A Pet Scan Is Used To Detect Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
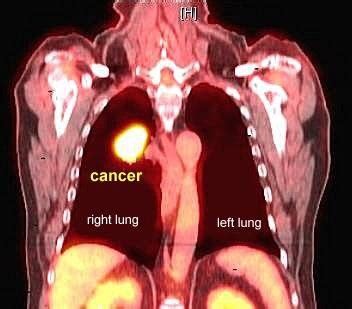
Table of Contents
A PET Scan is Used to Detect: A Comprehensive Guide
A Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan is a powerful imaging technique used in modern medicine to detect a wide range of diseases. It's not a single-purpose tool; instead, it offers unique insights into the body's metabolic activity, providing crucial information that other imaging methods like X-rays or CT scans simply cannot. This article delves deep into the applications of PET scans, exploring what conditions they're used to detect, how the procedure works, and its limitations.
What is a PET Scan?
A PET scan uses a radioactive tracer, often glucose (sugar), that's injected into the body. Cancer cells, for example, tend to have a higher metabolic rate than normal cells, meaning they consume more glucose. The radioactive tracer binds to these cells, and as it decays, it emits positrons. These positrons collide with electrons in the body, producing gamma rays that are detected by the PET scanner. The scanner then creates a 3D image showing the areas of increased metabolic activity. This is why a PET scan is often described as visualizing function, not just structure like an X-ray or CT scan.
Key Advantages of PET Scans:
- Early Detection: PET scans can detect cancerous tumors and other diseases at earlier stages than other imaging techniques, sometimes even before symptoms appear.
- Precise Localization: The images provide detailed information on the location and size of abnormalities.
- Staging Cancer: PET scans are crucial for staging cancer, determining the extent of the disease, and identifying metastases (spread of cancer to other parts of the body).
- Monitoring Treatment Response: PET scans can track the effectiveness of cancer treatment by showing whether tumors are shrinking or growing.
- Evaluating Treatment Efficacy: Used in conjunction with other imaging, it helps in evaluating the effectiveness of treatment plans across various diseases.
- Non-Invasive Procedure: Compared to surgical biopsies, it's a less invasive approach to diagnosis.
What Conditions Can a PET Scan Detect?
PET scans are highly versatile and used to detect a broad spectrum of diseases. Their primary application remains in oncology, but their use is expanding into cardiology, neurology, and other fields.
Oncology: The Main Application
- Cancer Detection: PET scans are exceptionally useful in detecting various types of cancer, including lung, breast, colorectal, lymphoma, and melanoma. It aids in identifying primary tumors, assessing their size and location, and detecting metastatic spread.
- Cancer Staging: Accurate staging is critical for determining the best treatment plan. A PET scan provides vital information on the extent of cancer involvement, including lymph node involvement and distant metastases.
- Treatment Response Monitoring: Following treatment, a PET scan helps assess the effectiveness of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery by visualizing the reduction in tumor size and metabolic activity. It can identify residual disease or recurrent cancer.
- Recurrence Detection: After successful treatment, a PET scan can be used to monitor for recurrence, detecting any reappearance of cancer cells early.
Cardiology: Assessing Heart Function
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Though not a primary diagnostic tool for CAD, PET scans can provide valuable information about myocardial perfusion (blood flow to the heart muscle), aiding in assessing the severity of the disease.
- Myocardial Viability: PET scans help determine which parts of the heart muscle are still alive and functioning after a heart attack, assisting in treatment planning.
Neurology: Diagnosing Neurological Disorders
- Alzheimer's Disease: PET scans can detect amyloid plaques and tau tangles, characteristic hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease, providing insights into disease progression.
- Dementia: PET scans aid in differentiating between various types of dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia, and vascular dementia.
- Seizures: PET scans can help pinpoint the location of seizure activity in the brain, assisting in epilepsy surgery planning.
Other Applications:
- Infections: PET scans can detect areas of inflammation and infection, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various infectious diseases.
- Neurological Disorders: Beyond Alzheimer's, PET scans contribute to evaluating several neurological disorders, offering insights into brain metabolism and function. This can assist in early diagnosis and guiding treatment strategies for various conditions.
How a PET Scan is Performed: A Step-by-Step Guide
The PET scan process is relatively straightforward, although preparation and the injection of a radioactive tracer are involved.
-
Preparation: The patient might need to fast for several hours before the scan, depending on the specific tracer used. This is crucial to ensure accurate results as it affects the glucose metabolism and tracer uptake.
-
Injection: A small amount of radioactive tracer, typically FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose), is injected intravenously. This tracer is a modified glucose molecule. The specific tracer used may vary depending on the clinical question.
-
Waiting Period: The patient then waits for a period of time, usually 45-60 minutes, to allow the tracer to be absorbed by the body's tissues. During this waiting period, the patient typically can relax and even read.
-
Scanning: The patient is then positioned on a scanning table that moves through the PET scanner. The scanner detects the gamma rays emitted by the decaying tracer, creating a series of images. The entire process usually takes about 30-60 minutes.
Interpreting PET Scan Results: What to Expect
Radiologists experienced in interpreting nuclear medicine images analyze PET scan results. The images are usually presented in two formats:
- Transaxial Images: These are cross-sectional images of the body, similar to CT scans.
- Coronal and Sagittal Images: These provide side and front views of the body, offering additional perspectives to understand the location and extent of findings.
The results are then presented in a report, which indicates the presence, location, and extent of any abnormalities. The report often correlates PET scan findings with other imaging studies, such as CT or MRI scans, for a more complete clinical picture. Higher metabolic activity typically is depicted as brighter areas on the images; these areas are of specific interest for the radiologist interpreting the results.
Limitations of PET Scans
While a powerful diagnostic tool, PET scans have some limitations:
- Cost: PET scans are expensive compared to other imaging techniques, making them less accessible to some individuals.
- Radiation Exposure: While the amount of radiation used is relatively low, it's still an ionizing radiation source, raising concerns about long-term effects, particularly in repeated procedures.
- False Positives and Negatives: Like all medical tests, PET scans can produce false positives (indicating a problem when none exists) and false negatives (missing a problem that is actually present).
- Specific Tracer Limitations: The specific tracer used determines what kind of biological activity the scan can detect. Some tracers may not be suitable for certain conditions, limiting the overall capability of the technology.
- Kidney Function: In some cases, certain tracers may impose a heavier burden on the kidneys. This factor is crucial for patients with pre-existing kidney conditions.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of PET Scans in Modern Medicine
PET scans have revolutionized the way many diseases are detected, diagnosed, and treated. Their ability to visualize metabolic activity offers unparalleled insights into various physiological processes. From the early detection and staging of cancer to monitoring treatment response and assessing heart function, PET scans play an invaluable role in modern medicine. While limitations exist, including cost and potential for false results, the benefits of this powerful technology far outweigh the drawbacks in many clinical situations. Understanding its capabilities and limitations is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients alike. This helps in determining when a PET scan is appropriate and how best to interpret the results for optimal patient care.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Did Quizlet Get Rid Of Q Chat
Mar 18, 2025
-
Myasthenia Gravis Is An Autoimmune Disease In Which Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Fun Sex Questions For Couples Quizlet With Answers
Mar 18, 2025
-
Crack Is Regarded As More Addictive Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Pet Scan Is Used To Detect Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
