A Risk Analysis For The Security Rule Is Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 7 min read
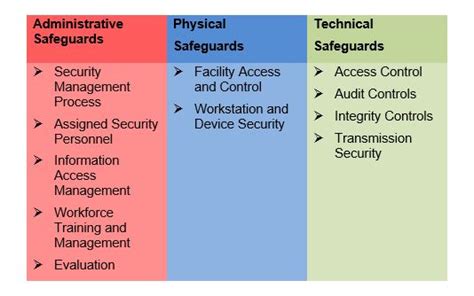
Table of Contents
A Risk Analysis for the Security Rule: A Comprehensive Guide
The HIPAA Security Rule mandates the protection of electronic protected health information (ePHI). Understanding and mitigating the risks associated with this rule is crucial for healthcare organizations. This article provides a comprehensive risk analysis framework for the HIPAA Security Rule, focusing on key areas and offering practical strategies for mitigation. We'll explore various threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts, providing a detailed guide for organizations to strengthen their security posture. This detailed analysis goes beyond simple Quizlet-style questions and answers, delving into the complexities and nuances of real-world HIPAA compliance.
Understanding the HIPAA Security Rule and its Components
The HIPAA Security Rule outlines three main safeguards: administrative, physical, and technical. A thorough risk analysis must consider each of these categories, identifying specific risks within them.
1. Administrative Safeguards: The Foundation of Security
Administrative safeguards focus on policies, procedures, and processes related to ePHI security. These are the foundational elements of a robust security program.
-
Risk Analysis: This is the cornerstone. A comprehensive risk analysis identifies potential threats, vulnerabilities, and the likelihood and impact of a security breach. This analysis should be documented, regularly reviewed, and updated. It should not merely be a checklist exercise; rather, it needs to be a dynamic process reflecting the evolving threat landscape.
-
Security Management: This includes establishing a security management process, assigning responsibilities, and ensuring regular training and awareness for all staff. Failing to adequately train staff on security protocols is a significant administrative vulnerability.
-
Sanction Policy: Implementing clear policies regarding disciplinary actions for security breaches is essential for accountability. Consistent enforcement demonstrates a commitment to security.
-
Workforce Security: This encompasses background checks, access control policies, termination procedures, and regular security awareness training for all employees, contractors, and business associates. Strict adherence to these policies minimizes insider threats.
-
Information Access Management: Establishing clear policies governing who can access ePHI and under what circumstances is crucial. Principle of least privilege should be strictly enforced, granting only the necessary access to individuals.
2. Physical Safeguards: Protecting the Physical Infrastructure
Physical safeguards focus on protecting the physical components of the IT infrastructure that houses ePHI.
-
Facility Access Controls: This includes limiting physical access to areas where ePHI is stored or processed. Access control measures such as keycard systems, security cameras, and visitor logs are essential.
-
Workstation Security: This involves securing workstations from unauthorized access and ensuring data is protected at rest and in transit. Password protection, screen savers, and physical security measures such as locks are critical.
-
Device and Media Controls: This encompasses policies and procedures for controlling access to and disposal of portable devices and media containing ePHI. Secure disposal methods, like shredding or data wiping, are necessary.
-
Environmental Controls: This includes safeguards against environmental hazards such as fire, water damage, and power outages. Regular maintenance, backup power systems, and fire suppression systems are crucial.
3. Technical Safeguards: Protecting Data in Transit and at Rest
Technical safeguards focus on protecting ePHI through technological means.
-
Access Control: This involves controlling who can access ePHI based on their roles and responsibilities. Authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls, are essential.
-
Integrity: This involves ensuring the accuracy and completeness of ePHI. Mechanisms like audit trails, digital signatures, and encryption can maintain data integrity.
-
Transmission Security: This involves protecting ePHI during transmission. Encryption using protocols such as TLS/SSL is necessary for securing data transmitted over networks.
-
Audit Controls: This involves tracking and logging system access and activities. Regular review of audit logs can help identify potential security breaches and ensure accountability.
-
Integrity Controls: This involves using technical measures to ensure that ePHI is not altered or destroyed without authorization. Hashing algorithms and digital signatures are common integrity controls.
