
It's important to distinguish physical security from logical security, often referred to as cybersecurity. While both are vital for comprehensive protection, they operate in different domains.
Logical security focuses on protecting digital assets and information. This involves measures like firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems (IDS) for networks, access control lists (ACLs), data encryption, and robust password policies. These measures prevent unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, and sensitive data.
The key difference lies in the tangible nature of physical security versus the intangible nature of logical security. Physical security addresses threats involving physical interaction, while logical security addresses threats involving digital interaction.
The Case of the Non-Physical Security Feature
Now, let's consider a hypothetical scenario. Suppose we present a list of options, and you must identify which is not a physical security feature. For example:
- A. Security Cameras: These are undeniably a physical security feature, visually monitoring an area and recording events.
- B. Biometric Access Control System: This is also a physical security measure, employing physical characteristics (fingerprints, iris scans) for authentication.
- C. Firewall: This is a software-based security system; therefore, it's a logical security feature, not physical.
- D. Security Guards: Human security personnel are a crucial physical security element, providing deterrence and immediate response capabilities.
- E. Access Card Readers: This hardware-based system is a fundamental physical access control mechanism.
- F. Intrusion Detection System (IDS): While an IDS can have physical components (sensors), its core functionality is detecting malicious network activity—a logical security concern. However, some components could overlap. A network-based IDS is primarily logical; a physical intrusion detection system using sensors is primarily physical.
The answer is C (Firewall) and potentially F (depending on the specifics of the IDS). A firewall, by its nature, is a software program that controls network traffic. It doesn't involve physical barriers or physical interaction. Similarly, a network-based IDS focuses on digital network traffic analysis, primarily falling under logical security. A physical intrusion detection system (using physical sensors, for example), on the other hand, would absolutely fall under physical security.
Expanding the Scope: Hybrid Security Measures
It's worth noting that some security measures blur the lines between physical and logical security. For instance, a sophisticated access control system might combine physical access cards with digital authentication factors like PINs or biometrics. In these cases, the system incorporates both physical and logical components working in tandem to achieve enhanced security.
The Importance of Integrated Security
Effective security relies on a holistic approach that integrates physical and logical security measures. A robust strategy considers the potential threats and vulnerabilities across both domains. A strong physical perimeter will do little good if the internal network is vulnerable to cyberattacks. Likewise, a watertight cyber security strategy is ineffective if physical access to servers is easily obtained. The combination of both is crucial for a comprehensive security posture.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Physical Security Technologies
Physical security is constantly evolving, with technological advancements leading to more sophisticated and efficient systems. Some examples include:
- Intelligent Video Analytics: This goes beyond basic CCTV, employing AI and machine learning to analyze video footage, identifying anomalies, and triggering alerts based on pre-defined parameters. This drastically reduces the burden on human operators and increases efficiency.
- Perimeter Intrusion Detection Systems: These advanced systems utilize a variety of technologies like fiber optic sensors, radar, and thermal imaging to detect intrusions along the perimeter with greater accuracy and range than traditional methods.
- Access Control Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS): Modern systems allow for seamless integration with BMS, enabling control of lighting, HVAC, and other building systems based on occupancy data provided by the access control system. This enhances efficiency and security.
- Robotics and Automation: Robots and drones are increasingly being used for perimeter patrols, providing enhanced surveillance and threat detection capabilities.
Addressing the Human Element: Training and Awareness
Regardless of the sophistication of the technological solutions, the human element remains crucial in physical security. Effective security relies on well-trained personnel who understand their roles and responsibilities. Regular security awareness training is essential to ensure that employees are aware of potential threats and know how to respond appropriately. This includes educating employees on best practices like password security, reporting suspicious activities, and adhering to security protocols.
Conclusion: A Multi-Layered Approach to Security
Ultimately, the strength of a security system hinges on a well-defined strategy that integrates various physical and logical security measures. While understanding the distinction between physical and logical security is critical, the goal is not to focus on one over the other, but to implement a multifaceted, layered approach that ensures comprehensive protection of assets, personnel, and facilities. Remember, a robust security posture involves a continuous cycle of assessment, adaptation, and improvement, constantly evolving to address emerging threats and technological advancements. Only through this holistic approach can one achieve true and lasting security.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Aetnas Pdp Members Have Access To 65000 Pharmacies Nationwide
Mar 28, 2025
-
Most Construction Drawings Today Are Hand Drawn By Drafters
Mar 28, 2025
-
Credit And Money Ap World Unit 2
Mar 28, 2025
-
From The Family Systems Perspective Symptoms Are Often Viewed As
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Three Categories Of Distractions Include Visual Manual And
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which One Of These Is Not A Physical Security Feature . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
