Which Statements Regarding Apoptosis Are Correct Select All That Apply
Breaking News Today
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
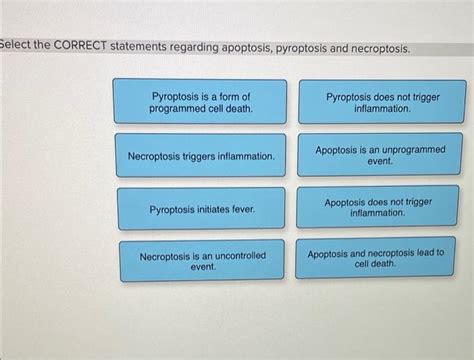
Table of Contents
Which Statements Regarding Apoptosis are Correct? Select All That Apply. A Deep Dive into Programmed Cell Death
Apoptosis, the elegant and precisely orchestrated process of programmed cell death, is crucial for a multitude of biological processes. From embryonic development to immune system regulation and disease prevention, its role is paramount. Understanding apoptosis is key to grasping many aspects of biology and medicine. This article delves into the intricacies of apoptosis, examining various statements regarding its mechanisms and implications, and clarifying which statements are indeed correct. We’ll explore its key characteristics, molecular pathways, and the consequences of its dysregulation.
Understanding Apoptosis: The Basics
Before we delve into specific statements, let's establish a foundational understanding of apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, a form of cell death resulting from injury or trauma, apoptosis is an active, genetically controlled process. It is characterized by several key features:
- Cell shrinkage: The cell shrinks and condenses, becoming smaller and denser.
- Chromatin condensation: The DNA within the nucleus becomes highly condensed and fragmented.
- Formation of apoptotic bodies: The cell breaks down into membrane-bound fragments called apoptotic bodies, containing cellular organelles and DNA.
- Lack of inflammation: Unlike necrosis, apoptosis doesn't trigger an inflammatory response in the surrounding tissue. This is crucial to prevent collateral damage.
Key Molecular Pathways in Apoptosis
Two major pathways orchestrate apoptosis: the intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway and the extrinsic (death receptor) pathway.
1. The Intrinsic (Mitochondrial) Pathway:
This pathway is primarily activated by intracellular stress, such as DNA damage, ER stress, or growth factor deprivation. The key player here is the mitochondria. When stressed, the mitochondria release cytochrome c, a crucial protein that initiates a cascade of events leading to apoptosis.
- Bcl-2 family proteins: This family of proteins acts as crucial regulators of the intrinsic pathway. Pro-apoptotic proteins like Bax and Bak promote cytochrome c release, while anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL inhibit it. The balance between these proteins determines whether apoptosis is triggered.
- Caspases: A family of cysteine-aspartic acid proteases, caspases are central executioners of apoptosis. Initiator caspases (like caspase-9) are activated upon cytochrome c release, triggering a cascade that activates executioner caspases (like caspase-3 and caspase-7). These executioner caspases cleave various cellular proteins, leading to the morphological changes characteristic of apoptosis.
2. The Extrinsic (Death Receptor) Pathway:
This pathway is triggered by extracellular signals, primarily through death receptors on the cell surface. These receptors belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily, including Fas (CD95) and TRAIL-R1/R2.
- Ligand binding: When a death ligand, such as Fas ligand (FasL) or TRAIL, binds to its corresponding death receptor, it triggers receptor trimerization.
- Death-inducing signaling complex (DISC): This trimerization leads to the formation of the DISC, which recruits and activates initiator caspase-8.
- Caspase cascade: Caspase-8 then activates executioner caspases, leading to the same downstream effects as the intrinsic pathway.
Analyzing Statements about Apoptosis: Which are Correct?
Now, let's consider several statements about apoptosis and determine their accuracy. Remember that the correct answers will reflect the detailed mechanisms and features discussed above.
Statement 1: Apoptosis is a passive process of cell death.
INCORRECT. Apoptosis is an active, energy-dependent process requiring gene expression and protein synthesis. It's a precisely regulated program, not a passive response to damage.
Statement 2: Apoptosis involves the formation of apoptotic bodies.
CORRECT. Apoptotic bodies are membrane-bound vesicles that result from the fragmentation of the dying cell. This ensures the controlled removal of cellular debris without triggering inflammation.
Statement 3: The intrinsic pathway of apoptosis is triggered by extracellular signals.
