Which Type Of Boot Authentication Is More Secure
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
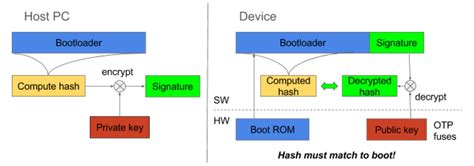
Table of Contents
Which Type of Boot Authentication is More Secure? A Deep Dive into Modern Security
Boot authentication is the cornerstone of system security, ensuring that only authorized software and hardware can initiate the boot process. Without robust boot authentication, systems are vulnerable to a wide array of attacks, including rootkits, malware injections, and unauthorized access. The choice between different boot authentication methods significantly impacts the security posture of a system. This article will delve into the strengths and weaknesses of various boot authentication methods, comparing their effectiveness and identifying which provides the strongest security.
Understanding the Landscape: Types of Boot Authentication
Several methods exist for authenticating the boot process, each with varying levels of security and complexity. These include:
1. BIOS/UEFI Secure Boot: The Foundation
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and its successor, UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), provide fundamental boot security features. While not inherently strong authentication methods on their own, they form the basis for more advanced techniques.
- BIOS: Offers limited security features, primarily focusing on preventing unauthorized boot sector modification. Its age and limitations make it susceptible to various attacks.
- UEFI Secure Boot: A significant improvement over BIOS, UEFI Secure Boot verifies the digital signature of bootloaders and operating system kernels before loading them. This prevents malicious code from being executed during the initial boot stages. However, its effectiveness depends on the implementation and the strength of the digital signature chain. A compromised key or a flawed signature verification process can undermine its security.
Security Considerations: While Secure Boot enhances security, it's not a foolproof solution. Sophisticated attackers can still bypass Secure Boot by manipulating the firmware itself or exploiting vulnerabilities in the UEFI implementation.
2. Measured Boot: Adding Transparency
Measured boot takes Secure Boot a step further by generating and recording measurements of each boot component's integrity. These measurements, often stored in a secure log, provide an auditable record of the boot process. This allows for post-boot verification of the system's integrity. Any discrepancies between the expected and measured values indicate a potential compromise.
Security Considerations: Measured boot significantly improves the detection of attacks, but it relies on the security of the measurement storage location. If an attacker can tamper with the measurement log, it negates the benefits of this approach.
3. Trusted Platform Module (TPM): Hardware-Based Security
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated hardware chip designed to secure cryptographic keys and provide hardware-rooted trust. It plays a crucial role in several advanced boot authentication methods. The TPM securely stores cryptographic keys, generates unique measurements of the boot process, and provides attestation capabilities.
Security Considerations: The TPM significantly enhances security by providing a tamper-resistant environment for storing sensitive data and performing cryptographic operations. However, vulnerabilities in the TPM firmware or hardware itself could still compromise the system.
4. Virtualization-Based Security (VBS): Isolating the Boot Process
VBS utilizes virtualization technologies to create a secure virtual machine (VM) for critical boot components. This isolates the boot process from the rest of the system, protecting it from malicious software and attacks. Hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI) is a common example, providing kernel-level protection against tampering.
Security Considerations: VBS offers strong protection, but its effectiveness depends on the security of the hypervisor and the VM configuration. A compromised hypervisor or vulnerabilities in the VM could still allow attackers to bypass its security measures.
5. Hardware Root of Trust (HRoT): The Ultimate Foundation
HRoT represents the most secure boot authentication method. It involves a secure element embedded directly into the system's hardware, providing a trusted foundation for the entire boot process. This element, often a specialized chip or a portion of the CPU, is tamper-resistant and provides cryptographic keys and measurements, ensuring the integrity of the boot chain.
Security Considerations: HRoT offers the highest level of security, but its implementation is more complex and expensive. It is commonly found in high-security environments and specialized hardware.
Comparing the Security Levels
The security levels of the various boot authentication methods can be ranked as follows, from least to most secure:
- BIOS: Offers minimal security, easily bypassed by attackers.
- UEFI Secure Boot: Provides basic integrity checks, but susceptible to sophisticated attacks.
- Measured Boot: Improves detection capabilities but relies on the integrity of the measurement log.
- VBS (with HVCI): Offers strong isolation, but dependent on the hypervisor's security.
- TPM-based Authentication: Significantly enhances security with hardware-backed cryptographic keys and measurements.
- HRoT-based Authentication: Provides the strongest security through a tamper-resistant hardware root of trust.
Real-World Implications and Considerations
The choice of the "most secure" boot authentication method depends on several factors:
- System Requirements: Some methods require specific hardware (e.g., TPM, HRoT), while others rely on software implementations (e.g., UEFI Secure Boot).
- Cost: HRoT solutions are generally more expensive to implement than simpler methods like UEFI Secure Boot.
- Complexity: Managing and maintaining more sophisticated systems like those utilizing TPMs or HRoTs requires specialized expertise.
- Threat Model: The level of security required depends on the system's sensitivity and the potential threats it faces. A personal computer may not require the same level of security as a server handling sensitive data.
Future Trends in Boot Authentication
The field of boot authentication is constantly evolving. We can expect future advancements in:
- Improved Hardware Security: More advanced tamper-resistant hardware components will further strengthen boot security.
- AI-powered Threat Detection: Artificial intelligence and machine learning can be used to detect subtle anomalies and patterns that indicate potential attacks.
- Remote Attestation: Techniques for remotely verifying the integrity of a system's boot process will become increasingly important for managing large networks.
- Integration with other Security Mechanisms: Boot authentication will continue to integrate with other security layers, such as encryption and access control, to create a more robust and comprehensive security architecture.
Conclusion
While there is no single "most secure" boot authentication method that fits all scenarios, the choice should be based on a careful assessment of the system's security requirements, the available resources, and the potential threats. For maximum security, combining several methods like UEFI Secure Boot, Measured Boot, TPM, and VBS offers a layered approach that significantly mitigates the risk of attacks. While solutions utilizing HRoT offer the strongest theoretical protection, their cost and complexity may not be justifiable for all applications. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method is crucial for making an informed decision and implementing a robust boot authentication strategy. Prioritizing security through a combination of best practices and regularly updating firmware and software remains essential in the ongoing battle against evolving cyber threats.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Fire Department Line Personnel Are Responsible For
Mar 22, 2025
-
Compare Group Selection To Single Tree Selection
Mar 22, 2025
-
New York State Notary Exam Study Guide
Mar 22, 2025
-
Cpr Will Not Be Effective If The Patient Is
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Marine Corps Order For Records Management
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Type Of Boot Authentication Is More Secure . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
