Which Sexually Transmitted Infection Is Caused By Human Papillomavirus Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
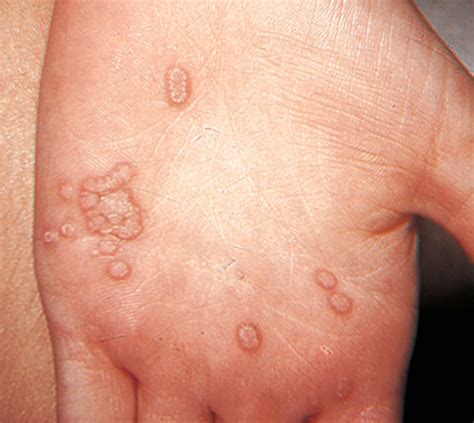
Table of Contents
Which Sexually Transmitted Infection is Caused by Human Papillomavirus? A Comprehensive Guide
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can cause a range of health problems, from genital warts to cancer. Understanding HPV, its transmission, prevention, and treatment is crucial for maintaining sexual health. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the topic, answering the question: Which sexually transmitted infection is caused by human papillomavirus? We'll explore the various types of HPV, their associated health risks, and the ways to protect yourself.
Understanding Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a group of over 200 related viruses, with over 40 types affecting the genital area. These viruses are transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Not all HPV types are high-risk; some are low-risk and cause minimal health problems, while others are high-risk and significantly increase the risk of certain cancers.
Low-Risk HPV Types:
Low-risk HPV types typically cause genital warts. These warts are usually benign and can be treated, but they can be unsightly and uncomfortable. Some individuals may not even experience any symptoms. Genital warts are the primary STI directly caused by low-risk HPV types.
High-Risk HPV Types:
High-risk HPV types are far more concerning. These types can persist in the body for years, leading to precancerous changes and eventually cancer. Persistent infection with high-risk HPV is a major cause of several cancers, including:
- Cervical cancer: This is the most common cancer associated with HPV infection, particularly in women. Regular Pap smears are crucial for early detection and prevention.
- Anal cancer: Similar to cervical cancer, HPV infection is a major risk factor for anal cancer in both men and women.
- Oropharyngeal cancer: This type of cancer affects the back of the throat, base of the tongue, and tonsils. Oral sex is a significant mode of transmission in this case.
- Vulvar cancer: Cancer of the vulva (the external female genitalia) is also linked to high-risk HPV infection.
- Vaginal cancer: HPV is a significant risk factor for vaginal cancer.
- Penile cancer: While less common, penile cancer can also be caused by high-risk HPV infection.
HPV Transmission and Risk Factors
HPV is highly contagious and easily spread through sexual contact. The risk of infection increases with:
- Multiple sexual partners: Having multiple sexual partners increases your exposure to various STIs, including HPV.
- Early age of sexual debut: Starting sexual activity at a younger age increases the risk of HPV infection.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immune systems (e.g., due to HIV/AIDS) are more susceptible to HPV infection and its complications.
- Smoking: Smoking is linked to an increased risk of persistent HPV infection and its associated cancers.
Symptoms of HPV Infection
Many individuals infected with HPV experience no symptoms. This is why regular screening is so important. When symptoms do occur, they vary depending on the type of HPV:
- Genital warts: These appear as small, fleshy bumps or cauliflower-like growths on the genitals, anus, or surrounding areas. They can be itchy or painful.
- Precancerous changes: These are not visible and are only detected through screening tests like Pap smears.
Diagnosis and Screening
Diagnosis of HPV infection usually involves:
- Visual examination: A doctor can visually inspect the genital area for warts.
- Pap smear (for women): This test screens for precancerous changes in the cervix.
- HPV DNA test: This test detects the presence of HPV DNA in cells.
- Colposcopy: This procedure uses a magnifying instrument to examine the cervix for abnormalities.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample may be taken for laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of precancerous or cancerous cells.
Treatment for HPV Infection
Unfortunately, there's no cure for HPV infection itself. However, treatments are available to manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications:
- Genital warts: Treatments include topical creams, freezing (cryotherapy), laser surgery, and surgical excision.
- Precancerous changes: Treatment options range from observation to surgical procedures to remove abnormal cells.
- Cancer: Treatment for HPV-related cancers depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
Prevention of HPV Infection
The best way to prevent HPV infection is through vaccination and safe sex practices.
HPV Vaccination:
The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection with the high-risk types of HPV that cause most HPV-related cancers. The vaccine is recommended for both boys and girls, typically starting around age 11 or 12. It can also be given to young adults up to age 26.
Safe Sex Practices:
Practicing safe sex can significantly reduce the risk of HPV infection and other STIs. This includes:
- Using condoms: Condoms can reduce the risk of HPV transmission, but they don't provide complete protection because skin-to-skin contact can still occur.
- Limiting the number of sexual partners: Reducing the number of sexual partners lowers your exposure to HPV and other STIs.
- Getting tested regularly: Regular STI testing, including HPV testing, can help detect infections early, allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of complications.
The Importance of Regular Screenings
Regular screenings are crucial, especially for women, to detect precancerous changes and cancer early. Regular Pap smears and HPV DNA tests can significantly reduce the risk of cervical cancer mortality. For individuals with a higher risk of HPV-related cancers, more frequent screening may be recommended.
Living with HPV: Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions
Many people feel anxiety and concern after receiving an HPV diagnosis. It's crucial to understand that:
- HPV is very common: Many individuals are infected with HPV at some point in their lives.
- Most HPV infections clear on their own: The body's immune system often successfully clears the infection without causing any long-term health problems.
- Treatment is available: Effective treatments exist to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Vaccination is effective: The HPV vaccine provides strong protection against infection.
Understanding the facts about HPV, its transmission, and its potential consequences empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual health. Open communication with healthcare providers is vital in addressing concerns and ensuring appropriate management of HPV infection.
Conclusion: Protecting Yourself Against HPV
The question "Which sexually transmitted infection is caused by human papillomavirus?" is answered definitively: various STIs, including genital warts and, in cases of persistent high-risk HPV infection, several types of cancer. However, the focus should not solely be on the diseases caused but on proactive prevention and early detection. By understanding HPV, practicing safe sex, getting vaccinated, and undergoing regular screenings, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing HPV-related health problems. Remember, knowledge is power, and taking control of your sexual health is an essential aspect of overall well-being. Early detection and proactive management remain the cornerstones of a successful approach to HPV.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Treaty Of Tordesillas Established A Territorial Dividing Line Between
Mar 25, 2025
-
Match The Style Of String Playing With Its Corresponding Meaning
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Side Salad Is Served With The Dressing Ihop
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Does The Dagger Of The Mind Passage Symbolize
Mar 25, 2025
-
Recibi Un Aumento De 1 Of 1 Este Mes
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Sexually Transmitted Infection Is Caused By Human Papillomavirus Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
