A Disorder Caused By Hyperthyroidism Is Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 7 min read
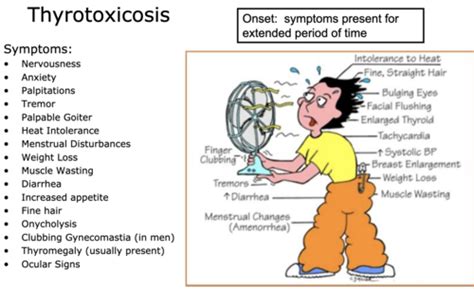
Table of Contents
A Disorder Caused by Hyperthyroidism: A Comprehensive Guide
Hyperthyroidism, a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, can lead to a range of disorders that significantly impact various bodily systems. Understanding these disorders is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of hyperthyroidism-related disorders, providing detailed explanations and exploring the various ways they manifest.
Understanding Hyperthyroidism
Before we delve into the specific disorders, let's establish a foundational understanding of hyperthyroidism itself. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones that regulate metabolism, affecting everything from heart rate and body temperature to weight and energy levels. In hyperthyroidism, the thyroid produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). This hormonal surge disrupts the body's delicate balance, triggering a cascade of symptoms and potential complications.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Several factors can contribute to the development of hyperthyroidism:
- Graves' Disease: This autoimmune disorder is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. The body's immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, stimulating it to produce excessive hormones.
- Toxic Multinodular Goiter (TMG): This condition involves the development of multiple nodules (lumps) on the thyroid gland, some of which may produce excessive thyroid hormones.
- Toxic Adenoma: A single nodule on the thyroid gland can become hyperactive and produce an excess of hormones.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland, often caused by viral or bacterial infections, can lead to a temporary release of stored thyroid hormones, resulting in hyperthyroidism.
- Excessive Iodine Intake: While iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, excessive intake can trigger hyperthyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism-Related Disorders: A Detailed Exploration
The excessive thyroid hormones in hyperthyroidism exert widespread effects throughout the body, leading to a spectrum of disorders. Let's examine some of the most prevalent:
1. Graves' Ophthalmopathy (GO)
Often associated with Graves' disease, GO affects the eye muscles and tissues surrounding the eyes. Symptoms include:
- Proptosis (Bulging Eyes): This is a hallmark feature of GO, caused by inflammation and swelling behind the eyes.
- Eyelid Retraction: The eyelids may appear retracted, making the whites of the eyes more visible.
- Diplopia (Double Vision): Swelling and inflammation can affect eye muscle function, resulting in double vision.
- Dry Eyes: Reduced tear production can lead to dry, irritated eyes.
- Pain and discomfort: Patients may experience pain, pressure, and discomfort in and around the eyes.
Treatment for GO ranges from observation to medications like steroids and orbital decompression surgery in severe cases.
2. Graves' Dermopathy
Similar to GO, Graves' dermopathy is an autoimmune manifestation associated with Graves' disease. It's characterized by skin changes, including:
- Pretibial Myxedema: Thickening and swelling of the skin, typically on the shins and lower legs, causing a waxy or orange-peel-like appearance.
- Skin changes on other areas of the body: In some cases, skin thickening can occur on other areas of the body as well.
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, often involving topical or systemic corticosteroids.
3. Cardiovascular Disorders
Hyperthyroidism significantly impacts the cardiovascular system. The excess thyroid hormones increase heart rate (tachycardia), increase cardiac output and can lead to:
- Atrial Fibrillation: An irregular and rapid heartbeat that can increase the risk of stroke.
- Heart Failure: In severe cases, the heart may become unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
- Increased Blood Pressure: Hyperthyroidism can contribute to hypertension.
- Angina: Chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
Management involves controlling thyroid hormone levels through medication or other treatments and addressing the specific cardiovascular complications.
4. Gastrointestinal Disorders
The digestive system is also affected by the excess thyroid hormones, leading to:
- Increased Bowel Movements: Frequent, loose stools are common due to increased intestinal motility.
- Diarrhea: Excessive bowel movements can lead to diarrhea.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms are less common but can occur.
- Weight Loss: Increased metabolism can lead to unintentional weight loss, despite adequate food intake.