INCORRECT. The intrinsic pathway is primarily triggered by intracellular stress signals such as DNA damage, ER stress, or growth factor withdrawal. The extrinsic pathway is the one initiated by extracellular signals.
Statement 4: Caspases are a family of proteases that play a crucial role in apoptosis.
CORRECT. Caspases are cysteine-aspartic acid proteases that are essential executioners of apoptosis. Their activation leads to the cleavage of numerous cellular proteins, causing the characteristic morphological and biochemical changes of apoptosis.
Statement 5: Apoptosis is always a pathological process.
INCORRECT. While dysregulation of apoptosis contributes to many diseases, it is essential for normal physiological processes. It plays a critical role in development, immune system function, and tissue homeostasis. Think of its role in removing damaged cells or sculpting the developing embryo.
Statement 6: The Bcl-2 family of proteins regulates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway.
CORRECT. The Bcl-2 family includes both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins. The balance between these proteins determines the sensitivity of the cell to apoptotic stimuli. Bax and Bak promote apoptosis, whereas Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL inhibit it.
Statement 7: Apoptosis contributes to the development of autoimmune diseases.
INCORRECT. While apoptosis is generally beneficial, its dysregulation (either too much or too little) is implicated in autoimmune diseases. Insufficient apoptosis can lead to the persistence of self-reactive immune cells.
Statement 8: Apoptosis does not trigger inflammation.
CORRECT. One of the hallmarks of apoptosis is its lack of inflammatory response, unlike necrosis. Apoptotic cells are efficiently cleared by phagocytes without inducing an inflammatory cascade.
Statement 9: The extrinsic pathway of apoptosis involves death receptors on the cell surface.
CORRECT. This pathway is initiated by the binding of death ligands to their corresponding death receptors, leading to the formation of the DISC and activation of the caspase cascade.
Statement 10: Dysregulation of apoptosis is implicated in cancer development.
CORRECT. Defects in the apoptotic machinery can allow damaged or cancerous cells to survive and proliferate, contributing to tumorigenesis. Cancer cells often evade apoptosis through various mechanisms, allowing them to escape normal cellular controls.
Statement 11: Apoptosis is involved in the development of the nervous system.
CORRECT. Programmed cell death during neural development is crucial for sculpting the nervous system. Excess neurons are eliminated during development via apoptosis to ensure proper wiring and neuronal connectivity. This highlights the crucial role of apoptosis in shaping organ structure.
Statement 12: Cytochrome c release from the mitochondria is a key event in the intrinsic apoptotic pathway.
CORRECT. The release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria is a critical step that initiates the caspase cascade in the intrinsic pathway. It acts as a crucial signaling molecule for apoptosis.
Statement 13: The extrinsic apoptotic pathway can be inhibited by certain viral proteins.
CORRECT. Some viruses encode proteins that specifically inhibit the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, allowing them to evade immune system surveillance and promote their own replication. This highlights the sophisticated mechanisms that both hosts and pathogens utilize to influence the outcome of apoptosis.
Statement 14: Apoptosis is a crucial mechanism for maintaining tissue homeostasis.
CORRECT. The removal of damaged or infected cells through apoptosis maintains tissue integrity and prevents the propagation of harmful cells within the organism. Constant cellular turnover and the removal of unwanted cells are part of this delicate balance.
Statement 15: Understanding apoptosis is crucial for developing new cancer therapies.
CORRECT. Manipulating the apoptotic pathways is a major goal in cancer therapy. Strategies aimed at sensitizing cancer cells to apoptosis or blocking their ability to evade apoptosis are actively being developed.
Conclusion
Apoptosis, a tightly regulated process of programmed cell death, is fundamental to numerous biological processes. Understanding its intricacies, including the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways and the role of key molecular players like caspases and Bcl-2 family proteins, is crucial. Many statements regarding apoptosis can be evaluated based on this knowledge. By correctly identifying the accurate statements, we gain a deeper understanding of this essential cellular mechanism and its implications in health and disease. The complex interplay of pathways and regulatory molecules underscores the importance of continued research in this field and its relevance to a wide range of medical and biological applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When Writers Use Long Paragraphs In Business Messages It
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Safest Technique Used For Steering Wheel Control Is
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Indication For Mouth To Mouth Rescue Breaths
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Quienes Les Escribiste Las Postales A Ellos
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Serious Problem Following The Revolutionary War Was That
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statements Regarding Apoptosis Are Correct Select All That Apply . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
