Which Sign Or Symptom Is Associated With Gout Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
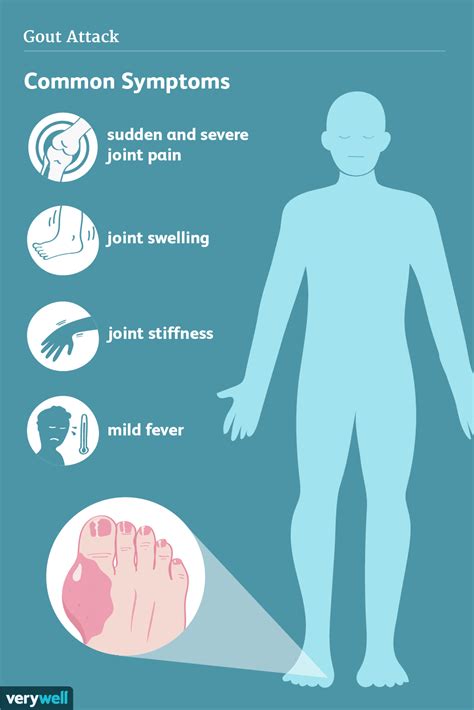
Table of Contents
Which Sign or Symptom is Associated with Gout? A Comprehensive Guide
Gout, a painful form of arthritis, is characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints. Understanding the signs and symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and management. This comprehensive guide explores the various symptoms associated with gout, offering a detailed look at what to expect during an acute attack and beyond. We'll also touch upon differential diagnosis, as some symptoms can mimic other conditions.
Understanding Gout: A Quick Overview
Before diving into the specifics of gout symptoms, let's establish a foundational understanding of the condition itself. Gout is caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a byproduct of the body's breakdown of purines, found in certain foods and drinks. When uric acid levels become too high (hyperuricemia), crystals can form, leading to the inflammation and intense pain characteristic of a gout attack.
Key Signs and Symptoms Associated with Gout
The symptoms of gout can vary in intensity and duration, but some common indicators are almost universally experienced:
1. Intense Joint Pain:
- Sudden Onset: Gout attacks often begin abruptly, usually at night or early in the morning. The pain can be so severe that even a light touch on the affected joint is excruciating.
- Severe Pain: The pain is described as a sharp, throbbing, and intense burning sensation. It's often described as the "worst pain ever experienced."
- Location: The most commonly affected joint is the big toe (podagra), but gout can also affect other joints, including the ankles, knees, wrists, hands, and elbows.
- Progression: The pain intensifies over several hours or even days before gradually subsiding.
2. Swelling and Inflammation:
- Redness: The affected joint becomes noticeably red and inflamed. This inflammation is a direct result of the body's immune response to the uric acid crystals.
- Swelling: Significant swelling occurs around the affected joint, making it look larger and puffy. The skin over the joint may feel warm to the touch.
- Tenderness: The joint is extremely tender to the touch. Even the weight of bedsheets can be unbearable.
3. Limited Range of Motion:
- Stiffness: The affected joint becomes stiff and difficult to move. This stiffness is exacerbated by the pain and inflammation.
- Functional Impairment: Daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or even simple movements like gripping objects, can become extremely challenging during a gout attack.
4. Tophi (Advanced Gout):
- Lumps under the Skin: In chronic, untreated gout, hard, white nodules called tophi can develop under the skin, particularly around the joints.
- Uric Acid Deposits: These tophi are deposits of uric acid crystals that have accumulated in the tissues.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Tophi can be unsightly and may even rupture, releasing a chalky white material.
5. Kidney Stones:
- Uric Acid Nephropathy: High levels of uric acid can also lead to the formation of kidney stones. These stones can cause significant pain and complications.
- Kidney Damage: Chronic hyperuricemia can eventually damage the kidneys, leading to potential long-term health issues.
Differentiating Gout from Other Conditions: A Crucial Step
Several other conditions can mimic the symptoms of gout, making accurate diagnosis crucial. It's vital to consult a healthcare professional for proper assessment and treatment. Some conditions that share similar symptoms include:
- Cellulitis: A bacterial skin infection that can cause redness, swelling, and pain. Unlike gout, cellulitis typically affects the skin's surface rather than the joint itself.
- Septic Arthritis: A bacterial infection of the joint, leading to severe pain, swelling, and fever. Septic arthritis requires urgent medical attention due to the potential for serious complications.
- Pseudogout: Caused by calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposits in the joints, leading to symptoms similar to gout.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: A chronic inflammatory condition affecting multiple joints. While rheumatoid arthritis can cause pain and swelling, it typically involves a wider range of joints and has a different pattern of progression.
- Osteoarthritis: Degenerative joint disease, causing pain and stiffness, but generally lacking the intense, acute flare-ups characteristic of gout.
Diagnosing Gout: Tests and Procedures
A healthcare professional will conduct a thorough physical examination and review your medical history to assess the likelihood of gout. Diagnostic tests may include:
- Joint Fluid Analysis: A sample of fluid from the affected joint is examined under a microscope to detect the presence of uric acid crystals. This is the most definitive test for gout.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests measure uric acid levels in the blood. Elevated uric acid levels suggest a predisposition to gout but don't confirm a diagnosis on their own, as many people with high uric acid never develop gout.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays may be used to rule out other conditions and assess the extent of any joint damage.
Managing Gout: Treatment Strategies
Managing gout involves controlling uric acid levels and relieving symptoms during acute attacks. Treatment strategies include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids are used to manage pain and inflammation during acute attacks. Long-term medications, such as allopurinol or febuxostat, help lower uric acid levels to prevent future attacks.
- Lifestyle Changes: Dietary modifications, such as limiting purine-rich foods (red meat, organ meats, seafood) and alcohol consumption, can significantly reduce uric acid levels. Maintaining a healthy weight and increasing physical activity also play a crucial role.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush uric acid from the body.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Management
Early diagnosis and prompt management of gout are crucial to prevent long-term complications. Untreated gout can lead to:
- Joint Damage: Chronic inflammation can damage cartilage and bones, leading to chronic pain and disability.
- Kidney Disease: High uric acid levels can damage the kidneys.
- Tophi Formation: Uric acid deposits can form under the skin, causing cosmetic issues and potential complications.
Conclusion: Understanding and Managing Gout
Gout is a painful and potentially debilitating condition. However, with proper diagnosis, effective management strategies, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can effectively control their symptoms and prevent long-term complications. Understanding the various signs and symptoms associated with gout is the first step towards successful management and a better quality of life. Remember, if you experience any symptoms consistent with gout, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for prompt diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive guide provides valuable information, but should not replace professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of a healthcare provider for any health concerns.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Everyone Reacts To Stress In The Same Way
Mar 24, 2025
-
A Food Handler May Chew Tobacco In
Mar 24, 2025
-
An Organism That Makes Its Own Food
Mar 24, 2025
-
A Distributor Is Sometimes Referred To As A An Blank
Mar 24, 2025
-
Writer Louis D Brandeis Was Also
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Sign Or Symptom Is Associated With Gout Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