Management involves dietary adjustments and medication to control thyroid hormone levels.
5. Musculoskeletal Disorders
Hyperthyroidism can affect muscles and bones, leading to:
- Muscle Weakness: This can range from mild weakness to significant muscle atrophy.
- Osteoporosis: Increased bone turnover can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
- Tremors: Fine tremors in the hands and fingers are frequently observed.
6. Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders
The effects of hyperthyroidism extend to the nervous system, leading to:
- Anxiety and Irritability: The increased metabolic rate can lead to heightened anxiety and irritability.
- Insomnia: Difficulty sleeping is a common complaint.
- Tremors: Fine tremors, as mentioned earlier, can affect fine motor skills and hand steadiness.
- Cognitive Impairment: In some cases, hyperthyroidism can affect cognitive function, including memory and concentration.
- Depression: While less common than anxiety, depression can also be a consequence of hyperthyroidism.
Treatment focuses on managing the hyperthyroidism and addressing any underlying mental health conditions.
7. Menstrual Irregularities
In women, hyperthyroidism can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to:
- Oligomenorrhea (Infrequent Periods): Periods may become less frequent.
- Amenorrhea (Absence of Periods): In some cases, periods may cease altogether.
- Irregular Bleeding: Menstrual bleeding may become irregular and unpredictable.
Treatment focuses on controlling thyroid hormone levels.
8. Reproductive Issues
Hyperthyroidism can affect fertility in both men and women. In women, it can lead to irregular ovulation and difficulty conceiving. In men, it can decrease sperm production and affect sexual function.
Management involves controlling hyperthyroidism and addressing any specific reproductive challenges.
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism-Related Disorders
Diagnosing hyperthyroidism and its associated disorders involves a combination of:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will assess symptoms and perform a physical exam, including checking the thyroid gland for enlargement.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are essential to measure thyroid hormone levels (T3, T4, and TSH). Elevated T3 and T4 levels with a suppressed TSH indicate hyperthyroidism.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visualize the thyroid gland and detect any abnormalities.
- Specialized Tests: Further tests may be necessary to identify specific disorders, such as ophthalmologic exams for Graves' ophthalmopathy and skin biopsies for Graves' dermopathy.
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism-Related Disorders
Treatment strategies for hyperthyroidism and its associated disorders are tailored to the individual's specific condition and severity. Common approaches include:
- Antithyroid Medications: These drugs help block thyroid hormone production.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment destroys thyroid tissue, reducing hormone production.
- Thyroidectomy (Surgical Removal of the Thyroid Gland): Surgery may be necessary in certain cases.
- Beta-blockers: These medications help control symptoms like rapid heart rate and tremors.
- Symptom-Specific Treatments: Specific treatments are used to manage individual disorders such as Graves' ophthalmopathy and dermopathy.
Living with Hyperthyroidism and its Disorders
Living with hyperthyroidism and its related disorders requires a multifaceted approach:
- Regular Medical Monitoring: Regular checkups and blood tests are crucial to monitor thyroid hormone levels and assess treatment effectiveness.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Dietary changes, stress management techniques, and regular exercise can contribute to overall well-being.
- Medication Adherence: Strictly following the prescribed medication regimen is critical for managing the condition.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with hyperthyroidism can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding the condition, its potential complications, and treatment options empowers individuals to actively participate in their healthcare.
Conclusion
Hyperthyroidism is a complex endocrine disorder that can manifest in a variety of ways, impacting multiple organ systems. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial to prevent serious complications and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. Through careful monitoring, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can effectively manage hyperthyroidism and its related disorders, leading fulfilling and healthy lives. Remember, seeking medical advice and engaging with your healthcare team is vital for personalized care and effective management of this condition. This guide provides comprehensive information, but individual cases require the expertise of healthcare professionals. Always consult with your doctor or a qualified healthcare provider before making any decisions related to your health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
National Highway Safety Administration Drug And Alcohol Test Answers
Apr 01, 2025
-
Firms Are Motivated To Minimize Production Costs Because
Apr 01, 2025
-
Where Should A Food Handler Check The Temperature
Apr 01, 2025
-
Your Drivers License May Be Suspended For
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Major Depression
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Disorder Caused By Hyperthyroidism Is Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
