Why Are You Performing The Test With Catalase And Water
Breaking News Today
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
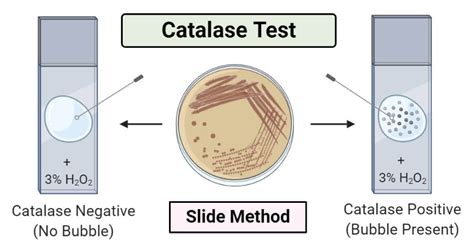
Table of Contents
Why Are You Performing the Test with Catalase and Water? Understanding the Catalase Enzyme Assay
The catalase test, a simple yet informative experiment often conducted in introductory biology and biochemistry labs, involves the reaction between catalase enzyme and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂). While water is often present as a solvent, it's crucial to understand that the water itself doesn't directly participate in the core reaction. The focus is entirely on observing the catalytic activity of catalase on hydrogen peroxide. This article delves deep into the rationale behind this test, exploring the enzyme's role, the reaction's mechanics, its applications, and the importance of controlling variables like water's presence.
The Role of Catalase: A Biological Guardian
Catalase is a ubiquitous enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen. Its primary function is to detoxify hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), a highly reactive and potentially damaging byproduct of cellular metabolism. Hydrogen peroxide, if left unchecked, can cause significant oxidative stress, damaging cellular components like proteins, lipids, and DNA. Catalase acts as a crucial defense mechanism, protecting cells from this harmful compound.
The Catalase Reaction: Breaking Down Hydrogen Peroxide
Catalase catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas:
2H₂O₂ → 2H₂O + O₂
This reaction is remarkably efficient. A single catalase molecule can break down millions of hydrogen peroxide molecules per second. The rapid production of oxygen gas is visually evident in the catalase test, often manifesting as bubbling or effervescence. This observable reaction is the core of the experiment.
Why Water is Present: The Importance of the Solvent
While water doesn't directly participate in the chemical reaction itself, its presence is essential for the experiment to function properly. Water serves as the solvent for both the catalase enzyme and the hydrogen peroxide substrate. It provides the medium in which the molecules can interact and the reaction can occur.
Maintaining Optimal Conditions for the Enzyme
Catalase, like all enzymes, functions optimally within a specific range of conditions, including temperature and pH. Water helps maintain these conditions. The solution's temperature and pH can significantly influence catalase's activity. Using water as a solvent allows for greater control over these parameters. Buffer solutions are often used in more precise experiments to maintain a constant pH.
Facilitating Molecular Interactions
Water molecules interact with both catalase and hydrogen peroxide, influencing their conformation and interactions. The precise nature of these interactions isn't always straightforward, but they are critical for the enzyme to bind to the substrate and catalyze the reaction.
Controlling Experimental Variables
The use of water as a solvent helps standardize the experimental conditions. Using the same solvent ensures consistency between different trials, allowing for accurate comparison and analysis of results. If different solvents were used, it would introduce uncontrolled variables, making it difficult to interpret the results.
Beyond the Basics: Variations and Applications of the Catalase Test
The simple catalase test with water as a solvent can be expanded and adapted for various purposes:
1. Assessing Catalase Activity in Different Organisms:
The rate of oxygen gas production can be used as a quantitative measure of catalase activity. This comparison can be applied to different organisms or tissues, revealing variations in their respective antioxidant defense mechanisms. For instance, one could compare the catalase activity in plant vs. animal tissues.
2. Investigating the Effects of Environmental Factors on Catalase Activity:
By varying the temperature, pH, or introducing inhibitors, researchers can examine how these factors impact catalase activity. This information is valuable in understanding how environmental stressors affect cellular function. For example, one might investigate the effect of temperature changes on catalase activity in bacteria.
3. Studying Enzyme Kinetics:
More sophisticated versions of the catalase test can be used to study enzyme kinetics – the relationship between the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the concentration of the substrate (hydrogen peroxide). This information helps provide crucial insights into how catalase functions at a molecular level.
4. Detecting Catalase Presence in Samples:
The simple observation of bubbling can be used as a quick and qualitative test for the presence of catalase in an unknown sample. This can be applied in various contexts, from microbiology to food science.
The Importance of Controls in the Catalase Test
A well-designed experiment requires appropriate controls to ensure that the observed effects are due to the variable being investigated (catalase activity) and not other factors. In the catalase test, the following controls are important:
- Positive Control: A sample known to contain high levels of catalase activity (e.g., liver tissue). This control serves to validate the assay's ability to detect catalase activity.
- Negative Control: A sample known to lack catalase activity (e.g., boiled liver tissue). This control helps rule out other factors that might cause bubbling, ensuring that the observed reaction is due to catalase.
- Blank Control: A sample containing only water and hydrogen peroxide. This helps identify any background bubbling not attributable to catalase activity.
Interpreting Results: What the Bubbles Tell Us
The vigorousness of the bubbling in the catalase test correlates with the amount of catalase present. More bubbling generally indicates higher catalase activity. However, quantitative measurements are needed for precise comparisons. This can involve techniques like measuring the volume of oxygen produced over time or using specialized equipment to quantify the rate of reaction.
Conclusion: The Simple Test with a Deep Meaning
While the catalase test appears straightforward – simply mixing catalase with hydrogen peroxide in water – its simplicity belies its significance. This experiment provides a powerful introduction to fundamental concepts in enzymology, biochemistry, and experimental design. Understanding the role of the enzyme, the importance of water as a solvent, and the necessity of controls are crucial for interpreting the results accurately and drawing meaningful conclusions. The test's versatility makes it applicable in various settings, highlighting the catalase enzyme's crucial role in protecting living organisms from oxidative stress. By mastering this simple yet informative experiment, students gain invaluable skills in experimental design, data analysis, and an appreciation for the intricacies of biological processes. Its implications extend beyond the laboratory, offering insights into fundamental biological mechanisms and their significance in the broader context of life itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which One Would Be Considered Critical Information
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Are Three Components Of Human Resource Planning
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Two Properties Are Required For Every Field
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Makeup Procedural Steps Comes First
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Widespread Financial Insecurity Of Americans Is Primarily Because
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Why Are You Performing The Test With Catalase And Water . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
