What Is The Magnification Of The Ocular Lens
Breaking News Today
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
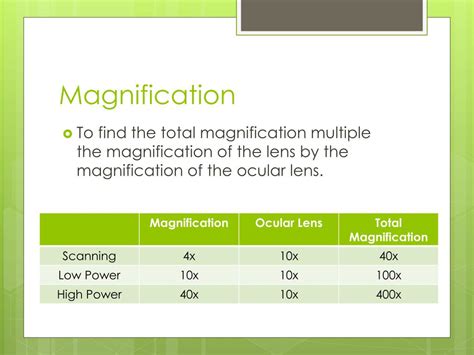
Table of Contents
What is the Magnification of the Ocular Lens? Understanding Microscope Optics
The ocular lens, also known as the eyepiece, is a crucial component of any microscope. It's the lens you look through to view the magnified specimen. Understanding its magnification is essential for comprehending the total magnification of the microscope and ultimately, the quality of the image you observe. This article delves deep into the magnification of the ocular lens, explaining its role, how it interacts with other lenses, common magnifications, and the impact of its characteristics on overall image quality.
The Role of the Ocular Lens in Microscopy
The ocular lens isn't solely responsible for magnification; it works in tandem with the objective lens. The objective lens is the lens closest to the specimen, performing the initial magnification. The ocular lens then takes this already magnified image and magnifies it further, projecting the final image to your eye. Think of it as a two-stage magnification process. The objective lens provides the detailed resolution, while the ocular lens increases the apparent size for comfortable viewing.
Beyond Simple Magnification: The Ocular's Other Functions
While magnification is the ocular's most obvious function, its role extends beyond simply making things bigger. High-quality ocular lenses also contribute to:
-
Image Correction: Many ocular lenses incorporate corrective lenses to minimize aberrations, such as chromatic aberration (color fringing) and spherical aberration (blurring at the edges). These corrections significantly improve the clarity and sharpness of the final image.
-
Field of View: The ocular lens determines the field of view – the area of the specimen visible through the microscope. Different ocular lenses offer varying field of views; wider fields allow for a broader perspective, while narrower fields offer increased detail at higher magnifications.
-
Eye Relief: Eye relief refers to the distance between the ocular lens and your eye where you can see the entire field of view comfortably. This is particularly important for users who wear eyeglasses. A longer eye relief is generally more comfortable and convenient.
-
Ergonomics: The design and construction of the ocular lens directly influence the overall ergonomics of the microscope. A well-designed ocular lens promotes comfortable and fatigue-free viewing, especially during extended observation periods.
Common Magnifications of Ocular Lenses
Ocular lenses are typically available in standard magnifications, although specialized lenses with unique magnification levels exist for specific applications. The most commonly encountered magnifications include:
-
10x: This is the most prevalent magnification for ocular lenses. It provides a good balance between magnification and field of view. Its widespread use makes it a versatile choice for many microscopy applications.
-
15x: Offering higher magnification than the standard 10x, a 15x ocular lens is frequently used when higher magnification is desired, often in conjunction with high-power objective lenses.
-
Other Magnifications: While less common, you might encounter ocular lenses with magnifications such as 5x (for extremely low magnifications), 20x (for very high magnification, often requiring specialized microscopes), and even higher. These are usually tailored to specific needs.
Understanding the Relationship Between Ocular and Objective Magnification
The total magnification of a microscope is the product of the ocular and objective lens magnifications. For example:
-
10x Ocular + 4x Objective = 40x Total Magnification
-
10x Ocular + 10x Objective = 100x Total Magnification
-
10x Ocular + 40x Objective = 400x Total Magnification
-
15x Ocular + 100x Objective = 1500x Total Magnification (high-power microscopy)
This simple calculation highlights the significant contribution of both lenses to the overall magnification. Choosing the right combination of ocular and objective lenses is critical for achieving the desired level of magnification and image quality for a given task.
Factors Affecting Ocular Lens Performance
Several factors beyond simple magnification impact the performance of an ocular lens:
-
Lens Quality: High-quality ocular lenses are constructed from superior optical glass with multiple lens elements, often treated with anti-reflective coatings to minimize light loss and improve image clarity. Lower-quality lenses might exhibit more aberrations, leading to a less satisfactory image.
-
Field Flatness: A perfectly flat field of view is ideal; however, some curvature is inherent in lenses. High-quality ocular lenses minimize this curvature, ensuring a sharp image across the entire field of view.
-
Chromatic Aberration Correction: This refers to the ability of the lens to minimize color fringing, a common optical aberration where different wavelengths of light focus at slightly different points. Good ocular lenses compensate for this, resulting in a more accurate representation of color.
-
Spherical Aberration Correction: This involves correcting blurring at the edges of the field of view. High-quality ocular lenses minimize this effect for a consistently sharp image from center to edge.
-
Eyepoint: The eyepoint, the location where the eye should be positioned for optimal viewing, is crucial for comfortable viewing. Well-designed ocular lenses offer a comfortable eyepoint, reducing eye strain during prolonged observations.
Choosing the Right Ocular Lens
Selecting the appropriate ocular lens depends heavily on the specific application and the type of microscope. Here are some considerations:
-
Microscope Type: Different types of microscopes, such as compound light microscopes, stereo microscopes, and fluorescence microscopes, might require different types of ocular lenses, often with specific mounting mechanisms.
-
Magnification Requirements: The desired magnification should dictate the choice of ocular lens, considering its interaction with the objective lenses available.
-
Budget: High-quality ocular lenses often come with a higher price tag. Balancing budget constraints with desired performance is vital.
-
Ergonomic Factors: Consider the eye relief and field of view offered by the ocular lens, particularly if extended observation periods are anticipated.
-
Compatibility: Ensure the ocular lens is compatible with the microscope's eyepiece tubes, both in terms of size and threading.
Advanced Ocular Lens Features
Modern microscopy often incorporates advanced features in ocular lenses:
-
Diopter Adjustment: Some ocular lenses include a diopter adjustment ring, allowing users to compensate for differences in their eyesight and achieve a sharper image.
-
Reticle or Micrometer: Ocular lenses can be fitted with reticles (crosshairs or calibrated scales) for accurate measurements within the microscope's field of view.
-
Photographic Adapters: Some ocular lenses are designed to accommodate photographic adapters, allowing for easy image capture.
-
Wide-Field Oculars: These oculars provide a significantly larger field of view compared to standard oculars, particularly advantageous when observing larger specimens or requiring a broader perspective.
Conclusion: The Ocular Lens – A Vital Component
The ocular lens, while often overlooked, plays a critical role in the overall performance of a microscope. Its magnification, in conjunction with the objective lens, determines the total magnification. However, its contribution extends beyond mere magnification to encompass image quality, comfort, and overall viewing experience. Understanding the characteristics of ocular lenses, such as their magnification, field of view, and aberration correction, is crucial for selecting the optimal lens for specific applications and achieving high-quality microscopic observations. Choosing the right ocular lens ensures clear, sharp images, contributing significantly to the success of any microscopy endeavor. The factors detailed above should guide you towards making an informed decision, ensuring your microscopic work is as accurate and efficient as possible.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unit 1 The Living World Ap Exam Review
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Image Is An Example Of An Angular Unconformity
Mar 26, 2025
-
Multiple Exemplar Training Involves Teaching Target Words As
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Demand Curve For A Normal Good Is
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of These Is A Characteristic Of Modernist Writing
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Magnification Of The Ocular Lens . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
