A Ketogenic Diet Limits The Intake Of Which Macronutrient
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
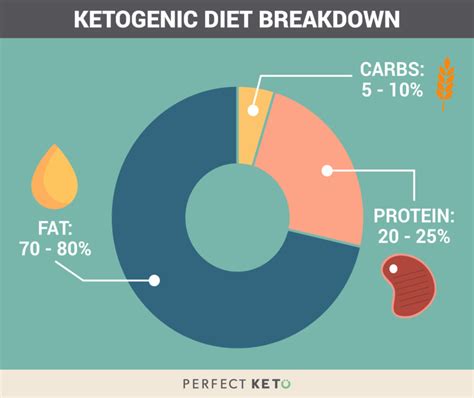
Table of Contents
A Ketogenic Diet: Deep Dive into Macronutrient Restriction
The ketogenic diet, often shortened to "keto," has surged in popularity as a weight-loss strategy and for managing certain medical conditions. But what exactly is a ketogenic diet, and which macronutrient does it drastically limit? The answer is carbohydrates. This article will explore the ketogenic diet in detail, explaining its core principles, benefits, drawbacks, and the crucial role of carbohydrate restriction in its effectiveness.
Understanding Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of Your Diet
Before diving into the specifics of keto, let's review the three macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These provide your body with energy.
-
Carbohydrates: These are your body's primary energy source. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels your cells. Sources include bread, pasta, rice, fruits, and sugary drinks.
-
Proteins: Essential for building and repairing tissues, proteins are also used for energy if carbohydrate intake is low. Good sources include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, and lentils.
-
Fats: Fats are the most energy-dense macronutrient, providing more than twice the calories per gram compared to carbohydrates and proteins. They're crucial for hormone production, cell function, and nutrient absorption. Sources include oils (olive, avocado, coconut), nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
The Ketogenic Diet: A Low-Carb, High-Fat Approach
The ketogenic diet dramatically reduces carbohydrate intake, forcing the body into a metabolic state called ketosis. In ketosis, the body shifts from using glucose (from carbohydrates) as its primary fuel to using ketones. Ketones are produced from the breakdown of fats in the liver.
This significant reduction in carbohydrate intake is the defining characteristic of the ketogenic diet. While the exact macronutrient ratios can vary, a typical ketogenic diet consists of:
- High Fat (70-80%): This forms the primary energy source in ketosis.
- Moderate Protein (20-25%): Essential for maintaining muscle mass and overall health.
- Very Low Carbohydrates (5-10%): This is the crucial element that triggers and sustains ketosis. This usually translates to around 20-50 grams of net carbs per day, depending on individual factors like activity level and body composition.
Why Limit Carbohydrates on Keto?
The primary reason for drastically limiting carbohydrate intake on a ketogenic diet is to induce ketosis. When carbohydrate consumption is low, the body depletes its glycogen stores (stored glucose). This triggers a metabolic shift where the liver begins to break down fats into ketones, providing an alternative energy source.
This metabolic switch has several potential benefits, which we'll explore further below.
Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet has shown promise in various areas:
Weight Loss:
One of the most significant benefits is weight loss. By reducing carbohydrate intake and shifting to a fat-burning metabolism, many individuals experience significant weight loss on a ketogenic diet. However, it's important to note that sustainable weight loss depends on a holistic approach including regular exercise and mindful eating habits.
Blood Sugar Control:
The ketogenic diet can be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance. By limiting carbohydrate intake, it helps stabilize blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. This can reduce the need for medication in some cases, but it's crucial to consult a doctor before making dietary changes if you have diabetes.
Epilepsy Management:
The ketogenic diet has a long history of use in managing epilepsy, particularly in children who don't respond well to medication. While the exact mechanisms aren't fully understood, it's believed that ketones have neuroprotective effects.
Other Potential Benefits:
Some studies suggest that the ketogenic diet may also be beneficial for:
- Heart health: By improving cholesterol levels and reducing inflammation.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): By regulating hormones and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Certain types of cancer: Some research suggests a potential role in slowing cancer growth, but more studies are needed.
- Alzheimer's disease: Emerging research explores the potential benefits of ketones in protecting against brain damage.
Drawbacks and Potential Side Effects of the Ketogenic Diet
While the ketogenic diet offers several potential benefits, it's not without drawbacks and potential side effects:
The "Keto Flu":
Many individuals experience a period of flu-like symptoms in the initial days or weeks of starting a ketogenic diet. These symptoms, known as the "keto flu," can include headaches, fatigue, nausea, constipation, and dizziness. This is primarily due to electrolyte imbalances caused by the change in metabolism.
Nutrient Deficiencies:
Restrictive diets can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned. It's crucial to focus on nutrient-dense foods and consider supplementation to ensure adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals.
Long-Term Effects:
The long-term effects of the ketogenic diet are still being researched. Some concerns include kidney stones, potential cardiovascular issues in susceptible individuals, and nutritional deficiencies if the diet isn't well-planned.
Social Challenges:
The restrictive nature of the ketogenic diet can make social situations challenging. Eating out or attending social gatherings involving food can require careful planning and consideration.
Difficulty in Adherence:
Maintaining a ketogenic diet can be difficult in the long term for some people. The strict limitations on carbohydrate intake can make it challenging to sustain the diet without compromising on social activities or enjoyment of food.
Planning a Ketogenic Diet: Key Considerations
Successfully navigating a ketogenic diet requires careful planning and attention to detail:
Tracking Macronutrients:
Accurately tracking your macronutrient intake is crucial for ensuring you stay in ketosis. Many apps and websites can help you monitor your carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake.
Choosing the Right Foods:
Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods is key. Prioritize healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds. Include plenty of non-starchy vegetables and moderate amounts of protein from lean meats, poultry, fish, and eggs. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates.
Staying Hydrated:
Adequate hydration is essential, particularly during the initial stages of the diet, to help mitigate the "keto flu."
Electrolyte Balance:
Maintaining proper electrolyte balance (sodium, potassium, magnesium) is crucial to minimize side effects. Consider electrolyte supplements or consuming electrolyte-rich foods like bone broth.
Gradual Transition:
It's generally recommended to transition to a ketogenic diet gradually to reduce the severity of the "keto flu" and allow your body to adapt.
Ketogenic Diet and Specific Health Conditions
Before starting a ketogenic diet, especially if you have any underlying health conditions, it’s imperative to consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian. They can help you assess if it's suitable for you and guide you on how to implement it safely and effectively.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool, But Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
The ketogenic diet's core principle involves significantly limiting carbohydrate intake to induce ketosis. This metabolic shift can offer several potential health benefits, including weight loss, blood sugar control, and potential benefits for certain medical conditions. However, it's important to be aware of the potential drawbacks and side effects. It's not a magic bullet and requires careful planning, monitoring, and consideration of individual needs and health status. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any drastic dietary changes. The ketogenic diet, while powerful, is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and a personalized approach is crucial for optimal results and safety.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Pairs Is Not Correctly Matched
Mar 28, 2025
-
Form Of Communication That Reaches Large Audiences Without Personal Contact
Mar 28, 2025
-
Rn Learning System Medical Surgical Neurosensory Practice Quiz
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True About Machine Learning
Mar 28, 2025
-
On Net Does A Natural Disaster Create Jobs
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Ketogenic Diet Limits The Intake Of Which Macronutrient . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
