Which Statement Accurately Describes Type 2 Diabetes
Breaking News Today
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
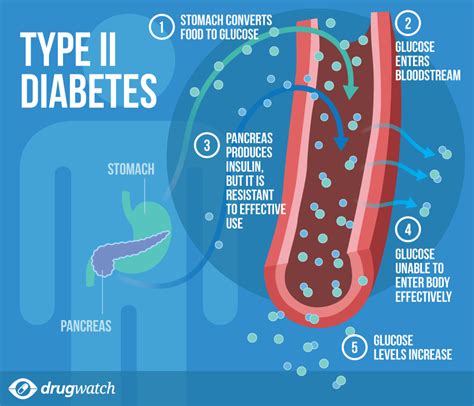
Table of Contents
Which Statement Accurately Describes Type 2 Diabetes? Understanding the Complexities of Insulin Resistance
Type 2 diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder, affects millions worldwide. Its complexity often leads to confusion regarding its accurate description. While many statements attempt to capture its essence, only a few accurately reflect its multifaceted nature. This comprehensive article delves deep into the nuances of type 2 diabetes, debunking common misconceptions and providing a clear, accurate understanding of this prevalent health concern.
What is Type 2 Diabetes? A Detailed Explanation
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar levels. This isn't simply a matter of consuming too much sugar; it's a much more intricate process involving insulin resistance and, eventually, insulin deficiency. Let's break this down:
Insulin Resistance: The Core Problem
The body produces insulin, a hormone that acts like a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream to enter and provide energy. In type 2 diabetes, the body's cells become resistant to the effects of insulin. This means the insulin key no longer works as efficiently, leaving glucose trapped in the bloodstream. This leads to persistently high blood sugar.
The Role of Insulin Secretion
Initially, the pancreas, the organ that produces insulin, compensates for this resistance by producing more insulin. However, over time, this compensatory mechanism fails, resulting in relative insulin deficiency. The pancreas struggles to keep up with the demand, leading to a further increase in blood glucose levels.
Beyond Blood Sugar: The Systemic Impact
Type 2 diabetes is far more than just high blood sugar. It's a systemic disease, impacting various organs and systems throughout the body. Chronic hyperglycemia can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, leading to a range of serious complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: High blood sugar damages blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease.
- Kidney Disease (Nephropathy): Damaged blood vessels in the kidneys can lead to kidney failure.
- Eye Disease (Retinopathy): High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, potentially leading to blindness.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): High blood sugar can damage nerves, causing numbness, tingling, and pain in the extremities.
- Foot Problems: Nerve damage and poor circulation can lead to foot ulcers, infections, and even amputation.
- Increased Risk of Certain Cancers: Type 2 diabetes is linked to an increased risk of several types of cancer.
- Cognitive Impairment: Some research suggests a link between type 2 diabetes and an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Debunking Common Misconceptions about Type 2 Diabetes
Many misconceptions surround type 2 diabetes, hindering accurate understanding and effective management. Let's address some of the most prevalent ones:
Myth 1: Type 2 Diabetes is caused solely by a poor diet and lack of exercise.
Reality: While lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of type 2 diabetes, they are not the sole culprits. Genetics, ethnicity, age, and other underlying health conditions can also increase the risk. Some individuals may develop type 2 diabetes despite maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It's a complex interplay of factors.
Myth 2: Type 2 diabetes is only a problem for older adults.
Reality: While the risk increases with age, type 2 diabetes is increasingly being diagnosed in younger individuals, including children and adolescents. This is partly due to rising obesity rates and increasingly sedentary lifestyles. It's a growing concern across all age groups.
Myth 3: Type 2 diabetes is a manageable condition that doesn't require medication.
Reality: While lifestyle modifications, including diet, exercise, and weight management, are crucial for managing type 2 diabetes, many individuals also require medication to control their blood sugar levels effectively. Medication is often necessary to prevent or delay complications.
Myth 4: Once you have type 2 diabetes, it's irreversible.
Reality: While type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, it's not necessarily irreversible. With diligent management, including lifestyle changes and medication if necessary, some individuals can achieve remission, meaning their blood sugar levels return to normal and they no longer require medication. However, this requires ongoing commitment and careful monitoring.
Myth 5: All symptoms of type 2 diabetes are easily noticeable.
Reality: Many individuals with type 2 diabetes experience no noticeable symptoms in the early stages. This makes early detection crucial, as the damage caused by high blood sugar can occur silently. Regular screenings, especially for those at high risk, are vital.
Accurate Statements Describing Type 2 Diabetes
Based on the information presented, here are several statements that accurately describe type 2 diabetes:
-
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from insulin resistance and, eventually, relative insulin deficiency. This statement encapsulates the core pathophysiological mechanisms.
-
Type 2 diabetes is a systemic disease that affects multiple organs and systems, leading to a range of potential complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, eye disease, nerve damage, and foot problems. This emphasizes the widespread consequences of the condition.
-
Type 2 diabetes develops due to a complex interplay of genetic predisposition, lifestyle factors, and environmental influences. This acknowledges the multifaceted etiology.
-
Effective management of type 2 diabetes typically involves lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, and weight management, often in conjunction with medication to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. This highlights the comprehensive approach to management.
-
Type 2 diabetes can be diagnosed through blood tests measuring fasting blood glucose, HbA1c levels, and other relevant markers. This outlines the diagnostic methods.
-
While type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, diligent management can lead to improved health outcomes, potential remission in some cases, and a reduction in the risk of long-term complications. This offers a message of hope and emphasizes the importance of proactive management.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding, Better Management
Understanding the accurate description of type 2 diabetes is critical for both individuals living with the condition and healthcare professionals. It moves beyond simplistic explanations and acknowledges the complexity of its causes, progression, and management. By dispelling common misconceptions and emphasizing the importance of early detection, effective treatment, and ongoing monitoring, we can improve health outcomes for millions affected by this prevalent chronic disease. This comprehensive understanding empowers individuals to take control of their health and work towards a better future. Remember, seeking professional medical advice is paramount for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When A Patient Calls With A Complaint
Apr 03, 2025
-
According To The Theory Of Plate Tectonics The Plates Are
Apr 03, 2025
-
Group A Strep Screen Done Frequently In Pol
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Computers Do You Need To Build A Network
Apr 03, 2025
-
A Program That Replicates Itself And Clogs Computers And Networks
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement Accurately Describes Type 2 Diabetes . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