-
Person or Entity Authentication: Ensuring that only authorized individuals or entities can access ePHI is critical. Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and biometric authentication methods can enhance security.
Conducting a Comprehensive Risk Analysis
A comprehensive risk analysis for the HIPAA Security Rule involves several key steps:
-
Identify Assets: Determine all ePHI and related systems within the organization. This includes patient records, billing information, and any other data protected under HIPAA.
-
Identify Threats: Identify potential threats to the identified assets. These threats can be internal (e.g., disgruntled employees) or external (e.g., hackers, malware).
-
Identify Vulnerabilities: Determine weaknesses in the organization's security posture that could be exploited by threats. This could include weak passwords, outdated software, or lack of security training.
-
Assess Risk: Determine the likelihood and impact of each identified threat exploiting a vulnerability. This often uses a risk matrix to categorize risk levels (e.g., low, medium, high).
-
Implement Safeguards: Implement appropriate safeguards to mitigate identified risks. This could involve technical controls (e.g., encryption, firewalls), administrative controls (e.g., policies, procedures), or physical controls (e.g., access controls, surveillance).
-
Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of implemented safeguards and review the risk analysis process to ensure it remains current and relevant. The threat landscape is constantly evolving, necessitating ongoing vigilance.
Common Threats and Vulnerabilities
-
Malware: Viruses, ransomware, and other malicious software pose significant threats to ePHI. Regular software updates, antivirus software, and employee education are crucial safeguards.
-
Phishing Attacks: These attacks deceive users into revealing sensitive information. Employee training on recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts is vital.
-
Insider Threats: Disgruntled employees or malicious insiders can pose significant risks. Strong access control, monitoring, and regular security awareness training can mitigate this threat.
-
Data Breaches: Data breaches can result from various factors, including hacking, malware, or insider threats. Robust security measures, incident response plans, and breach notification procedures are essential.
-
Physical Theft or Loss: Physical theft or loss of devices containing ePHI is a significant concern. Strong physical security measures, asset tracking, and device encryption are crucial.
-
Network Vulnerabilities: Weaknesses in network security can expose ePHI to unauthorized access. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits can help protect against these vulnerabilities.
-
Lack of Security Awareness Training: Employees who are unaware of security risks and best practices can unintentionally compromise ePHI. Regular and comprehensive security awareness training is critical.
Mitigation Strategies: Practical Steps to Reduce Risk
-
Implement Strong Access Controls: Use strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control to limit access to ePHI.
-
Regular Security Audits and Assessments: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
-
Employee Training and Awareness: Provide regular security awareness training to educate employees about security risks and best practices.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to effectively handle security incidents.
-
Data Encryption: Encrypt ePHI both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
-
Regular Software Updates: Keep all software and systems up-to-date to patch security vulnerabilities.
-
Data Backup and Recovery: Implement a robust data backup and recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of a data loss.
-
Vendor Risk Management: Carefully vet and manage vendors that access ePHI to ensure they have adequate security measures in place.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring of systems and networks to detect and respond to security threats in real-time.
Conclusion: Proactive Security is Key
A thorough risk analysis for the HIPAA Security Rule is not a one-time event; it's an ongoing process. Regular review, updates, and adaptation to the ever-changing threat landscape are crucial for maintaining compliance and protecting ePHI. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article, healthcare organizations can significantly reduce their risk exposure and safeguard the sensitive data they hold. Remember, proactive security is far more effective and cost-efficient than reactive remediation. A robust security program is not just a compliance requirement; it's a critical business imperative for protecting patient trust and maintaining operational integrity. This detailed approach extends beyond the simplicity of a Quizlet review, providing a practical framework for building a truly secure and compliant healthcare environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Elite Theory Of Government Maintains That
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Magnification Of The Ocular Lens
Mar 24, 2025
-
A No Standing Sign At A Certain Location Means
Mar 24, 2025
-
World War 2 In The Pacific Map
Mar 24, 2025
-
Folder Is To Document As Envelope Is To
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Risk Analysis For The Security Rule Is Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
