Abnormally Low Levels Of The Neurotransmitter Serotonin Are Associated With
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
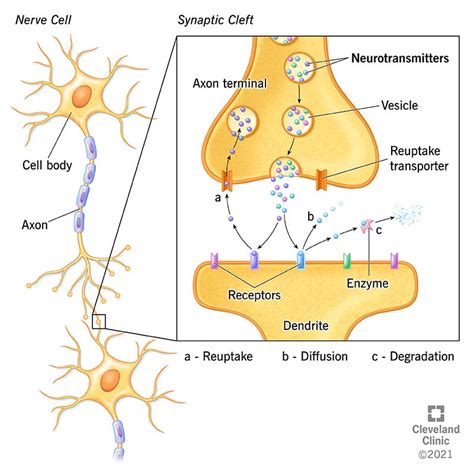
Table of Contents
Abnormally Low Levels of the Neurotransmitter Serotonin are Associated With: A Comprehensive Overview
Serotonin, a crucial neurotransmitter, plays a pivotal role in regulating a vast array of physiological and psychological processes. While often simplified as the "happy chemical," its functions are far more complex and nuanced. Abnormally low levels of serotonin, also known as serotonergic deficiency, are strongly implicated in a wide range of conditions, impacting mood, behavior, sleep, digestion, and overall well-being. This article will explore the diverse associations between abnormally low serotonin levels and various health conditions, examining the current research and understanding surrounding this vital neurotransmitter.
The Multifaceted Roles of Serotonin
Before delving into the consequences of serotonin deficiency, it's essential to understand the breadth of its normal functions. Serotonin's influence extends far beyond mood regulation, encompassing:
Mood Regulation:
- Happiness and Well-being: This is perhaps the most widely known association. Serotonin contributes significantly to feelings of happiness, contentment, and overall emotional stability. Deficiencies are often linked to depressive symptoms.
- Anxiety Reduction: Serotonin plays a crucial role in managing anxiety levels. Inadequate serotonin can lead to heightened anxiety and nervousness.
- Emotional Stability: It helps regulate emotional responses, preventing excessive emotional swings and promoting a sense of calm.
Sleep Regulation:
- Sleep-Wake Cycle: Serotonin contributes to the regulation of the circadian rhythm, the body's natural sleep-wake cycle. Imbalances can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or excessive sleepiness.
- REM Sleep: It's involved in the regulation of REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, a crucial phase for memory consolidation and cognitive function.
Digestive Health:
- Gastrointestinal Motility: Serotonin influences gut motility and function. Low serotonin levels are implicated in gastrointestinal issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Appetite Regulation: It plays a role in appetite control and satiety, influencing food intake and weight management.
Cognitive Function:
- Memory and Learning: Serotonin is involved in processes crucial for learning and memory consolidation.
- Attention and Focus: It contributes to maintaining attention and focus. Deficiencies can lead to difficulties with concentration.
Bone Metabolism:
- Bone Density: Serotonin influences bone metabolism and density. Imbalances are linked to increased risk of osteoporosis.
Cardiovascular Function:
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Serotonin has a role in regulating blood pressure. Disruptions in serotonin levels may contribute to cardiovascular issues.
Conditions Associated with Abnormally Low Serotonin Levels
The consequences of serotonergic deficiency are far-reaching, manifesting in a variety of conditions:
1. Depression:
Strong Evidence: Depression is perhaps the most prominently researched and widely understood consequence of low serotonin. Many antidepressant medications, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain. However, it's crucial to remember that depression is a complex disorder with multiple contributing factors, and serotonin is only one piece of the puzzle.
2. Anxiety Disorders:
Strong Evidence: Various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder (SAD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), are frequently linked to low serotonin levels. SSRIs are often prescribed for these conditions due to their serotonin-boosting effects.
3. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
Strong Evidence: OCD is characterized by intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors. Research suggests a significant role for serotonin dysfunction in the development and maintenance of OCD symptoms.
4. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
Moderate Evidence: PTSD, a debilitating condition stemming from traumatic experiences, is associated with dysregulation of various neurotransmitters, including serotonin. While the precise role of serotonin in PTSD is still being investigated, low levels are frequently observed.
5. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
Moderate Evidence: The gut-brain axis plays a vital role in health. Serotonin is produced extensively in the gut, influencing its motility and function. Low levels are implicated in the symptoms of IBS, including abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation.
6. Migraine Headaches:
Moderate Evidence: Migraines, characterized by severe headaches, are associated with imbalances in various neurotransmitters, including serotonin. Triptans, a class of migraine medication, target serotonin receptors to alleviate symptoms.
7. Sleep Disorders:
Moderate Evidence: Insomnia, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, and other sleep disorders are frequently associated with serotonin dysfunction. Serotonin's role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle contributes to this relationship.
8. Eating Disorders:
Moderate Evidence: Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder are often associated with neurotransmitter imbalances, including serotonin deficiency. These conditions impact appetite regulation and satiety, further complicating the issue.
9. Fibromyalgia:
Moderate Evidence: Fibromyalgia, a chronic pain condition, is often linked to abnormalities in neurotransmitter function, including serotonin. The precise mechanisms are still under investigation.
10. Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD):
Moderate Evidence: PMDD is a severe form of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) characterized by intense mood swings, irritability, and other debilitating symptoms. Fluctuations in serotonin levels during the menstrual cycle are believed to contribute to its development.
Diagnosing and Treating Serotonin Deficiency
Diagnosing low serotonin levels directly is challenging. There isn't a single, definitive test to measure serotonin levels in the brain. Instead, diagnosis relies heavily on clinical assessment, evaluating symptoms and ruling out other potential causes. Methods may include:
- Comprehensive Psychiatric Evaluation: A thorough evaluation by a psychiatrist or other mental health professional is crucial to assess symptoms and diagnose underlying conditions.
- Neurological Examination: In some cases, neurological examinations may help identify potential neurological contributions.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can rule out other medical conditions that may be mimicking symptoms.
Treatment strategies for suspected serotonin deficiency typically focus on increasing serotonin levels, either through lifestyle modifications or medication:
-
Medication: SSRIs are commonly prescribed to increase serotonin levels in the synapse, the space between nerve cells. Other antidepressants, such as serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), also impact serotonin levels.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle modifications play a vital role in supporting serotonin production and function. These include:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity stimulates serotonin release.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in tryptophan, an amino acid precursor to serotonin, is essential. Foods like turkey, bananas, eggs, and dairy products are good sources.
- Sufficient Sunlight Exposure: Sunlight helps regulate the circadian rhythm and serotonin production.
- Stress Management Techniques: Stress significantly impacts serotonin levels. Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing sleep allows the body to restore and regulate serotonin levels.
Conclusion
Serotonin plays a crucial role in maintaining physical and mental health. Abnormally low levels of this neurotransmitter are strongly associated with a wide range of conditions, highlighting its complex and multifaceted influence on the body. While diagnosing serotonin deficiency directly is difficult, careful clinical assessment and treatment strategies focusing on increasing serotonin levels through medication and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve outcomes for those affected. It’s crucial to remember that the information presented here is for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Further research continues to unravel the intricate relationship between serotonin and various health conditions, paving the way for more effective and targeted interventions in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When Titrating Inspired Oxygen Which Arterial Oxyhemoglobin
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Community Health Nurse Is Made Aware That Several Children
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Major Flaw In The Asch Conformity Study
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Statement Is True Regarding Gestational Diabetes
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Area Marked X On The Map Was Part Of
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Abnormally Low Levels Of The Neurotransmitter Serotonin Are Associated With . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
