Which Test Helps Id Reproductive Tract Fibroids Tumors And Fistulas
Breaking News Today
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
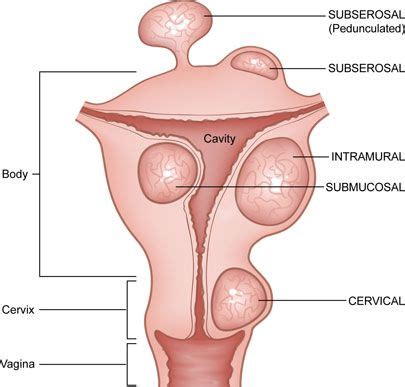
Table of Contents
Which Test Helps ID Reproductive Tract Fibroids, Tumors, and Fistulas?
Identifying reproductive tract issues like fibroids, tumors, and fistulas requires a multi-pronged approach using various diagnostic tests. There's no single "magic bullet" test; the best approach depends on the individual's symptoms, medical history, and the suspected condition. This article will explore the common diagnostic methods used to identify fibroids, tumors, and fistulas in the reproductive tract.
Understanding the Conditions
Before delving into the tests, let's briefly review the conditions themselves:
Fibroids
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They vary in size and location, ranging from microscopic to large masses that distort the uterus. Symptoms can include heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, frequent urination, constipation, and infertility.
Tumors
Tumors of the reproductive tract encompass a broad category, including both benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) growths. These can occur in the uterus, ovaries, cervix, vagina, or vulva. Symptoms vary greatly depending on the type, location, and size of the tumor. They may present with abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, changes in bowel or bladder function, or unexplained weight loss.
Fistulas
A fistula is an abnormal connection between two organs or between an organ and the skin. In the reproductive tract, fistulas can form between the vagina and rectum (rectovaginal fistula), vagina and bladder (vesicovaginal fistula), or vagina and bowel (enterovaginal fistula). Common symptoms include leakage of stool, urine, or gas into the vagina.
Diagnostic Tests: A Comprehensive Overview
Several diagnostic tests are employed to identify fibroids, tumors, and fistulas. The choice of tests is often guided by a patient's clinical presentation and the physician's assessment.
1. Pelvic Examination: The Foundation
A thorough pelvic examination is the cornerstone of diagnosis. The physician will assess the size, shape, and consistency of the uterus and ovaries, checking for any abnormalities. This physical examination can sometimes suggest the presence of fibroids or masses but cannot definitively diagnose them.
2. Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS): Imaging the Pelvis
TVUS is a highly effective imaging technique that uses sound waves to create images of the pelvic organs. A transducer is inserted into the vagina to provide a clearer view of the uterus, ovaries, and surrounding structures. TVUS is excellent for detecting fibroids, assessing their size and location, and identifying ovarian cysts or tumors. It can also help identify some fistulas, though it might not be sufficient for all types.
3. Transabdominal Ultrasound (TAUS): An External Approach
TAUS uses a transducer placed on the abdomen to create images of the pelvic organs. While not as detailed as TVUS, it's a non-invasive option that is useful as a preliminary screening tool. It's often used in conjunction with TVUS to provide a more comprehensive view.
4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Detailed Structural Analysis
MRI provides highly detailed images of the pelvic organs, offering superior visualization compared to ultrasound. It's particularly useful for characterizing fibroids, differentiating them from other masses, and assessing their relationship with surrounding structures. MRI is also very helpful in identifying and characterizing complex fistulas.
5. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A Complementary Tool
CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body. While less frequently used than MRI for reproductive tract issues, CT scans can be helpful in certain situations, such as evaluating the extent of a large tumor or assessing for potential spread to other organs.
6. Hysterosalpingography (HSG): Visualizing the Uterine Cavity
HSG involves injecting a contrast dye into the uterus and fallopian tubes. X-rays are then taken to visualize the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. HSG is primarily used to assess tubal patency (openness) but can also reveal uterine abnormalities, such as fibroids or polyps that may distort the uterine cavity.
7. Hysteroscopy: Direct Visualization of the Uterus
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure where a thin, flexible telescope is inserted into the uterus through the vagina and cervix. This allows for direct visualization of the uterine lining and identification of fibroids, polyps, or other abnormalities. It can also be used to remove small fibroids or polyps during the procedure.
8. Laparoscopy: Exploring the Abdominal Cavity
Laparoscopy involves inserting a small incision in the abdomen to introduce a laparoscope, a thin, lighted instrument with a camera. This provides a direct visual examination of the pelvic organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. It's often used to diagnose and treat endometriosis, ovarian cysts, and certain types of tumors. It can also be used to repair some types of fistulas.
9. Biopsy: Confirming the Diagnosis
A biopsy involves removing a small tissue sample for microscopic examination. This is crucial for determining whether a tumor is benign or malignant. A biopsy can be performed using various methods, including a needle biopsy (for tumors that are easily accessible) or during a hysteroscopy or laparoscopy.
10. Cystoscopy and Proctosigmoidoscopy: Evaluating Fistulas
Cystoscopy (for bladder fistulas) and proctosigmoidoscopy (for rectal fistulas) are procedures where a thin, flexible scope is inserted into the bladder or rectum, respectively, to visualize the fistula tract and assess its extent. These are critical for identifying and staging fistulas accurately.
Choosing the Right Tests: A Tailored Approach
The selection of diagnostic tests depends on several factors:
-
Symptoms: The nature and severity of symptoms guide the initial investigation. For example, heavy menstrual bleeding might prompt an ultrasound, while urinary or fecal incontinence suggests the possibility of a fistula, prompting cystoscopy or proctosigmoidoscopy.
-
Medical History: A patient's past medical history, including previous surgeries or reproductive health issues, informs the choice of tests.
-
Suspected Diagnosis: If a specific condition is suspected based on symptoms and physical examination, targeted tests are chosen to confirm the diagnosis. For instance, if fibroids are suspected, ultrasound is usually the first choice.
-
Risk Factors: Certain risk factors, such as age, family history of cancer, and genetic predispositions, influence the decision-making process.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Diagnosis
Identifying fibroids, tumors, and fistulas in the reproductive tract often necessitates employing a combination of diagnostic tools. While imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI play a vital role in visualizing these conditions, procedures like hysteroscopy, laparoscopy, cystoscopy, and proctosigmoidoscopy may be necessary for definitive diagnosis and treatment planning. A careful assessment of individual symptoms, medical history, and risk factors is crucial to tailor the diagnostic approach and ensure accurate and timely management of these complex conditions. Always consult with a healthcare professional for any concerns regarding reproductive health. Early detection and appropriate intervention are crucial for optimal outcomes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Self Worth Accomplishment And Confidence Represent The
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Food Establishment That Serves Raw Oysters
Apr 01, 2025
-
Atls Test Questions And Answers 10th Edition
Apr 01, 2025
-
Label The Map Of Costa Rica Based On Panorama
Apr 01, 2025
-
When Using A Visual Signal To Support Your Recovery Efforts
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Test Helps Id Reproductive Tract Fibroids Tumors And Fistulas . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
